In this guide, we will delve into testing for EV charger earth leakage and faults in EV charger installations especially focusing on your EV charger grounding installation, providing you with step-by-step instructions, accessories required, and essential tips for testing for EV charger earth leakage and faults to ensure your EV charging setup operates efficiently and safely.
Whether you’re a homeowner installing a new charger using DIY methods or a technician maintaining EV charging infrastructure, understanding these testing procedures is crucial.
Table of Contents
What Causes EV Charger Earth Leakage and Faults
EV charger earth leakage, also known as an EV charger ground fault, can occur in EV chargers for a few reasons:
- Damage to the wires within the electric vehicle branch circuit, charging cable, or the EV’s charging port can create unintended electrical paths. This can happen due to wear and tear, cuts, or loose connections.
- Corrosion caused by moisture or debris buildup on the connections can compromise their integrity and lead to leakage.
- Internal issues within the electric vehicle branch circuit or the EV’s onboard charging system, like faulty sensors or control units, can also cause malfunctions that result in earth leakage.
Luckily, EV chargers and electric vehicle branch circuits are equipped with safety measures to detect and prevent these faults.
- Residual Current Device (RCD): This is a vital component that cuts off power in case of a leakage current exceeding a safe limit. Many EV chargers use a special type of RCD called a Type B that can detect both AC and DC currents, providing better protection.
- GFCI EV Charger Circuit Breaker: Installing a dedicated EV charger is also a safety measure against earth leakage and faults in EV charger installations, the EV charger circuit breaker will trip when they detect ground faults in your EV charger installations.
Testing EV Charger Earth Leakage and Faults
To test for EV charger earth leakage and faults you will need a specialized low-range Ohms meter to test your EV charger grounding system which should be close to 0 ohms of resistance – the lower the resistance the safer the electric vehicle branch circuit, most home digital multimeters are not capable of checking for low resistance or continuity, we use a specialized Vici VC480C+ LCD Digital Micro-ohm Meter that is capable of measuring low resistance or continuity of EV charger grounding systems.
We use the Vici VC480C+ LCD Digital Micro-ohm Meter and test the resistance or continuity of the EV charger electrode conductor by connecting the red probe to the main grounding bus of the EV charger electric panel, and the black probe to the EV charger earth lead if the black probe cant reach the EV charger earth rod we use a trailing lead as shown in the image below:
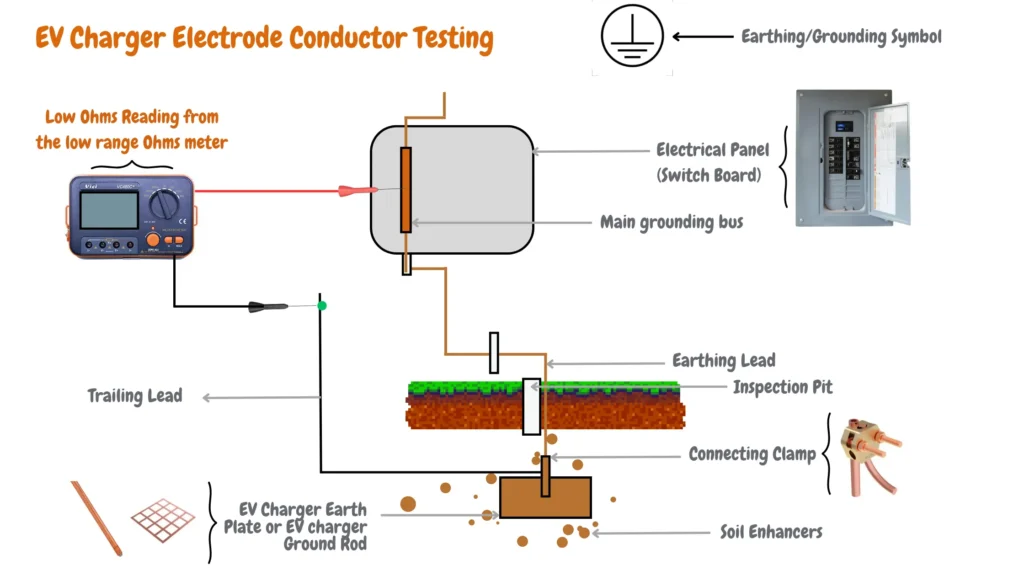
If the resistance or continuity of the EV charger electrode conductor is low by checking with a low range Ohms meter as shown in the image above and you are still experiencing EV charger earth leakage and EV charger leakage fault the culprit can be the electric vehicle branch circuit grounding system.
