As electric vehicles (EVs) become more popular, many homeowners are seeking sustainable ways to power them. One of the best solutions is installing solar panels to charge your EV right at home. Not only does this reduce reliance on the grid, but it also helps lower your energy bills and carbon footprint.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you step-by-step through the process of installing residential solar panels for EV charging. From designing a solar EV charging system to navigating permits and regulations, we’ll cover everything you need to know. Whether you’re considering a DIY installation or planning to hire a professional solar installer, this guide will provide valuable insights to ensure your system is efficient, cost-effective, and tailored to your needs.
Table of Contents
- Getting Started with Home Solar EV Charging
- How Much Solar Power Do You Need to Charge Your EV?
- EV Charging Solar Panel Installation: DIY or Professional?
- Home Solar EV Charging Installation Process
- Inspection and Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions
Getting Started with Home Solar EV Charging
Before diving into solar EV charging, it’s essential to understand how solar energy works. Solar panels, or photovoltaic (PV) panels, capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, which can then be used to power your electric vehicle. Each panel is composed of solar cells made from semiconductors that absorb sunlight and release electrons, generating an electrical current as shown in the diagram below:
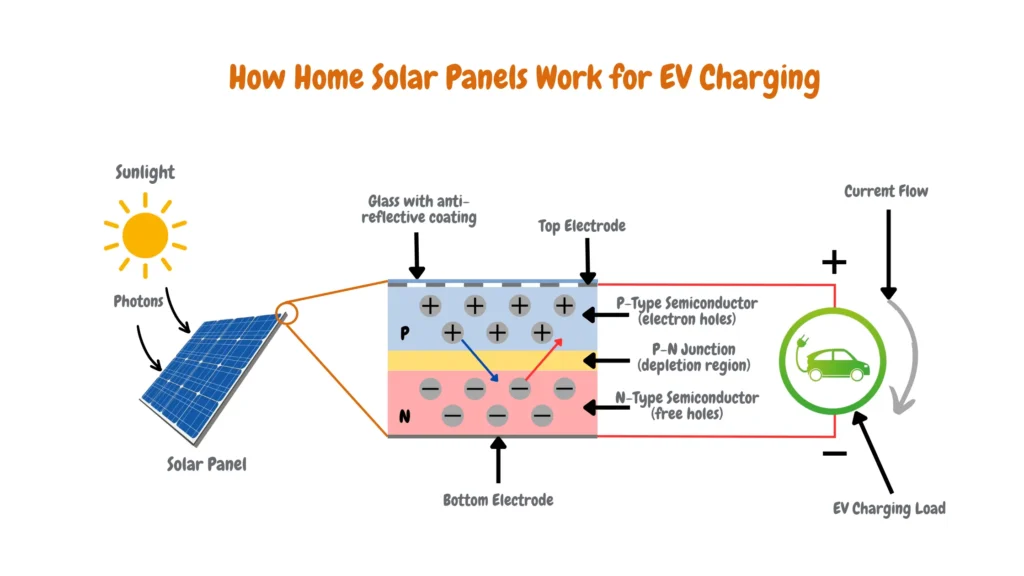
To efficiently meet your charging needs, you can either increase the number of solar panels you install or opt for higher-wattage panels. If your EV has a high-capacity battery, either approach will help ensure that your solar system produces enough energy to keep your EV charged.
Solar EV charging is not only environmentally friendly but can also help cut down on your energy costs. By using solar power to charge your vehicle, you reduce your carbon footprint and save on electricity. While the initial cost of installing solar panels for EV charging can be high, the savings over time help recover that investment. As your energy bills decrease, the long-term financial and environmental benefits make solar EV charging a smart, sustainable choice.
How Much Solar Power Do You Need to Charge Your EV?
