An EV charger pedestal is a freestanding mounting structure designed to securely support electric vehicle charging stations, cables, and management kits in both outdoor and indoor installations. It protects the equipment from water, dirt, and impact while providing easier access for users. This essential EV charging accessory serves both a mechanical and electrical function, acting as the charger’s physical foundation and ensuring safe, convenient access to the charging station.
When shopping for an EV charger pedestal, it’s important to understand the different terms used to describe it. Terms like EV pedestal, EV charger stand, EV charging bollard, and EV charger mounting post all refer to the same type of equipment, though their popularity can vary depending on search trends and industry usage. Being familiar with these terms will help you navigate product listings such as online marketplaces like Amazon to help you find the ideal EV charger pedestal for your EV charger.
EV charger pedestal kits are becoming an increasingly popular choice for residential EV charger installations. With EV charger pedestal mounts now more affordable and accessible, many homeowners are opting for home EV charger pedestals instead of wall-mounted, hardwired chargers.
EV charger pedestals offer greater EV charger installation flexibility, making them ideal for homes where easy access, convenience, and the ability to place the charger in a location that suits your needs are crucial for a seamless charging experience.
Unlike wall-mounted chargers, pedestals can be placed in a variety of locations such as:
- Residential driveways where wall access may not be available
- Parking lots and curbside spaces
- Sidewalks and open-air garages
- Fleet depots or EV-ready business campuses
Table of Contents
- Components of an EV Charger Pedestal
- EVSE Mounting and Compatibility
- EV Charger Pedestal Electrical Protection and Integration
- EV Charger Pedestal Circuit Breaker Mounting Rail or Brackets
- EV Charger Pedestal Grounding Systems
- EV Charger Pedestal Lightning Protection
- EV Charger Pedestal Overvoltage Protection
- EV Charger Pedestal Undervoltage Protection
- EV Charger Pedestal Surge Protection
- EV Charger Pedestal Wiring Terminals
- EV Charger Pedestal Internal Wiring Access/Cover Panels
- EV Charger Pedestal Charging Cable Management
- EV Charger Pedestal Structural Support and Stability
- Future-Proofing Your EV Charger Installation
Components of an EV Charger Pedestal
The image below illustrates the key components that make up a typical EV charger pedestal:

EV charger pedestal components ensure a secure, reliable, and efficient EV charger installation and charging experience. Below, we’ve grouped these components by their primary function:
EVSE Mounting and Compatibility
The first step when purchasing your EV charger pedestal is making sure your EV charger is compatible with the EV Charger pedestal, some of the components you should investigate include:
EV Charger (EVSE)
Whether you’re installing a Level 1 or Level 2 EV charger on a dedicated pedestal, one of the first decisions you’ll need to make is the charger’s installation type—hardwired or plug-in via a NEMA outlet.

Hardwired EV Charger Pedestal Installation
If the EV charger is hardwired, it should come with a power supply cable long enough to reach the wiring access point or cover panel on the pedestal. Most hardwired EVSE units include a 1–2 ft supply cable designed to connect directly to a branch circuit via a junction box within the pedestal or a nearby wall enclosure.

For detailed steps, check out our [Hardwired EV Charger Pedestal Installation Guide].
Plug-In EV Charger Pedestal Installation
For plug-in EV chargers, ensure the pedestal either includes a built-in NEMA outlet receptacle box or provides a suitable mounting location for one. The NEMA outlet should match the plug type of the EV charger. This simplifies installation and adds flexibility, making it easier to move or replace the EVSE when needed.
The image below shows a NEMA outlet installed outside the EV charger pedestal.

The image below shows a NEMA 14-50 outlet installed inside a wider vertical column of the BMZX Tesla charger pedestal for a cleaner and safer plug-in EV charger installation.
