Supported by you via insider access, and when you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. See our Affiliate Disclosure.
EV Charger Surge Protection Devices
EV charger surge protection devices (SPDs) protect your home electrical system and EV charging branch circuit, including the EV charger, EV charging accessories, and electric vehicle, from harmful voltage spikes caused by lightning, utility grid switching, electrical faults, or internal noise. These devices detect and redirect transient overvoltages away from sensitive components, ensuring safe, reliable EV charging, especially in areas with frequent outages or power instability.
Common Types of EV Charger Surge Protection Devices
EV charger SPDs are classified by installation location, protection type, and performance class. Below are the most commonly used surge protection devices for residential and light-commercial EV charging applications in North America.
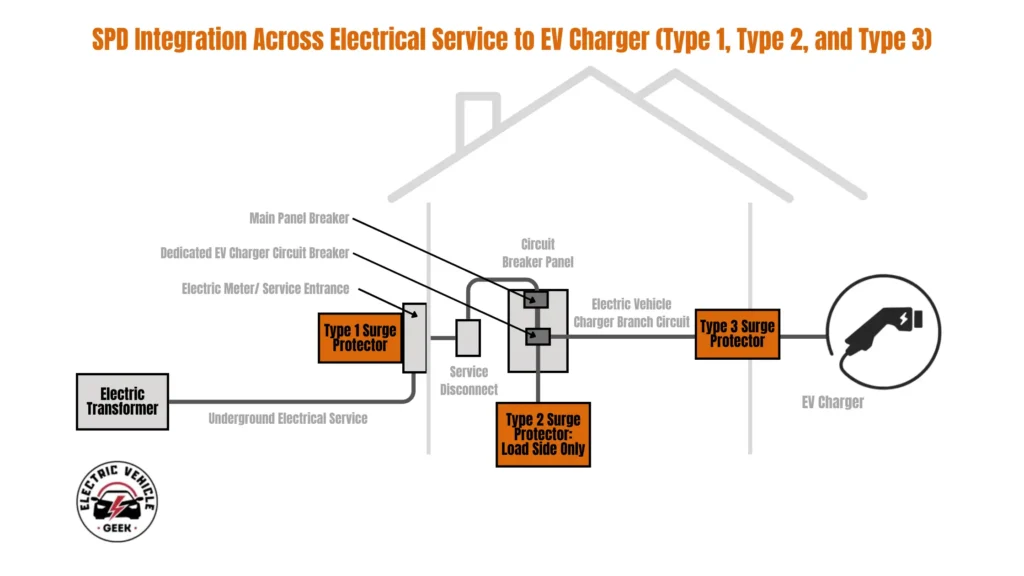
Type 1 SPD (Whole-Home Surge Protection at the Service Panel)
Type 1 SPDs are installed between the utility meter and main service disconnect, offering broad protection for the entire home, including the EV charger. They are designed to absorb large surges from lightning strikes or grid-side faults before they enter your electrical system.
These units are often hardwired directly into the main panel or mounted externally near the service entrance. Because they protect everything downstream, they are the first line of defense against catastrophic surges.
We recommend a UL 1449-listed Type 1 SPD for homes in storm-prone regions or rural areas with overhead power lines. It’s a must-have if your EV subpanel is over 50 feet from the main panel, as long wire runs increase susceptibility to high-voltage spikes.
Type 2 SPD (Panel or Subpanel Mounted EV Charger Protection)
Reccomended Home EV Charger Surge Protection Device
Type 2 SPDs are the most commonly used surge protection devices for EV charger installations, particularly for residential Level 1 EV chargers and Level 2 EV chargers, as well as many commercial Level 3 installations. These devices are typically installed in or adjacent to the main service panel or dedicated EV subpanel, where they connect in parallel to the circuit breaker supplying the EV charger. This configuration effectively diverts transient surges away from the charger, enhancing safety and equipment longevity.
These SPDs are engineered to suppress internal surges caused by switching loads or backfed energy from solar or battery EV charging systems. Many residential EV charger installations now include both a Type 1 SPD at the main panel and a Type 2 SPD at the EV charger subpanel for layered protection.
We recommend a Type 2 SPD rated for at least 20kA to 50kA per mode for most Level 2 EV chargers. Look for devices with indicator lights or audible alarms to confirm protection status.
