A licensed electrician might recommend an EV charger subpanel if there are not enough circuit breakers, to organize and install the EV charger near the point of use, or if they might need additional space for other EV charging devices. Learn more about why a subpanel is recommended for EV charger installations.
To connect the EV charger subpanel to the main electrical subpanel you will need a three-wire cable for three-phase installations or two thick cables for two-phase installations. It’s best to hire a licensed EV charger installer, as installing an EV charger entails working and wiring with high-voltage electrical components.
This blog post is just a guide to explain the basics of installing a subpanel for EV charger installations to help you understand the process and electrical components involved.
Table of Contents
What Is an EV Charger Sub-Panel?
An EV charger subpanel is also called a service panel or a remote panel which can be installed indoors or outdoors, its purpose is to offer protection to the electrical vehicle and its charger against electrical faults, surges, and shocks, it also houses electrical devices for EV charging such as dedicated EV charging circuit breakers, and other EV charging devices such as EV charging smart meters.
On complex EV charger installations such as EV chargers integrated with renewable energy sources such as solar EV charging and bidirectional EV chargers, a subpanel offers a connection hub for easier organization and load management of the EV charging systems.
An EV charging subpanel offers a secure distribution and load management of electric power from the main panel for EV charging, an EV charging subpanel might have two circuit breakers or one in case a main lug subpanel is installed, alongside the hotwires and neutral wires, an EV charging subpanel also features a ground wire as shown in a typical EV charging subpanel circuit diagram below.
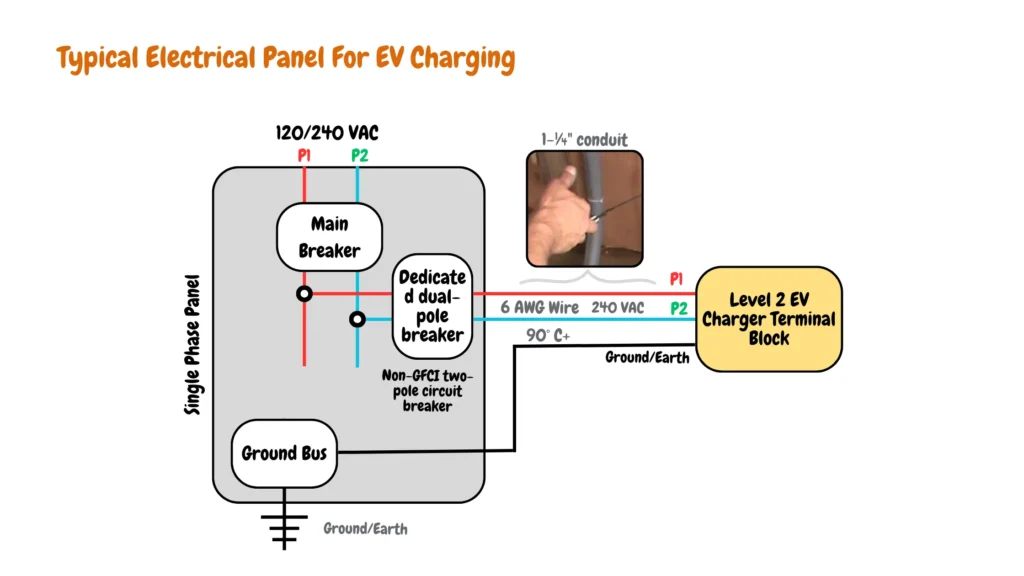
What You’ll Need
Here’s the essential list of tools and materials needed for wiring an EV charging subpanel.
- A set of Phillips and flathead screwdrivers in various sizes, typically ranging from #1 to #3 for Phillips and 3/16″ to 3/8″ for flathead.
- An adjustable wire stripper capable of stripping wires ranging from 10 to 22 AWG (American Wire Gauge) and capable of cutting wires cleanly.
- A reliable LED flashlight with a bright output for working in low-light conditions.
- A fish tape with a length of at least 25 feet for pulling wires through conduits and tight spaces.
- A non-contact voltage tester capable of detecting AC voltage from 12V to 1000V.
- A durable utility knife with a retractable blade for cutting insulation and other materials.
- A 100-amp or higher-rated sub-panel suitable for EV charging.
- A roll of high-quality electrical tape for insulating connections and securing wires.