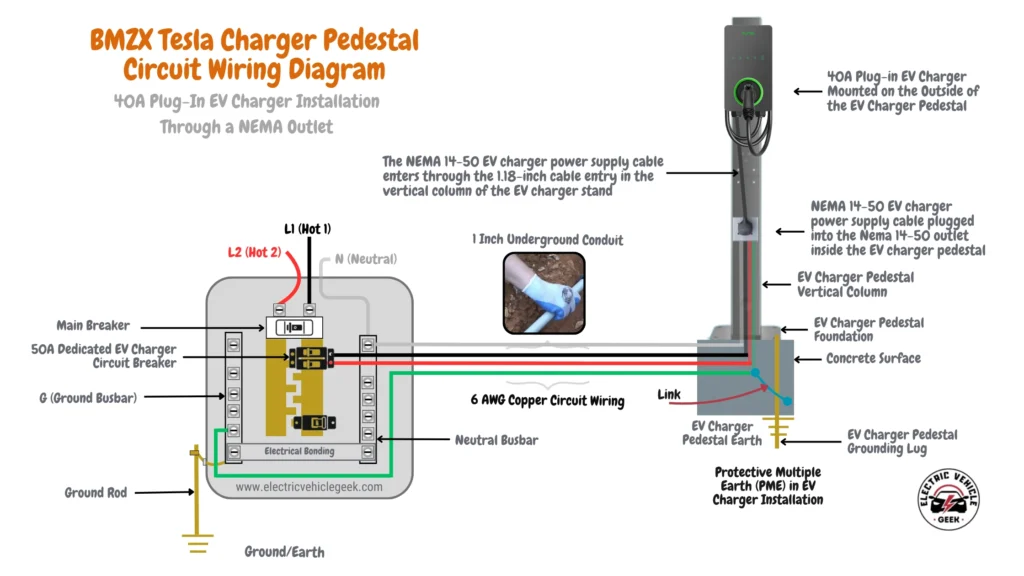
For more guidance, see our [Plug-In EV Charger Pedestal Installation Guide].
EV Charger Pedestal Charger Mounting Interface / Top Plate
Consider a branded EV charger pedestal to ensure optimal compatibility, durability, and aesthetics. Branded pedestals are typically designed to match specific EV charger models, offering pre-drilled mounting plates and a clean, professional look that simplifies installation and enhances long-term reliability.

It’s crucial to verify that the mounting pattern of your EVSE aligns with these holes or that an adapter plate is available. Mismatched mounting interfaces can delay installation or require custom modifications.
When researching or purchasing an EV charger pedestal, the first component to assess is the EV charger pedestal EV charger mounting interface or top plate, this is where the EV charger wall unit or lock box will be securely mounted, so it is essential to verify compatibility.

The mounting interface may vary depending on the charger model and mounting configuration. It could feature a larger or smaller interface, as well as single or dual mount options. Be sure to check for universal or brand-specific hole patterns to ensure compatibility with various EV chargers or EV charger lock boxes.
Key considerations include:
Compatibility with Your EV Charger or Lock Box
Ensure the mounting interface or top plate is appropriately sized for the specific EV charger or lock box you plan to install. Smaller body chargers, such as the Wallbox Pulsar Plus EV charger, will fit well with a smaller mounting interface. However, for larger units like Grizzle-E Smart EV chargers or EV charger lock boxes which are meant to house the EV charger, consider a larger mounting interface or top plate to ensure a secure fit.
For small-sized EV chargers such as the Wallbox EV chargers you are good with a small mounting interface, but for big-sized EV chargers such as Grizzle-E smart EV chargers or EV charger lock boxes consider a bigger mounting interface or to plate for secure fit.
Pre-drilled Holes and Bolt Compatibility
Check that the pre-drilled holes on the mounting interface or top plate align with the mounting holes of your EV charger or lockbox. Pay attention to the type of bolts used, and confirm the horizontal and vertical measurements of both the pedestal and the EV charger or lock box to ensure compatibility.
In cases where the EV charger pedestal does not include pre-drilled mounting holes, you may need to manually drill into the vertical support column to install additional EV charging accessories—such as NEMA receptacle boxes, as illustrated in the image below.