The suitability of a solar kilowatt (kW) system for electric vehicle (EV) charging depends on several factors, including the EV’s energy consumption, the location’s sunlight exposure, and desired charging coverage.
| System Size | Charging Capability | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 kW | Primarily supports Level 1 charging; partial supplement. | $8,500 – $11,500 |
| 2 kW | It covers most annual charging needs, especially for Level 2 charging. | $13,000 – $17,000 |
| 3 kW | Handles high-capacity EV batteries; provides surplus energy. | $18,000 – $23,000 |
| 4 kW | Likely sufficient for most EVs; supports Level 2 charging. | $23,000 – $29,000 |
| 6 kW | Handles high-capacity EV batteries; provides surplus energy for other EV charging processes such as bi-directional EV charging. | $33,000 – $42,000 |
Key considerations include the EV’s efficiency, driving habits, sunlight exposure, and the need for energy storage. For optimal solar charging, a 4 kW or larger system is often recommended, but smaller systems can still contribute. Individual circumstances, such as driving patterns and location, will determine the most appropriate system size and EV charger level.
EV Charging Solar Panel Installation: DIY or Professional?
When installing solar panels for EV charging, you must decide whether to tackle the project yourself or hire a professional. This crucial choice can greatly affect the success, safety, and efficiency of your solar power EV charging system.
A DIY installation might appeal due to potential cost savings and the satisfaction of handling the project yourself, but it demands careful planning and technical skills.
On the other hand, professional installation offers expertise and ensures that everything is done correctly and in compliance with local codes, often providing long-term benefits and peace of mind.
In this guide, we’ll weigh the pros and cons of each option to help you decide which route is best for you.
DIY Residential Solar Panel Installation for EV Charging
With the surge of DIY solar panel installation tutorials for EV charging on YouTube, many homeowners are considering taking on the project themselves. The high engagement on these videos shows growing interest in DIY home solar EV charging installations to power EVs. But is a DIY solar installation the best option? Below, we’ll cover the pros and cons to help you decide if it’s worth the effort.
Advantages of DIY Residential Solar Panel Installation for EV Charging
- Cost Saving: Labor costs account for about 10% of the total system costs when installing residential solar panels for EV charging. You can reduce overall costs by up to 10% by doing the installation yourself. However, it’s important to carefully weigh these savings against a DIY approach’s potential risks and challenges.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Successfully installing a residential solar panel system for EV charging can be a highly rewarding experience. Not only does it give you a deeper understanding of how your home solar system powers your EV, but it also equips you to handle minor repairs and upgrades with confidence. This hands-on approach provides valuable skills that many EV owners find empowering as they transition to more sustainable energy solutions.
Factors to Consider with DIY Residential Solar Panel Installation for EV Charging
- Expertise and Skill: Installing solar panels for EV charging requires specialized skills, including a strong understanding of electrical systems, experience with EV charger installations, and a solid grasp of solar technology. Mistakes during installation can cause major inefficiencies or create serious safety hazards such as EV charging fires.
- Time Commitment: A DIY solar EV charging installation can be time-consuming, often requiring significant research, planning, and hands-on work over several days or weeks. Depending on the size and complexity of your Solar EV charging system we recommend making sure you have the time, and patience to complete the installation.
- Warranty Implications: DIY solar panel installation for EV charging can void equipment warranties or manufacturer guarantees for electric vehicles, EV chargers, and solar systems, potentially making you responsible for expensive repairs or replacements.
Professional Residential Solar Panel Installation for EV Charging
As a certified EV charger installer, I can attest to the fact that not all certified EV charger installers can install residential solar panels installations, and not all solar installers can install an EV charger, making professional residential solar panel installation for EV charging a complicated process where finding a professional to complete solar and EV charging installation for you is a challenge especially where complex processes are involved such as bi-directional EV charging.
