Siemens QF250A 50 Amp GFCI Circuit Breaker for Level 2 EV Charger
The Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker delivers safe, consistent performance for 240V EV charger branch circuits that require ground fault protection. Its Class A GFCI protection, plug-in design, UL 943 self-test functionality, and compatibility with outdoor-rated Level 2 EV chargers make it the recommended choice for NEC-compliant EVSE installations in garages and exposed environments.
The Siemens QF250A is a 50 Amp, 2-pole GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breaker that excels in providing safety and compliance for residential and commercial 40A Level 2 EV charger installations. The circuit breaker is designed to meet NEC requirements for GFCI protection on 240V circuits, the QF250A offers UL 943-compliant technology with a 10,000 AIC interrupt rating, ensuring both reliability and enhanced safety for Level 2 EV charging branch circuit installations.
As an EV charger installer, I frequently work with homeowners upgrading their electrical systems to accommodate 40A Level 2 EV chargers like those using NEMA 14-50 outlets and NEMA 6-50 outlets, as well as hardwired EV chargers with amperage adjustment to 40A that require 50A dedicated circuit breakers to protect the electric vehicle branch circuit components and users. In some EV charger installations like this, especially in Level 2 EV chargers that plug into an outlet, GFCI protection is essential, especially for EV charger outlets located in damp-rated environments where the NEC mandates GFCI integration and compliance.
The Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker is an ideal choice that we recommend, offering Class A GFCI protection, which trips the dedicated EV charger circuit breaker in the event of leakage currents as low as 5 mA, ensuring protection against electric shock and EV branch circuit component damage – the QF250A GFCI breaker works best with EV chargers that do not have integrated Charging Circuit Interrupting Device (CCID) protection, as dual GFCI tripping can occur with chargers that have built-in CCID protection.
One standout feature of the Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker is its Self-Test and Lockout functionality, required by UL 943. This feature continuously tests the breaker to detect any potential issues in the EV charger branch circuit. If a malfunction occurs, the breaker trips and locks out, preventing homeowners from mistakenly resetting a compromised breaker, which could lead to serious hazards like EV charging fires. This added security ensures the system operates correctly and in the case of a malfunction, it will lock out the circuit until a licensed electrician or certified EV charger installer diagnoses and resolves the issue. This feature is especially beneficial in multi-dwelling units with shared EV chargers, where multiple users depend on the same installation.
We installed the QF250A GFCI breaker in a 50A EV charger circuit using 6 AWG solid copper THHN conductors in ¾-inch conduit, terminating at a NEMA 14-50R outlet covered by an outdoor-rated EV charger weatherproof enclosure. The branch circuit powered a 240V 40A plug-in EV charger rated for 9.60 kW continuous operation.
The Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker is designed for easy installation, featuring a plug-in mount that ensures compatibility with Siemens load centers. Unlike standard two-pole 50A dedicated EV charger circuit breakers such as the SIEMENS Q250H 50A Type QPH Circuit Breaker, the Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker requires an additional step: the breaker features an integral white neutral pigtail must be connected to the panel’s neutral bar – this connection is crucial for supporting the GFCI’s internal monitoring system, ensuring it operates as intended.
Over multiple overnight charging sessions, the QF250A GFCI breaker remained cool, stable, and never nuisance-tripped during testing which has been reported on some Level 2 EV chargers installations with GFCI breakers. The ground fault self-test engaged on power-up and during continuous use, with no chatter or false trips. This level of steady performance and ground fault reliability is essential when installing EVSEs in garages with concrete floors or outdoor carports exposed to moisture.
In case of nuisance dedicated EV charger tripping caused by dual GFCI protection when using the Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker, we recommend switching to a regular non-GFCI dedicated circuit breaker – we recommend also checking if your EV charger has integrated Charging Circuit Interrupting Device (CCID) protection which can cause dual GFCI tripping when using the Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker to protect the electric vehicle branch circuit of your CCID protected 40A Level 2 EV charger.
Wiring the Siemens QF250A GFCI Breaker for 240V Level 2 EV Chargers
Whether you need a GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breaker for an EV charger depends on several factors, including local electrical codes, the type of charger, and the installation environment—especially in damp or wet locations where NEC GFCI compliance is required. Class A GFCI protection safeguards against shock hazards by tripping on leakage currents as low as 5 mA. However, for certain EV charger brands like Emporia and Charge Point Home Flex EV Charger, which already have integrated Charging Circuit Interrupting Device (CCID) protection, a regular non-GFCI breaker should be used to avoid dual GFCI tripping issues, as recommended by the manufacturer.