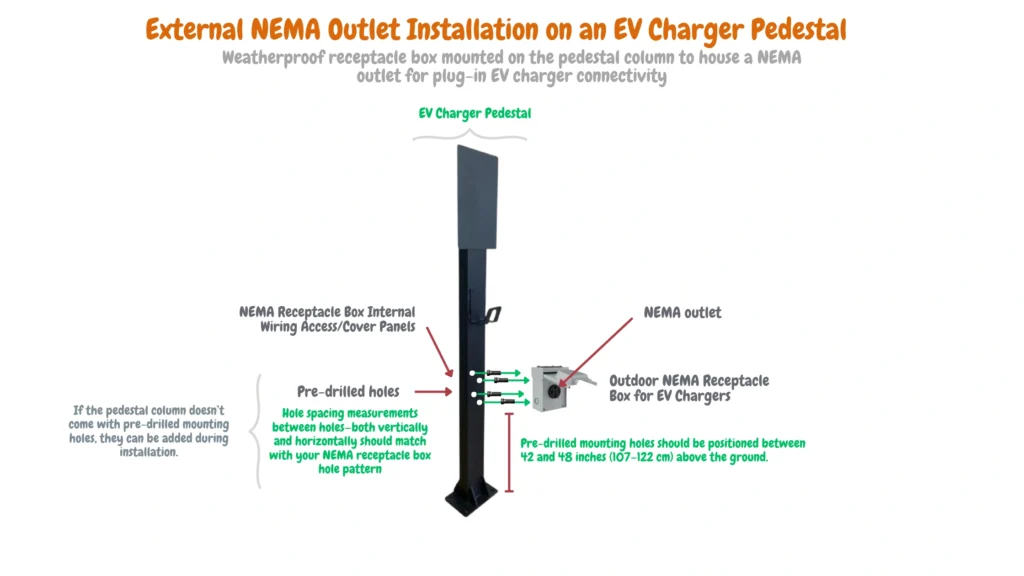
This is especially common with pedestal models that lack built-in support for surface-mounted devices. Ensure proper alignment and use of appropriate drill bits and hardware suitable for metal fabrication.
Dual-sided EV Charger Pedestal
When installing dual chargers, ensure the pedestal is equipped with dual mounting interfaces, designed for either side-by-side or back-to-back EV charger installations. Verify that the size, hole patterns, and mounting accessories are fully compatible with both chargers to ensure a stable and secure setup.
The dual-sided EV charger pedestal should be equipped with two cable management hooks and two plug holders for added convenience and organization.
Additionally, the pedestal must be structurally robust to support the combined weight of both EV chargers and their accessories, ensuring long-term durability and safety.
Installation Height Requirements (NEC Compliance)
The height of the EV charger pedestal mounting interface determines the final mounting height of the EV charger. According to Article 625 of the National Electrical Code (NEC):
- Outdoor EV chargers must be installed at least 24 inches above ground level.
- Indoor installations require a minimum height of 18 inches from the ground.
Ensure the pedestal’s mounting interface allows you to meet these requirements and also user-friendly heights, considering ADA accessibility guidelines. Proper installation height helps prevent environmental damage, improves accessibility, and ensures user safety.
EV Charger Pedestal Electrical Protection and Integration
EV Charger Pedestal Electrical Protection and Integration refers to the components and features designed to safeguard the electrical connections and ensure proper integration between the pedestal and the EV charger. These elements are vital for maintaining the safety, reliability, and efficiency of the charging system.
Here’s what they typically include:
EV Charger Pedestal Circuit Breaker Mounting Rail or Brackets
Some EV charger pedestals include circuit breaker mounting rails or brackets designed for the installation of dedicated EV charger circuit breakers. EV charger circuit breakers protect against electrical overloads and faults by automatically disconnecting power if an issue is detected, preventing damage to the system.
If the EV charger pedestal does not include circuit breaker mounting rails or brackets, we recommend installing a dedicated circuit breaker in the main electrical panel to protect the EV charger branch circuit.
Alternatively, if your pedestal lacks the necessary mounting hardware, you may consider purchasing an EV charger lockbox. Look for one that includes circuit breaker mounting rails or brackets, such as the BMZX for the Tesla Wall Charger Box. This will allow for the safe installation of dedicated EV charger circuit breakers.