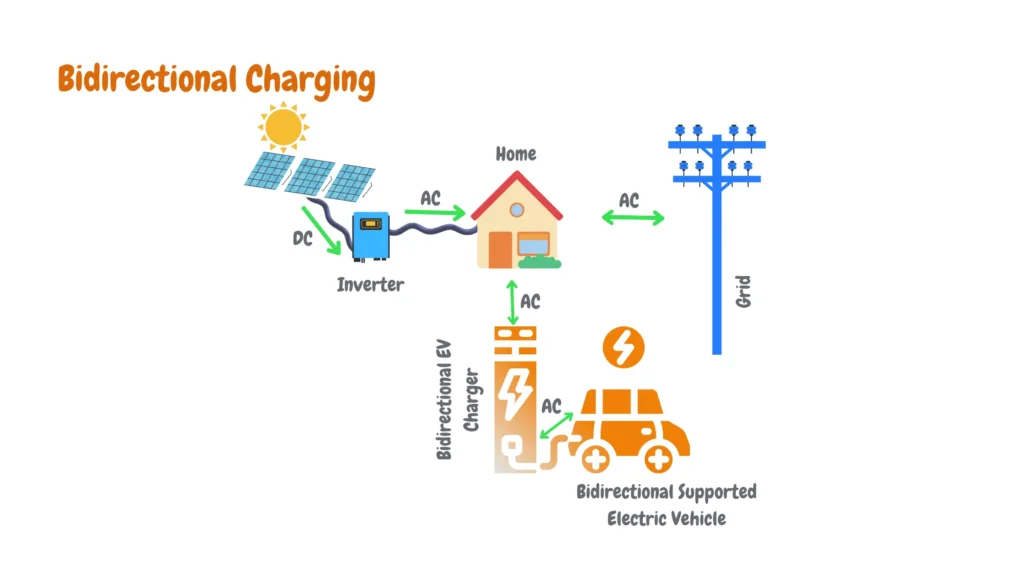
When hiring a professional for residential solar panel installation and EV charger setup, it’s crucial to ensure they hold certifications for both areas. If you cannot find a single installer with both certifications, consider hiring two separate specialists—one certified for EV charger installation and the other for solar panel installation. These experts can collaborate to ensure each system integrates seamlessly, sharing insights and coordinating their efforts for optimal performance.
This approach is far superior to hiring a certified EV charger installer who lacks expertise in solar panel installation, or a solar panel expert who is not knowledgeable about EV chargers. In both cases, the lack of specialized knowledge could lead to ineffective integration and suboptimal performance of your systems.
Collaborating with certified professionals in each area ensures that both the solar panel and EV charging systems are installed and integrated professionally for optimal efficiency and functionality.
Having addressed the #1 hidden complexities of professional residential solar panel installation for EV charging and provided guidance on ensuring a high-quality setup, let’s now explore the advantages and key factors to consider when opting for professional installation.
Advantages of Professional Residential Solar Panel Installation for EV Charging
- Expertise and Experience: Professional installers bring specialized knowledge and experience to handle their tasks, for example, certified EV charger installers are trained and certified in all aspects of EV charger installation while Solar panel installers are trained and certified in all aspects of solar panel installations. Their expertise ensures that each system is installed correctly and operates efficiently, minimizing the risk of issues and optimizing overall performance.
- Efficiency: We recommend hiring certified specialists for EV charger installation and solar panel installation separately due to their expertise in their respective fields. Each expert’s experience ensures that both systems are designed and installed to maximize energy efficiency. Conversely, hiring a professional without experience in either area may compromise the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the integrated system.
- Warranty Protection: Hiring qualified professionals for your residential solar panel and EV charger installation typically includes comprehensive warranty coverage. A certified solar panel installer ensures that the solar panel installation is covered by the manufacturer’s warranty, while a certified EV charger installer secures warranty protection for the charger. This approach provides peace of mind and protects you against potential issues, ensuring that both systems are well-covered and any problems can be addressed promptly.
Factors to Consider with Professional Residential Solar Panel Installation for EV Charging
- Costs: Labor costs for installing a residential solar panel system and EV charger typically account for about 10% of the total installation expense. This cost may increase based on the complexity of your solar-powered EV charging setup. However, investing in experienced installers can offer long-term benefits that outweigh the initial labor costs, ensuring a more efficient and reliable system.
- Choosing the Right Installer: Not all EV charger installers are adept at solar panel installations, and not all solar panel installers are experienced with EV chargers. It’s crucial to research and select reputable installers with proven success in both areas. We recommend obtaining multiple quotes from both EV charger and solar panel specialists. Thoroughly vet each candidate to ensure they are well-qualified in their respective fields, optimizing the effectiveness and integration of your systems.