EV Charger Wiring – 240V (4-Wire: L1, L2, Neutral, Ground) – QF250A GFCI Breaker
The 4-wire branch circuit configuration (L1, L2, Neutral, Ground) is standard for EV chargers rated for 40 amps including plug-in and hardwired EV charger installations. This wiring method is most commonly used with NEMA 14-50R outlets for plug-in NEMA 14-50 EV chargers and is also suitable for 40A hardwired EV chargers that require a neutral connection. It’s also often seen during conversions from NEMA 14-50 plug-in EV chargers to hardwired installations.
The branch circuit consists of two ungrounded (hot) conductors (typically 6 AWG for 50A), one grounded (neutral) conductor, and one equipment grounding conductor, forming a 4-wire connection between the EV charger and the electrical panel. The hot conductors terminate at the Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker terminals, the neutral conductor at the panel’s neutral busbar, and the ground conductor at the equipment grounding bar. Additionally, the Siemens QF250A GFCI Breaker integral white neutral pigtail must be securely connected to the neutral bus to activate the internal GFCI monitoring system as shown in the wiring diagram below: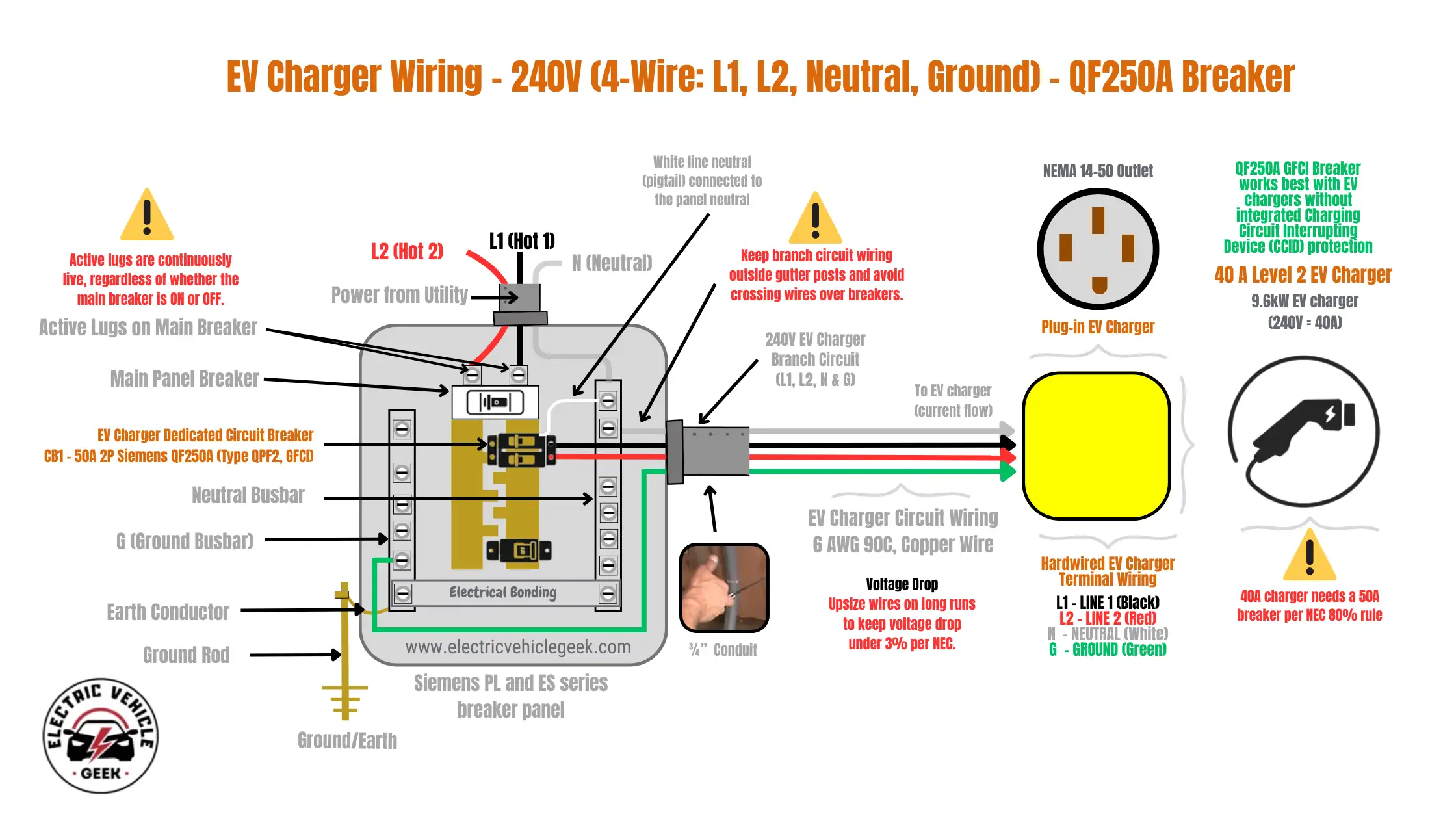
EV Charger Wiring – 240V (3-Wire: L1, L2, Ground) – QF250A GFCI Breaker
The 3-wire: L1, L2, Ground EV charger branch circuit configuration is suitable for outdoor or wet-location installations where GFCI protection is required. This setup is commonly used with NEMA 6-50 plug-in EV charger installations and 3-wire 40A hardwired EVSE setups that do not require a neutral conductor. The double pole Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker is installed with two hot wires and ground; the neutral terminal on the breaker may remain unused. However, the white line neutral (pigtail) must be connected to the panel’s neutral bar for the internal GFCI self-test and protection system to operate properly, as shown in the wiring diagram below: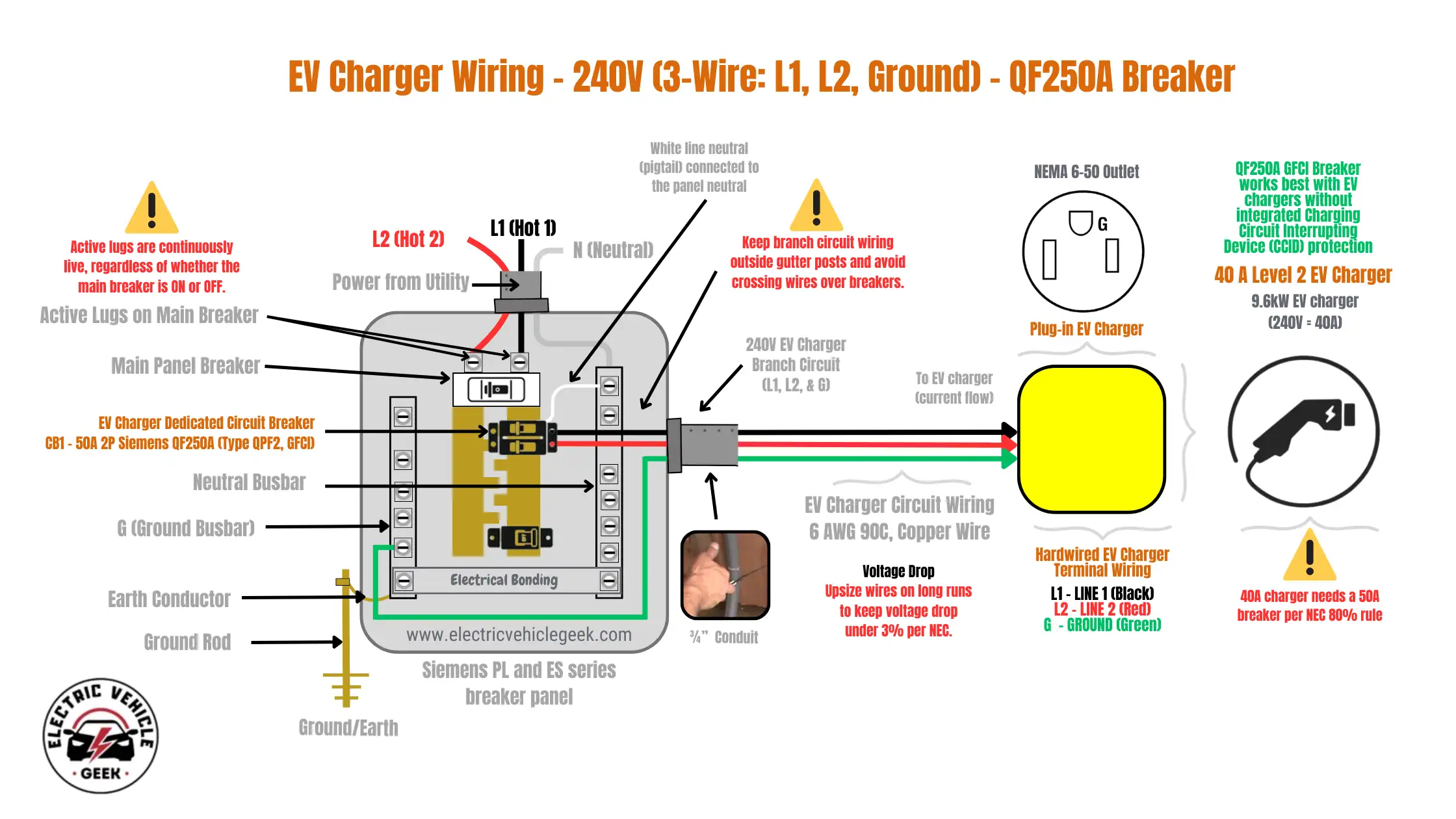