Make sure to install the correct amperage of the dedicated circuit breaker based on the amperage specifications of the EV charger, following the 80/20 rule as per the NEC (National Electrical Code). This ensures that the circuit breaker is properly sized to protect the system without causing unnecessary interruptions.
For more details on selecting the appropriate circuit breaker, check out our Electric Vehicle Charger Circuit Breaker Selection Guide (USA – NEC).
EV Charger Pedestal Grounding Systems
We also recommend considering an EV charger pedestal with an integrated grounding system. EV charger pedestal grounding systems are critical components designed to ensure the safety of your installation. EV charger grounding helps prevent electrical shocks, protects equipment from electrical surges, and ensures the proper operation of the EV charger mounted on the pedestal.

When installing an EV charger mounted on an EV charger pedestal, we recommend considering Protective Multiple Earthing (PME) for the pedestal and grounding all exposed metal components used in the EV charger pedestal installation as shown in the EV charger pedestal metal devices earthing diagram below.
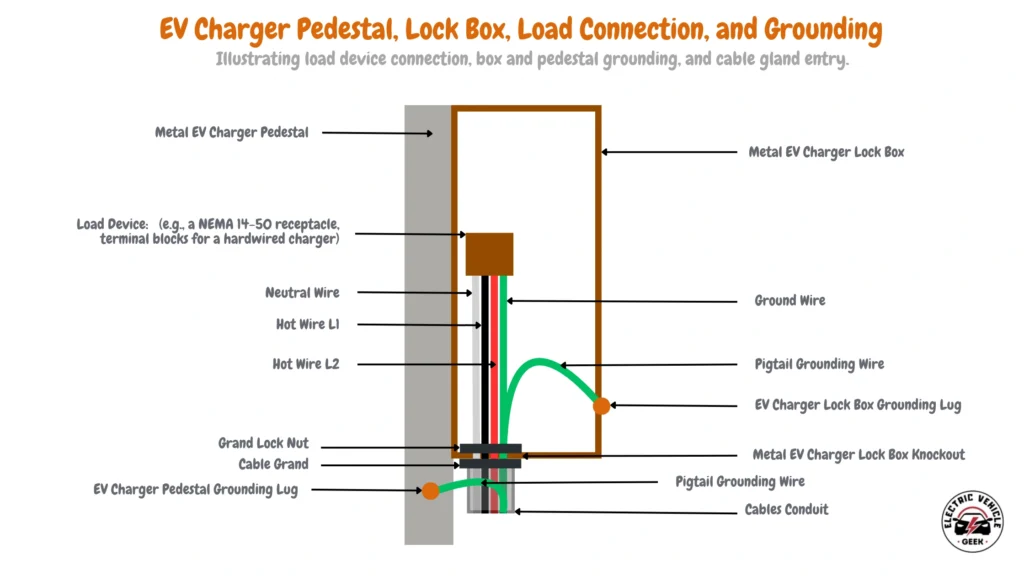
PME connects the electrical system to the ground at multiple points—both at the supply and within the EV charger source through the EV charger pedestal grounding lug —providing low-resistance paths to safely divert excess current into the earth.
EV Charger Pedestal Lightning Protection
Lightning protection in an EV charger pedestal is designed to protect the charging station from direct or indirect lightning strikes in outdoor EV charger pedestal installations. This system typically includes air terminals (lightning rods), grounding systems, and surge arresters that safely direct high-voltage lightning currents into the earth.
Without proper lightning protection, a nearby strike can cause severe damage to the charger’s internal components, compromise safety, or even start electrical fires. It’s especially important in outdoor or elevated installations.
EV Charger Pedestal Overvoltage Protection
Overvoltage protection safeguards the EV charger from voltage levels that exceed the system’s rated capacity—often caused by grid switching events, equipment faults, or lightning-induced surges.
Overvoltage conditions can degrade or permanently damage sensitive electronics inside the charger. Protection devices such as voltage clamping components or disconnect mechanisms are used to limit or isolate excess voltage before it reaches the EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment).