- Dedicated circuit breakers are compatible with the subpanel, usually 15-amp to 60-amp breakers for EV charging circuits, but check the specific requirements of your EV charger for the appropriate size.
Dedicated Circuit Breaker and Cable to Use
| Circuit Breaker (amps) | Cable to Use (600 Volt Copper Cables) | Maximum Output (amps) | Power at 240V (Kilowatt) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 6 gauge | 48 | 11.5kW |
| 50 | 6 gauge | 40 | 9.6kW |
| 40 | 6 gauge | 32 | 7.7kW |
| 30 | 10 gauge | 24 | 5.7kW |
| 20 | 12 gauge (Yellow) | 16 | 3.8kW |
| 15 | 14 gauge (White) | 12 | 2.8kW |
How to Wire an EV Charger SubPanel
Referring to the provided circuit diagram, you’ll find a standard EV charger setup, showcasing both the main electrical panel and the interconnected EV charging subpanel. By adhering to the outlined best practices, you can ensure that your subpanel wiring mirrors this safe and efficient configuration.
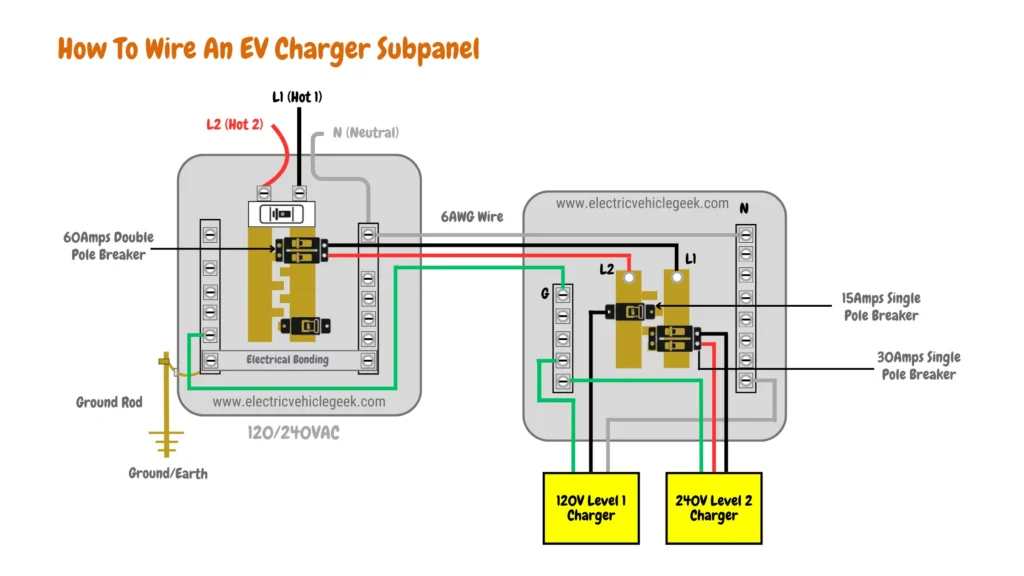
While this guide provides a general overview of subpanel wiring, it’s crucial to understand the inherent dangers of electrical work, especially when dealing with your main service panel.
- Prepare the SubPanel: Remove knockouts for the incoming main supply from the main electrical sub-panel and outgoing circuits. Use a screwdriver or chisel to break knockouts.
- Prepare the Main Panel: Install a dedicated subpanel breaker in the main panel. Connect the feeder wires (two hots and a neutral) following NEC and general wiring color codes: black for hot 1, red for hot 2, green or green/yellow stripe for ground, and white for neutral.
- Mount the Sub-Panel: Mount the subpanel securely, ensuring proper alignment with the service conduit and your chosen EV charger connection (junction box or NEMA 14-50R outlet).
- Wire the Sub-Panel: Use fish tape to pull the service wires from the main electrical panel through the conduit to the sub-panel. Connect the grounding wire to the grounding bus bar and the neutral wire to the neutral bus bar.
- Install Main Sub-Panel Circuit Breaker: Place the main circuit breaker for the subpanel (typically 100A to 200A) at the top of the sub-panel. Connect the two hot wires securely to the breaker.
- Wire Individual Dedicated Circuit Breakers: Install dedicated breakers sized for each EV charger’s current draw. For multiple chargers, distribute them evenly across both hot legs to balance the load.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.