Home Solar EV Charging Installation Process
Having reviewed the choice between DIY and professional installation, let’s examine the detailed process for installing residential solar panels and EV chargers. To streamline planning, management, and execution, we recommend dividing the project into two distinct phases: EV charger installation and solar panel installation. This step-by-step guide will offer a thorough understanding of what to expect during the installation of solar panels and EV charging systems on your property.
Residential Solar Powered EV Charger Installation.
Begin by evaluating the energy needs for your electric vehicle (EV) charging, including the overall energy demands of your home. Consider complexities such as multiple EVs or bi-directional charging, as these factors will influence the design and planning of both your EV charging circuit and solar energy system.
First, secure an electrical permit from your local building department and, if applicable, obtain approval from your homeowners’ association. Inform your utility company about potential impacts on your electrical load and apply for any additional building permits required by local government authorities.
Next, proceed with the installation of the solar-powered EV charger. Ensure the installation complies with all safety standards by scheduling and passing the necessary inspections. Obtain final approval or certification and maintain detailed records of all permits, approvals, and inspection reports for future reference.
Residential Solar Panel Installation for EV Charging
After the installation of the solar-powered EV charger, it is time for the installation of the solar energy system to power the EV charger. The first step involves designing and planning your EV-charging solar energy system:
EV Charging Solar Energy System Design and Planning
Designing and planning an EV-charging solar energy system requires a comprehensive assessment of several key factors. Start by evaluating your current and future EV charging needs, including the energy consumption of your electric vehicles. Consider regional solar radiation levels, local climate conditions, and shading effects to determine the optimal placement and orientation of your solar panels. Additionally, identify the requirements for solar EV charging accessories and battery storage to ensure a well-integrated and efficient system.
Simple Residential EV Charging Solar System
The Simple Residential EV Charging Solar System provides an easy-to-use solution for homeowners who want to power their electric vehicles with solar energy. The system typically includes solar panels that capture sunlight and convert photons into electricity, which flows through a solar inverter. This energy can then be used to charge the EV either directly or through a dedicated EV charger.
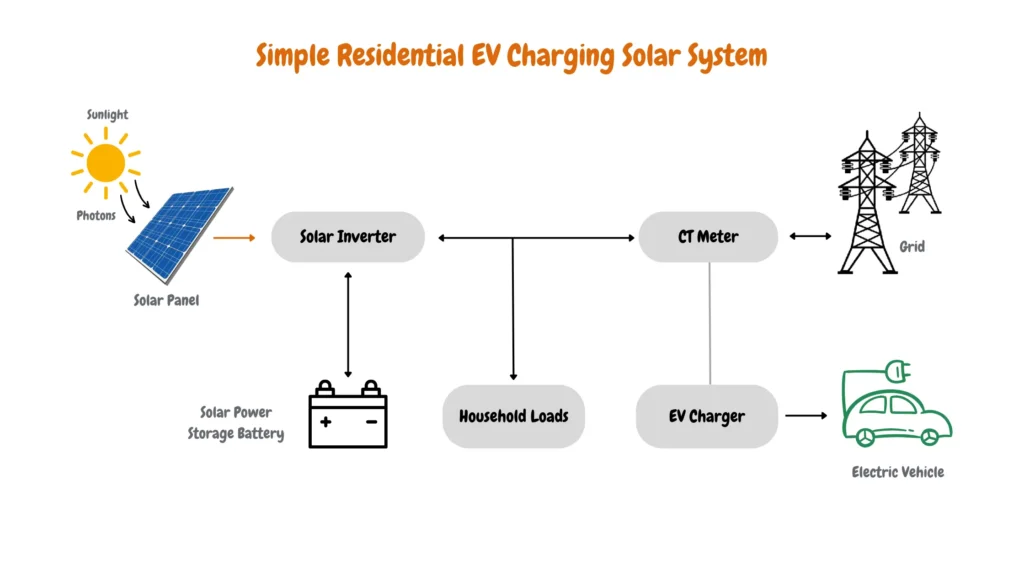
A solar power storage battery can store excess energy for later use, powering both household loads and the EV even when sunlight is unavailable. The system’s simplicity and cost-effectiveness make it an appealing option for households aiming to reduce their carbon footprint, while a CT meter helps monitor energy use and optimize grid independence.