EV Charger Wiring – 240V (3-Wire: L1, L2, Neutral, No Ground) – QF250A GFCI Breaker
This EV charger branch wiring configuration is not recommended for new installations, as NEC 250.90 and 250.134 require a separate equipment grounding conductor for all EVSE branch circuits. However, it may exist in legacy setups—such as NEMA 10-50 EV charger installations—where a neutral was present but the ground was not, as shown in the wiring diagram below: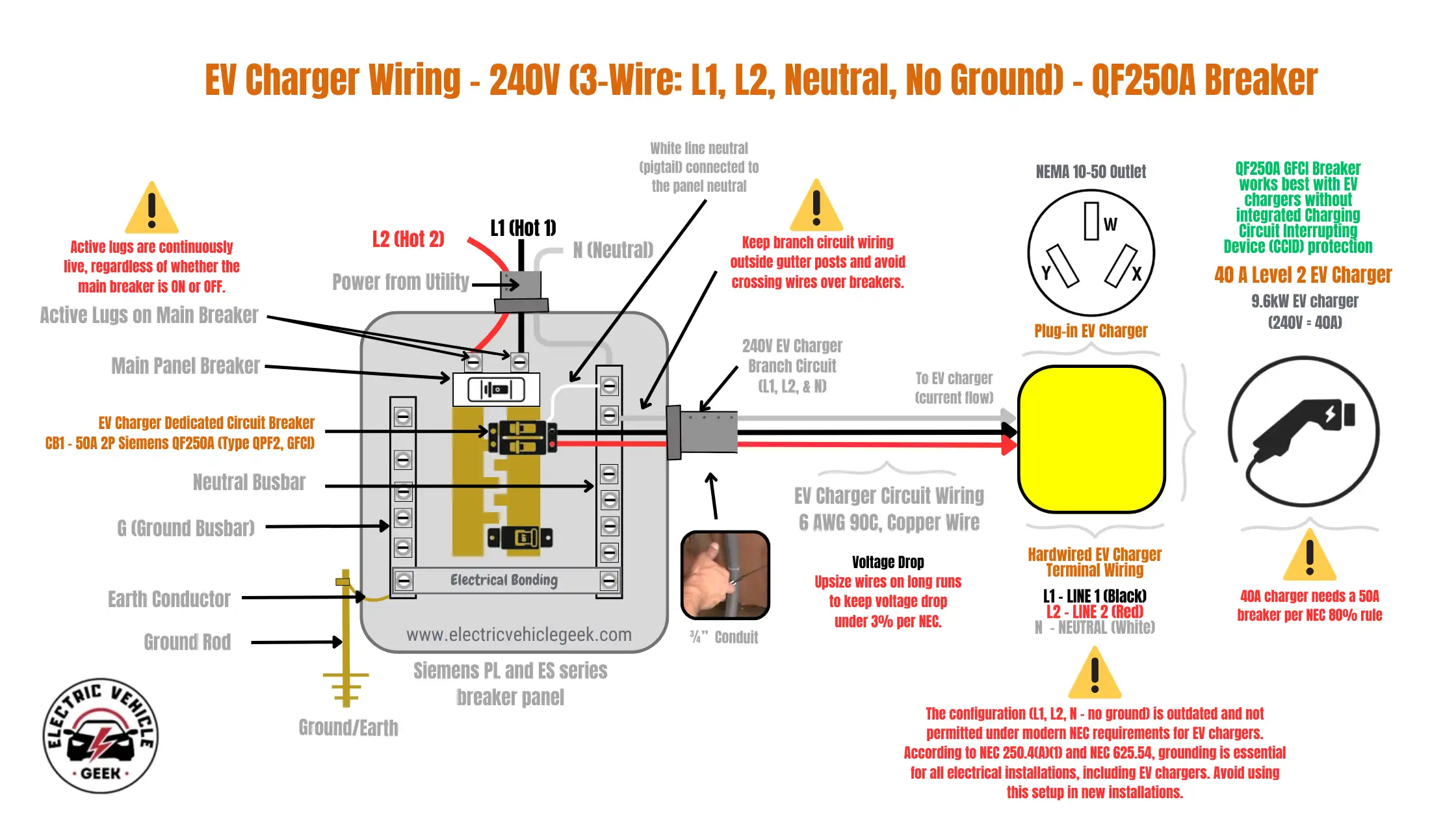
The Siemens QF250A GFCI breaker will still function, and GFCI protection will operate via the pigtail connection to the panel’s neutral bar. That said, this wiring is not compliant with modern code. For safety and inspection approval, always upgrade to a 4-wire system (L1, L2, Neutral, Ground or L1, L2, Ground) when replacing or upgrading the branch circuit.






There are no reviews yet.