Plug-in EV Chargers Earth Leakage and Faults
To ensure the proper operation of plug-in EV chargers using either a NEMA 14-50R or NEMA 5-15R outlet, you should measure the resistance or continuity of the electric vehicle branch circuit. Check from the main ground bus of the EV charger to the ground point of the NEMA 14-50R or NEMA 5-15R outlet. Ensure that the resistance or continuity is very low, as indicated below:
Level 1 EV Plug-in EV Chargers Earth Leakage and Faults Testing
Level 1 EV chargers such as Lectron Level 1 EV Charger and Lectron Level 1 Tesla Charger are capable of indicating earth leakage and faults in EV charger installations on their LED indicators, by using a low-level Ohms meter you can test resistance or continuity of the main electrical grounding system, and also the electric vehicle branch circuit from the NEMA 5-15R grounding terminal to the main electrical panel grounding bar as shown in the image below:
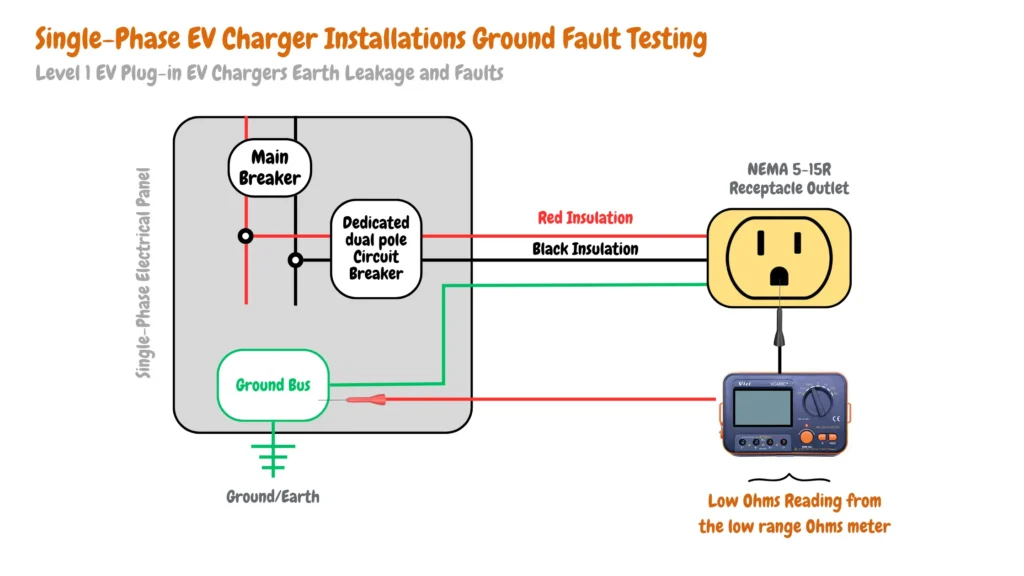
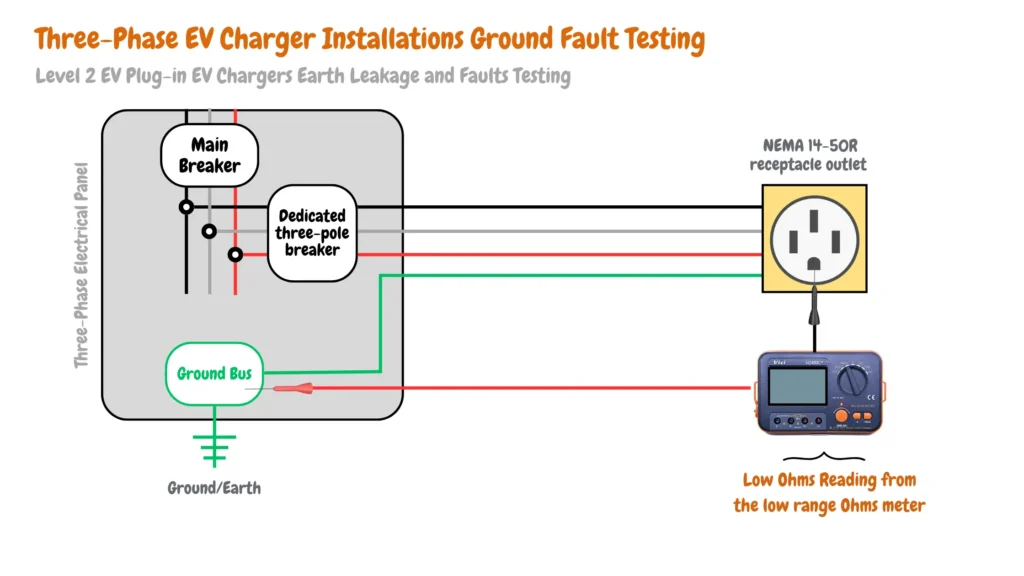
Level 2 EV Plug-in EV Chargers Earth Leakage and Faults Testing
For Level 2 EV plug-in EV chargers earth leakage and faults, you should test the resistance or continuity of the main electrical grounding system and the electric vehicle branch circuit grounding system from the NEMA 14-50R grounding terminal to the main electrical panel grounding bus as shown in the image below:
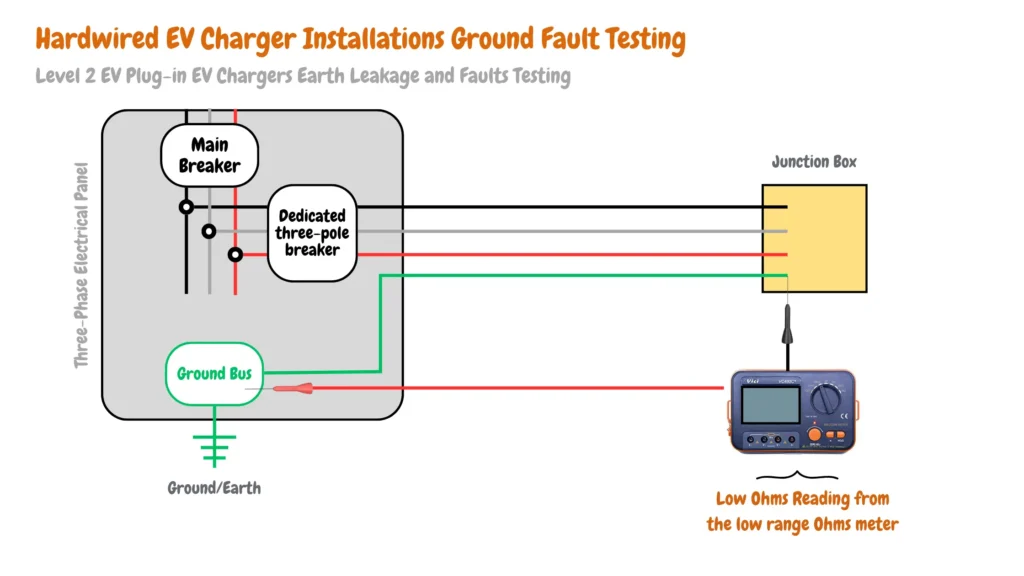
Hardwired EV Chargers Earth Leakage and Faults Testing
For hardwired EV chargers, where the charger is connected to the electric vehicle branch circuit via a junction box, it’s important to check the grounding cable. Verify the connection from the main ground bus on the electrical panel to the ground terminal on the junction box where the EV charger is connected to the branch circuit as shown in the illustrative image below:
Conclusions.
In conclusion, understanding and effectively testing for earth leakage and faults in EV chargers is crucial for ensuring safety and reliability in electrical installations.
By identifying potential issues early through comprehensive testing protocols outlined in this guide, including specific methods for plug-in and hardwired chargers at different voltage levels, operators can mitigate risks of electrical hazards and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Regular maintenance and adherence to testing procedures not only enhance operational efficiency but also uphold the integrity of EV charging infrastructure, fostering a safer environment for users and minimizing downtime due to electrical faults.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.
Last update on 2026-02-27 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API