EV Charger Pedestal Undervoltage Protection
Undervoltage protection prevents the EV charger from operating when the EV charger supplied voltage drops below safe operating levels. Low voltage can cause improper functioning, overheating, or inefficient charging. This protection system disconnects the charger when the voltage drops too low and reconnects only when stable voltage is restored—ensuring reliability and extending equipment lifespan.
EV Charger Pedestal Surge Protection
Surge protection is a critical safety system that absorbs and diverts transient voltage spikes—often caused by lightning, power outages, or switching surges. Surge protection devices (SPDs) are typically installed at the power input of the pedestal to prevent short bursts of high voltage from reaching the charger. Effective surge protection helps maintain charger uptime, protect user vehicles, and comply with electrical safety standards.
Surge Protection: Helps protect the system from power surges caused by lightning or other electrical disruptions, preventing damage to sensitive components.
Weatherproofing: Ensures that the electrical connections and components are resistant to environmental factors like moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures, preventing short circuits and corrosion.
EV Charger Pedestal Wiring Terminals
EV charger pedestal wiring terminals provide a secure and safe connection between the EV charger and the EV charger pedestal to the electric vehicle branch circuit. The terminals should be rated for the proper current capacity and offer an easy-to-access connection point for the wiring to ensure a reliable electrical link.
EV Charger Pedestal Internal Wiring Access/Cover Panels
These panels protect the internal wiring of the EV charger pedestal. They also provide easy access for maintenance, inspections, or upgrades.
A good access panel should support clean EV charger installation wires management. It should allow the safe installation of accessories like conduits, junction boxes, and terminal blocks.
This is especially useful for hardwired EV chargers. junction boxes and terminal blocks help connect the charger to the branch circuit wiring inside the pedestal.
EV Charger Pedestal Charging Cable Management
An EV charger pedestal typically includes integrated cable management features designed to organize, store, and protect the charging cable and connector. These components help extend the lifespan of the cable and connector by reducing wear, preventing tangling, and minimizing the risk of accidental damage.
They also enhance safety and maintain a clean, professional appearance around the charging station. Article 635 of the National Electrical Code (NEC) requires cable management systems for all EV charging cables over 25 feet in length. Even for shorter cables, a well-designed cable-handling solution offers significant benefits in terms of usability, protection, and site aesthetics.

Common cable management components found in EV charger pedestals include:
EV Charger Pedestal Integrated Hooks, Brackets, Holsters, or Retractors
Many EV charger pedestals include built-in cable management features such as hooks, brackets, holsters, or retractors. These components are typically integrated into the vertical column of the pedestal and are designed to keep the EV charger cable neatly stored when not in use. They help prevent tangling, reduce trip hazards, and protect the cable from weather-related damage.
When choosing an EV charger pedestal, ensure the cable management system is durable and strong enough to support your charger’s cable weight. It should allow for easy one-handed use—enabling the user to remove, operate, and store the cable effortlessly.
For low-maintenance and space-saving needs, consider compact options like pedestal-integrated hooks, loops, or holsters that require minimal upkeep and blend well with the overall design.
EV Charger Pedestal Integrated Plug Holder
Another key EV charger pedestal feature is the EV charger pedestal integrated plug holder, the dedicated plug holder is designed to store the charging plug securely when not in use, ensuring the plug is easily accessible and protected from wear.
When choosing an EV charger pedestal with an integrated plug holder, ensure the plug holder is compatible with your EVSE connector type, such as J1772 or Tesla connectors, this ensures a proper fit and secure connection.
For outdoor installations, select an EV charger pedestal with a weatherproof plug holder with a high IP rating to protect it from dust, rain, and UV exposure, this helps extend the life of the holder and also protects the plug from outdoor elements.
It’s crucial to consider both the integration type and positioning of the plug holder on your EV charger pedestal. The holder should be strategically placed on the EV charger pedestal column for easy access and convenience, ensuring it’s within reach while keeping the charging area organized. Additionally, opt for holders made from durable materials, such as ABS plastic or metal, to ensure long-term reliability and resistance to wear from frequent use.
We recommend choosing EV pedestals with plug holders that have a locking mechanism. This helps prevent others from using your charger without permission, protects the charging plug from falling and getting damaged, and keeps the cable neatly in place to avoid messy tangles. You can also look for plug holders designed for easy one-hand use.
