There are four primary types of electric vehicle energy storage systems: batteries, ultracapacitors (UCs), flywheels, and fuel cells.
Electric vehicle energy storage systems are used in electric vehicles to store energy that is used to power the electric motor of the vehicle, while batteries are the most common types of electric vehicle energy storage systems, other types of electric vehicle energy storage systems exist today, they aim to solve the problems experienced by batteries such as high electric vehicle battery costs, range, energy density, charge rate, battery life, cycle efficiencies, among others.
In this guide, we will highlight the four main electric vehicle energy storage systems in use or development today, how they work, and their advantages and disadvantages when used to store energy in an electric vehicle.
Table of Contents
Electric Vehicle Batteries
Electric vehicle batteries are advanced portable energy storage systems comprising electrochemical cells that include an anode, cathode, and electrolyte.
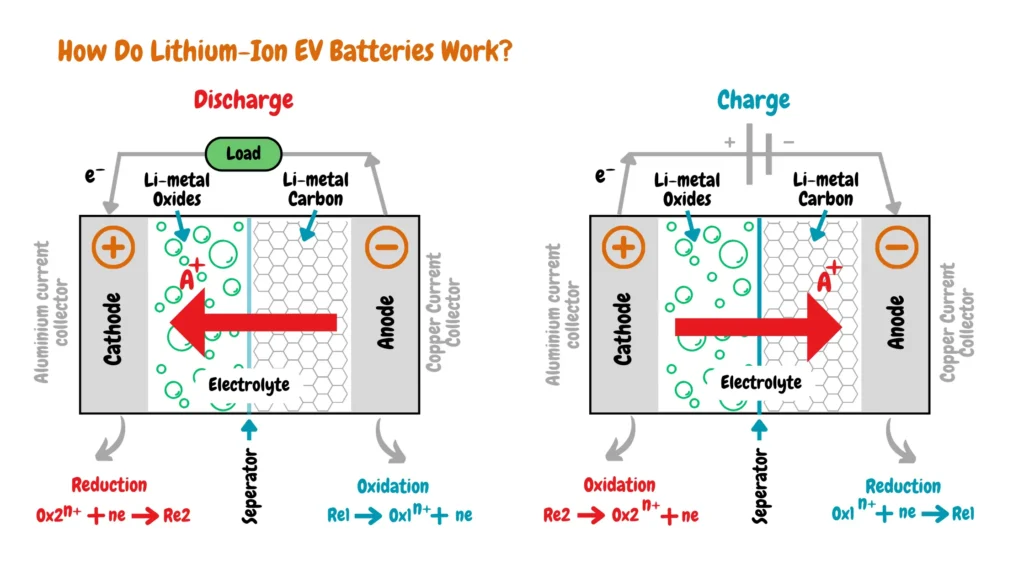
These components work together to efficiently convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy, delivering high performance with zero gas emissions, thereby minimizing environmental impact.
Several electric vehicle battery chemistries have been developed and used in electric vehicles, however, the most common and widely adopted electric vehicle battery chemistries are lithium-ion batteries, there are four electric vehicle battery geometries, small and large cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch battery geometries that are used in electric vehicle batteries depending on their intended application.
Electric vehicle batteries are the popular electric vehicle energy storage systems, this is because they have been integrated into popular all-electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles such as Tesla, Ford, Jeeps, and Toyota.
If you ask a random electric vehicle owner if they know of any other electric vehicle energy storage system apart from batteries they will say, they have never heard of or seen an electric vehicle using any other electric vehicle energy storage system apart from batteries, while electric vehicle readers who are geeky like us know a thing or two about fuel cells, which we will highlight later in this guide.
The popularity of electric vehicle batteries and their widespread adoption by manufacturers can be attributed to their ability to deliver peak and average power with exceptional efficiency. However, one of the significant challenges facing electric vehicle adoption remains the limitations related to electric vehicle battery range, size, and cost, which are the primary drawbacks of using batteries in electric vehicles.
The most important characteristics of electric vehicle batteries are battery capacities (Ah ), energy stored (kWh), and power measured in (kW), another important characteristic of batteries is state of charge (SOC) which tells us the percentage of energy available in the battery over time.
Other electric vehicle battery energy storage systems are currently in research and development to solve the technical demand for electric vehicle batteries such as high discharge rates, battery capacity, cycling capabilities, and recharge duration.