Bidirectional EV Charging Solar System
On the other hand, the Bidirectional EV Charging Solar System offers a more advanced and flexible solution. This system integrates several key components to optimize energy use. It begins with solar panels capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity. This energy is then managed by a DC-DC Converter with MPPT and directed to a bi-directional inverter, which not only charges the EV using solar power but also allows the vehicle to return excess energy to the home or the grid.
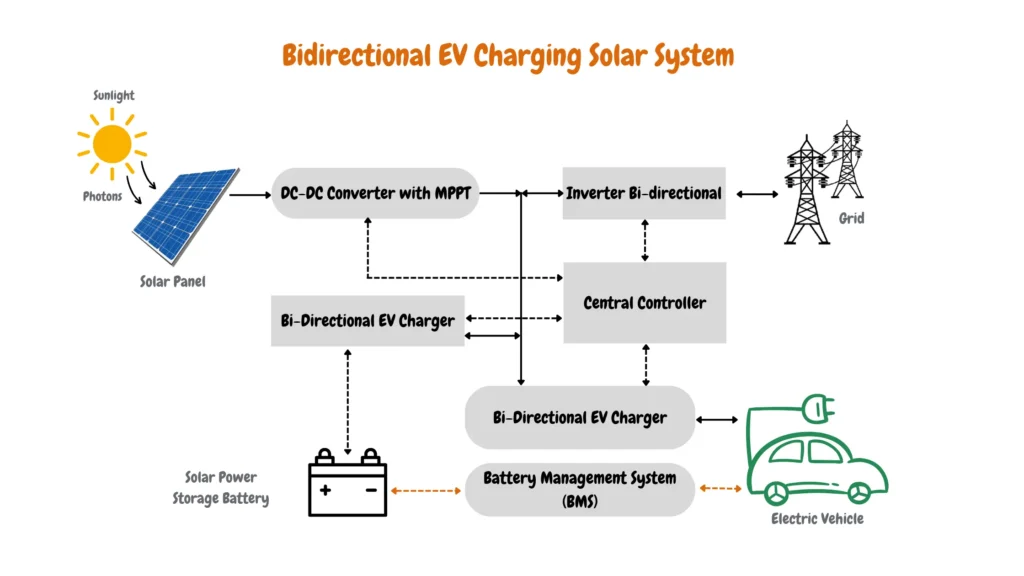
The system features a Bi-Directional EV Charger, allowing vehicles equipped with bidirectional EV charging capabilities such as the Tesla Cybertruck or the Ford F-150 Lightning to be charged with solar power while also enabling it to return excess energy to the home or the grid. This bidirectional functionality is supported by a Central Controller and a Battery Management System (BMS), which together ensure efficient operation and energy storage in the Solar Power Storage Battery.
This setup enhances energy efficiency, provides effective load balancing, and offers potential cost savings through energy trading. By utilizing these components, the Bidirectional EV Charging Solar System not only supports sustainable energy practices but also maximizes the benefits of solar power for residential energy management.
EV Charging Solar Panel Placement
When placing solar panels for electric vehicle (EV) charging, optimal location and positioning are key for maximizing energy efficiency. Here are some important factors to consider:
Roof Analysis
The first factor to consider when planning, designing, and placing solar roof panels is the structure and condition of your home’s roof. You should assess whether your roof can support the weight of the panels and evaluate factors like orientation, tilt, shading, and the compatibility of the mounting systems.