EV Charger Pedestal Structural Support and Stability
Structural support and stability are critical factors to consider when selecting an EV charger pedestal. A well-designed pedestal not only ensures a secure installation but also extends the life of your charging equipment.
The two key components that provide this support are the vertical support column and the pedestal foundation. Together, they anchor the pedestal firmly to the ground and provide the strength needed to hold the EV charger and its accessories in place.
EV Charger Pedestal Vertical Support Column
The vertical support column is the core structure of the EV charger pedestal. It provides the necessary strength and rigidity to hold the charger securely in place, even under heavy use or outdoor exposure.
Most support columns are made from powder-coated steel or aluminum, offering both durability and resistance to rust and corrosion. This ensures a long service life, especially in outdoor environments.
A slim vertical support column is generally sufficient for lightweight EV chargers. However, for heavier units—especially those with additional accessories mounted—a thicker support column provides greater stability and durability. We recommend using a robust vertical column to future-proof your EV charger installation and accommodate potential upgrades.
Many designs include internal conduit raceways, which safely route and protect electrical wiring from environmental damage, tampering, or wear—ensuring a clean and professional installation.
For smart EV charger installations, it’s important to plan for both electrical wiring and networking cables inside the vertical support column of the pedestal. Networking cables may be needed for internet connectivity, data communication, or linking multiple chargers in a networked system.
In addition, smart chargers often require accessories such as billing modules, usage monitors, RFID readers, or communication hubs. When selecting a pedestal, make sure its vertical support column has space and mounting options to support these accessories.
Lastly, check that the pedestal is compatible with the smart features of your EV charger system. Proper cable routing and mounting support through the vertical support column will help ensure a clean, reliable, and future-proof installation.
EV Charger Pedestal Foundation
The foundation forms the base that supports the entire pedestal. It is typically constructed from high-strength materials such as galvanized or stainless steel, ensuring resistance to impact, moisture, and shifting ground.
A solid foundation is crucial for both safety and longevity, especially in areas with harsh weather conditions or high foot traffic. It prevents tilting or movement over time.
Some pedestal foundations are designed for direct burial, while others are surface-mounted on concrete pads. Always choose a foundation suited for your installation environment.

EV Charger Pedestal Base Plate / Ground Anchor
The base plate (also called a ground anchor) connects the pedestal to the mounting surface—usually a concrete pad. It plays a key role in the overall stability and alignment of the charger.
Most base plates include pre-drilled bolt holes that align with standard anchor bolt patterns, making installation faster and more accurate. Look for models with integrated cable access holes as well.
Optional gasket seals between the base plate and the surface can help prevent water intrusion, adding extra protection for wiring and internal components.
EV Charger Pedestal Anchor Bolts
Anchor bolts are essential for securing the pedestal firmly to the concrete pad or mounting surface. They prevent movement and tipping, ensuring the charger remains stable over time.
These bolts are typically included with the pedestal kit, but it’s important to verify that they match your installation surface (e.g., concrete, asphalt, or pavers). Stainless steel options offer better corrosion resistance.
Tip: Choose EV charger pedestals that come with expansion bolts or concrete screws, they simplify the installation process.
Future-Proofing Your EV Charger Installation
If you want to future-proof your EV charger installation, start by evaluating the EV charger pedestal’s vertical support column. A future-ready column should include internal space not only for power cables but also for networking and data wiring, which are essential for smart charging features like usage tracking, load management, and remote access.
Next, consider the pedestal foundation. A strong, weather-resistant foundation made from durable materials (like galvanized steel) ensures long-term structural stability—especially when integrating with solar canopies, where the pedestal may bear additional weight or exposure. The foundation should also support secure anchoring on various surfaces and allow for adjustments or retrofits as your system expands.
Look for pedestal systems that support advanced features such as V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) readiness, dynamic load balancing, and smart grid connectivity. Choosing a pedestal with modular, swappable components will also make future upgrades easier—whether you’re adding new accessories, integrating payment systems, or scaling up to meet growing charging demand.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.