For more information about electric vehicle batteries, please check out our guide on electric vehicle batteries here >>
Electric Vehicle Ultracapacitors (UCs)
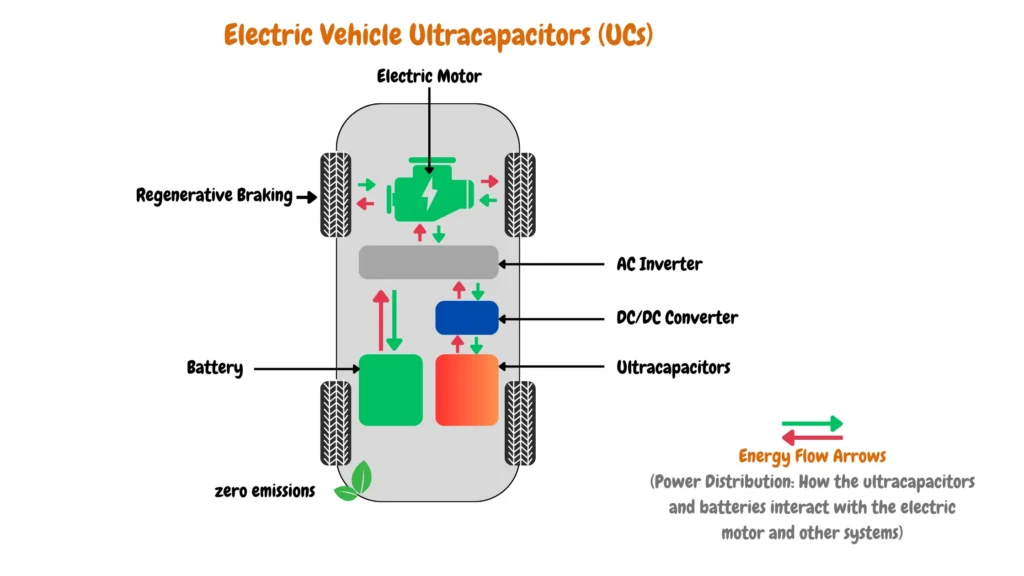
Electric vehicle ultra-capacitors are currently used as prototypes in an emerging electric vehicle, according to research and development data, electric vehicle ultra-capacitors have proved to offer fast charging speeds compared to electric vehicle batteries, and are more durable than electric vehicle batteries over time as they have energy storage system is charged and discharged, over time ultra capacities can withstand charging and discharging without degradation of the materials used in the manufacturing of the ultracapacitors.
Ultracapacitors have also proved to have a shorter charging time compared to electric vehicle batteries, there is a significant investment in the storage the use of ultracapacitors in electric vehicle batteries due to their unique characteristics such as maintenance-free operations, longer battery life of up to 40 years, insensitivity to changes in environmental conditions such as cold or hot weather, and shocks and vibrations experienced when they are integrated in real life mobility conditions.
One of the drawbacks of the use of ultracapacitors is the fact that they have a lower energy density than a similar-sized lithium-ion battery, however, development in nanotechnology promises an increased ion collection surface area of ultracapacitor to a quarter of the energy storage capacity currently available in lithium-ion batteries. There are also developments of hybrid electric vehicle energy storage systems that combine both ultracapacitors and battery technologies in an electric vehicle battery to make use of both ultracapacitors and battery technologies to offset the drawbacks of each electric vehicle energy storage system.
Electric Vehicle Flywheels
An electric vehicle flywheel is also known as an elector-mechanical battery, it converts and stores energy in a rotary mass, Flywheels used in electric vehicles consist of a carbon fiber wheel, a magnetic-floating bear, an electric motor, and power electronics control devices.
Flywheels tests in electric vehicles have shown that flywheels have an energy efficiency of 90%, and can be charged much faster compared to electric vehicle batteries, however, they have a higher specific power than batteries.
The use of flywheels generates no emissions, which makes them ideal for environmentally conscious electric vehicle buyers, they have zero maintenance requirements and have infinite charge and recharge cycles making them more durable than electric vehicle batteries.
Considerations of using electric flywheels in electric vehicles have been driven by the fact that their high charge and discharge cycles make them ideal for use in electric vehicles combined with regenerative braking.
Electric Vehicle Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are another form of electric vehicle energy storage system used in electric vehicles, they make use of hydrogen gas which is converted to mechanical energy by burning hydrogen with oxygen in an internal combustion engine to produce electricity that can be used to power an electric motor.
The use of electric vehicle fuel cells is not widely applied in electric vehicles since there exists operational problems relating to electro-catalysis, as well as issues with hydrogen generation, storage, and distribution, It is also important to note that the process of using fuel cells to power an electric vehicle is complex and the manufacturing costs are high.
Unfortunately, hydrogen tanks have a high specific energy and low volume energy density which makes them bulkier than gasoline tanks, which makes them unattractive to electric vehicle manufacturers and consumers.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.