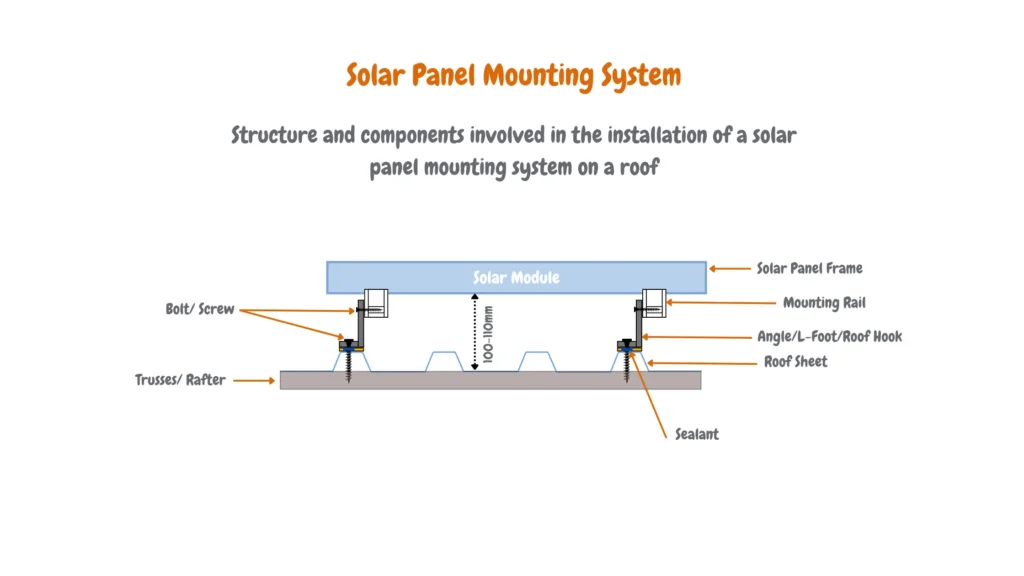
If your roof cannot handle the additional weight or doesn’t allow for an effective and functional setup, you might want to explore ground-mounted systems. Proper solar panel placement ensures the stability and longevity of your solar installation.
- Orientation and Tilt
Solar panels should be positioned to optimize sunlight exposure by facing the direction that captures the most sunlight throughout the day. In areas with seasonal variations, adjustable solar panel tilt mount brackets tilt help maximize energy production.
We use Newpowa adjustable solar panel tilt mount bracket kits (aluminum) with folding legs that allow us to adjust the solar panels for steeper or flatter angles as shown in the diagram below:
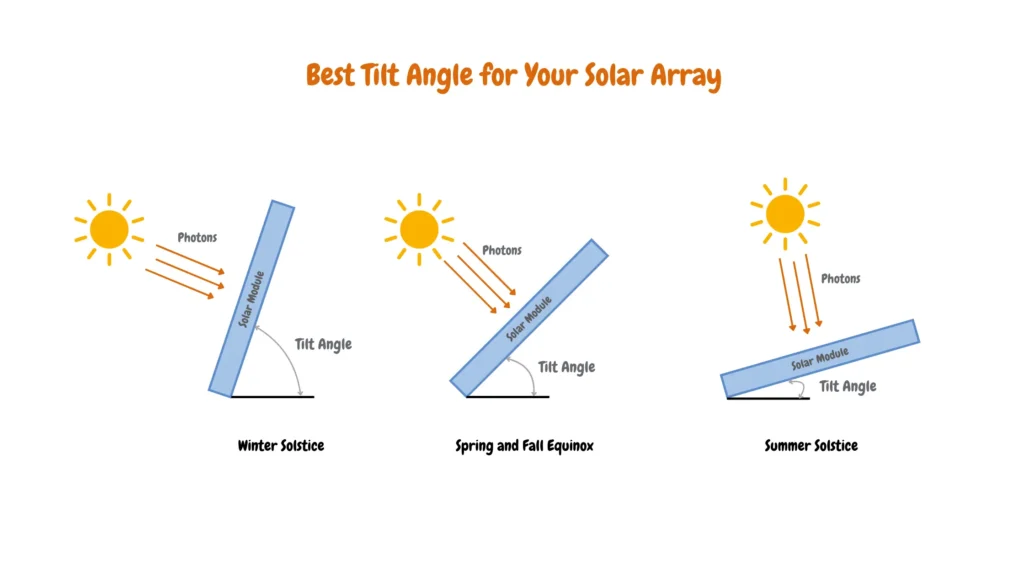
A steeper tilt angle is more effective during the winter months, while a flatter angle works better in the summer to capture more sunlight.