Type 3 SPD (Point-of-Use EV Charger Protection)
Type 3 Surge Protection Devices are installed directly near the EV charger point of use, such as the EV charger outlet or plug-in receptacle. These SPDs are designed for localized, point-of-use protection and are commonly built into the EVSE itself or added as plug-in units. They help suppress low-level surges and voltage spikes, offering fast response and low let-through voltage.
However, Type 3 SPDs are not designed to handle high-energy surges like those from lightning or utility switching. For full protection, they must be used in coordination with a Type 1 or Type 2 SPD upstream at the main or subpanel, ensuring layered defense throughout the charging system.
We recommend using Type 3 SPDs only as supplemental protection at the charger head, especially in areas with frequent micro-surges or sensitive EVSE electronics.
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Right EV Charger SPD
When selecting an SPD for your EV charger, key considerations include:
SPD Type (Series or Parallel)
Parallel SPDs are ideal for EV chargers, offering easier installation and no power interruption. Series SPDs protect continuously but may disrupt charging.
Voltage & Current Compatibility
Match SPD ratings with your system. Ensure proper MCOV, high surge current rating (kA), and durable nominal discharge current (In) for safety
SPD Category (Type 1, 2, 3)
Type 2 SPDs are best for EV chargers. Installed in panels, they protect against internal and external surges from grid or lightning.
UL & Code Certifications
Only choose UL 1449 or IEC-certified SPDs. Ensure compliance with NEC or local codes to guarantee safety and prevent installation rework.
Status Indicators & Alarms
SPDs with LED indicators or remote alarms alert you to failure or end-of-life status, ensuring uninterrupted EV charger surge protection.
Indoor or Outdoor Rated Enclosure
Choose SPDs rated for indoor or outdoor use. Check enclosure rating, mount style, and breaker-slot compatibility for correct, safe installation.
Brand Reputation & Warranty
Select reputable SPD brands. Quality surge protection backed by trusted support minimizes future charger issues or costly replacements.
Protection vs. Cost Balance
Avoid cheap SPDs. Prioritize protection quality and long-term reliability over price to protect expensive EV chargers and connected vehicle systems.
Coordination with Electrical Circuit
Ensure the SPD is compatible with your home electrical system, EV charging branch circuit, EV charger, and connected EV charging accessories.
Does an SPD Need Its Own Circuit Breaker?
Not always, but in most cases, yes. When a surge protective device (SPD) is connected in parallel to a branch circuit or subpanel, it can be installed using either a shared breaker or its dedicated breaker.
In some residential panels, the SPD may share a breaker with the EV charger, but only if the breaker supports two conductors and the SPD manual allows it. The breaker must also meet NEC sizing rules, handling 125% of the EV charger’s continuous load. While this setup is sometimes used in tight spaces, it’s not ideal for long-term protection or serviceability. A dedicated breaker is the safer, code-preferred option.
The preferred method is to install the SPD on its dedicated breaker, usually a 2-pole breaker for 120/240V split-phase systems. Even with a dedicated breaker, the SPD is still wired in parallel, not in series. This configuration allows for safer maintenance, easier replacement, and better compliance with manufacturer instructions and NEC (National Electrical Code) recommendations. Many commercial and high-end residential installations require dedicated SPD breakers for full code compliance.
Can a Low-Amperage SPD Breaker Protect a High-Amperage EV Charger?
Yes! When SPDs are wired in parallel to the EV charger branch circuit or panel bus, a low-amperage breaker (e.g., 20A–50A) can protect the SPD even when used on high-amperage EV charger circuits.
Surge Protective Devices (SPDs) do not carry the circuit’s load current. They’re installed in parallel with the dedicated EV charger circuit breaker and only activate during voltage surges to divert excess energy to ground.
The breaker protecting the SPD is sized to protect its internal conductors, not the load. This breaker (often 20A–50A) ensures safe wiring practices, even if the EV charger draws 48A, 60A, or 80A.
Explore our comprehensive EV Charger Surge Protection Guide, a must-read for homeowners, electricians, and EV charger installers. This expert-written resource breaks down everything from common surge types and SPD classifications (Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3) to installation methods, wiring configurations, and recommended surge protection devices for Level 1, 2, and 3 chargers. Whether you’re setting up a single home charger or managing a commercial multi-EV installation, this guide helps you select the right surge protection for maximum safety, performance, and long-term reliability.