- Shading
Shading is one of the biggest factors that can reduce solar panel efficiency. To ensure maximum energy output, it’s important to avoid any shading caused by trees, buildings, or other structures, especially during peak sunlight hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
We use the solar angle guide to help determine the optimal angle for your solar panels especially if you have adjustable solar panel tilt mount bracket kits.
We rely on the Keopuals solar panel guide to determine the optimal angle for panels mounted on adjustable solar kits. For single adjustments, we set the panels at the ideal angle to ensure maximum efficiency during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., ensuring optimal energy capture.
We also optimize our solar panel installations by selecting microinverters in multiple solar panel installations to minimize the effects of shading, learn more on Solar EV charging inverter selection.
- Roof vs. Ground Mount EV Charging Solar Panel Placement
If you have sufficient roof space, a roof-mounted system can be a convenient option for placing solar panels. It’s important to make sure that the roof’s slope and orientation are well-suited for solar energy capture.
Alternatively, if roof space is limited or not ideal, ground-mounted systems provide greater flexibility. Ground mounts allow you to choose the best possible location, orientation, and tilt for maximum solar efficiency. They also tend to stay cooler, which can slightly improve performance.
Solar EV Charging Inverter Selection
Solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity, but your home and EV charger require alternating current (AC). The right inverter choice is essential for optimizing system efficiency, especially for EV charging setups.
For EV charger solar panel installations, there are two main types of inverters: string inverters and microinverters. While string inverters provide a cost-effective solution, we recommend microinverters for superior performance and reliability. In most of our home solar EV charging systems, we use Enphase IQ8+ Microinverters, which allow each panel to operate independently, maximizing energy production even in cases of shading or panel issues.
We recommend Enphase IQ8+ Microinverters for home EV charging solar panel installations due to their ability to operate independently. This feature minimizes the impact of shading or panel malfunctions, ensuring consistent power output—an essential factor for meeting the high demand for EV charging. This setup optimizes the efficiency of your EV charger, delivering reliable performance with your solar system.
Solar Battery Integration
Incorporating solar batteries into your home EV charging system is an excellent strategy to maximize the benefits of your solar panels. Solar batteries capture and store excess electricity generated during the day, allowing you to use this energy in the evenings or when sunlight is limited. Here’s why integrating solar batteries is a valuable addition, along with some insights into battery chemistries to consider:
- Energy Storage: Solar batteries store surplus energy from your solar panels, providing a reliable power source even when the sun isn’t shining. This ensures that your electric vehicle remains charged without relying on the grid, which can help reduce your energy bills.
- Grid Independence: With solar batteries, you can achieve greater energy independence by using stored energy during power outages or peak electricity demand periods. This capability enhances your energy security and minimizes reliance on potentially expensive grid power.
- Optimized Self-Consumption: Solar batteries maximize the self-consumption of your solar energy. Instead of exporting excess power back to the grid, you store it for later use, reducing the amount of electricity you need to purchase. This increases your overall energy efficiency and lowers your costs.
When choosing a solar battery for your home EV charging system, it’s important to consider the available battery chemistries. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries are currently the most popular choices.
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their lower cost and efficient performance, making them a common choice for many applications. However, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries offer notable advantages, including longer lifespan, greater depth of discharge, better temperature tolerance, and minimal risk of thermal runaway.
| Feature | LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | Li-ion (Lithium-ion) |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Life | 1,000 to 10,000 cycles—exceptional durability | 500 to 1,000 cycles—moderate lifespan |
| Energy Density | 40-55 Wh per lb—balanced energy storage | 45-120 Wh per lb—higher energy concentration |
| Depth of Discharge | Full 100%—maximizes usable capacity | 80-95%—conserves battery health |
| Temperature Range | -4°F to 140°F—versatile performance in various climates | 32°F to 113°F—optimized for milder conditions |
| Thermal Safety | Extremely safe—low risk of thermal runaway | Cautious handling required—moderate risk of thermal issues |
| Best For | Efficient energy use and TOU (Time-of-Use) savings | Reliable backup power and cost-effectiveness |
| Cost | $$$—higher initial investment with long-term savings | $$—more budget-friendly with shorter lifespan |
Inspection and Testing
Upon completing the physical installation of your residential solar panel system, the final inspection and testing phase is essential to ensure everything complies with safety standards and code requirements. This comprehensive evaluation involves:
- Regulatory Compliance Review: A thorough review of the entire installation to confirm adherence to local codes and regulations. This includes checking that all components, including solar panels, wiring, and mounting systems, meet legal and safety standards.
- Electrical Connections Verification: Technicians use tools such as a multimeter and torque wrench to inspect all electrical connections. This process ensures that connections are securely fastened and have proper continuity, reducing the risk of electrical faults.
- System Performance Testing: Advanced equipment, including a solar irradiance meter and power analyzer, assesses the system’s performance. The solar irradiance meter measures the sunlight intensity hitting the panels, while the power analyzer checks the system’s energy output to confirm it operates at optimal efficiency.
- Inverter Functionality Check: The inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from the solar panels to alternating current (AC) for household use, is tested using diagnostic tools. This ensures the inverter operates correctly and efficiently.
- EV Charger Testing: The electric vehicle (EV) charger itself undergoes thorough testing. This involves:
- Load Testing: Verifying the charger’s ability to handle and distribute power safely under various loads. This ensures it can charge your EV efficiently and reliably.
- Communication Check: Testing the charger’s communication with the home energy management system and the EV to ensure proper interaction and functionality.
- Safety Features Assessment: Check the charger’s built-in safety features, such as ground fault protection, overcurrent protection, and thermal management systems, to ensure they are functioning as intended.
- Safety Equipment Inspection: Verification of safety equipment like circuit breakers, grounding systems, and overcurrent protection devices to confirm they meet safety requirements and function properly.
Once the final inspection is completed, your solar panel system and EV charger will be fully operational, ready to deliver clean, renewable energy for your home, and efficiently power your EV charging needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will solar panels save me money on my electricity bills?
Yes, solar panels can significantly reduce your reliance on the grid, leading to substantial cost savings on electricity bills. This is especially beneficial for households with electric vehicles (EVs), as charging can increase electricity consumption.
How much maintenance do solar panels require?
Solar panels require minimal maintenance. Regular cleaning to remove dirt, leaves, and other debris is recommended. Occasional professional inspections can help identify and address any issues.
What is the difference between grid-tied and off-grid solar systems?
Grid-tied systems connect to the electric grid, enabling you to sell any excess solar power back to the utility company, making them a popular choice for residential installations. In contrast, off-grid systems operate independently from the grid and rely on battery storage to supply power during nighttime or cloudy periods, making them ideal for remote locations that lack grid access.
Which type of solar kit is right for me?
For most homeowners with access to the grid, a grid-tied solar system is the best choice. If you live in a remote area without grid access or want to be completely energy-independent, an off-grid system might be more suitable.
Can solar panels fully power my EV?
The ability of solar panels to fully power your EV depends on factors such as the size of your solar system, your vehicle’s energy consumption, and your location’s solar irradiance. In many cases, solar panels can significantly reduce your reliance on the grid for EV charging but may not cover all your charging needs.
What factors should I consider when sizing my solar system for EV charging?
When sizing your solar system, consider your vehicle’s battery capacity and charging needs, your home’s overall energy consumption, your location’s solar irradiance, and your budget with financing options.
Do I need a permit to install solar panels?
Permitting requirements vary by location. Check with your local building department for specific guidelines.
How can I finance a solar panel kit?
Several financing options are available, including solar loans, solar leases, and tax incentives. Research the options available in your area to find the best fit for your needs.
How long will solar panels last?
Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25-35 years, but with proper maintenance, they can last even longer.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.
Last update on 2026-03-09 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API










