In an era where sustainability meets innovation, the electric vehicle (EV) market is surging at an electrifying pace. Recent research on Electric Vehicle Technology and Its Impacts reveals a significant finding: the electricity and heat sector emerges as the foremost contributor, responsible for a staggering 42% of CO2 emissions, with transportation trailing behind at 22% as shown in the chart below.
As the world shifts gears towards eco-conscious transportation to tackle these challenges, especially on electricity and transportation effects on the environment, the need to power up conveniently becomes paramount.
Enter the home EV charger – the game-changer in your journey towards sustainable mobility embracing the freedom to refuel right in your garage. The benefits are manifold: unparalleled convenience, long-term cost savings, and the lightning-fast speed of charging from the comfort of your own home.
In this guide, we’ll highlight the home EV charger installation process, providing insights into both do-it-yourself (DIY) solutions and professional installation options for plug-in home EV Chargers and Hardwired home EV Chargers just like we have them installed in our garage, and also how we install them for clients.
Considerations Before Installing Your EV Charger
Before diving into the exciting world of home EV charger installation, let’s take a moment to assess whether the DIY route is the right fit for you. There are two main paths you can take: tackling the project yourself or partnering with a qualified electrician.
DIY EV Charger Installation
If you’re comfortable with electrical work and enjoy tackling home improvement projects, DIY installation might be a viable option for you. Here’s what you need to consider:
- Skills and Tools: Possessing basic electrical knowledge and experience is crucial. You’ll need tools like wire strippers, crimpers, a voltage tester, and possibly a drill and saw depending on the installation complexity. Familiarize yourself with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and relevant safety regulations.
- Safety First: Ensure you understand and follow all safety protocols to avoid potential hazards. Invest in proper personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and safety glasses. Remember, even seemingly minor mistakes can have serious consequences.
Hiring Certified EV charger Installers
While the DIY path offers potential cost savings, there are situations where professional installation is the wiser choice. Here’s why:
- Complex EV Charger Installations: If your electrical system requires significant modifications, navigating the process alone can be daunting. Hiring a qualified electrician ensures the work meets safety standards and adheres to local building codes.
- Limited Expertise: If electrical tasks make you uneasy, prioritize safety and peace of mind. A professional brings their experience and knowledge to the table, guaranteeing a smooth and hassle-free installation.
- Warranty and Support: Most professional installations come with warranties, offering valuable protection and peace of mind in case of unforeseen issues. Additionally, you’ll have access to expert support should you need assistance in the future. Some EV chargers mandate certified installers for EV charger warranty coverage.
Ultimately, the decision rests on your individual comfort level, skills, and available resources. Weigh the pros and cons carefully, and remember, prioritizing safety should always be your top concern.
Choosing the Right Home Charger
Now that you’ve decided on your installation path, it’s time to choose your home EV charger! But with various home EV charger options out there, how do you pick the perfect one? highlighted below are some of the key considerations to guide you in choosing the right home EV charger for you.
Which Home EV Charger Is Trending? Find Out Now!Home EV Charger Levels
The world of EV chargers is categorized by “Levels,” each offering distinct charging speeds and capabilities. Home EV Charger levels include:
Level 1 Chargers (Trickle Charge)
These handy units come included with most EVs and plug into a standard 120V outlet. Think of them as slow and steady, adding around 2-5 miles of range per hour. While convenient for occasional top-ups, they’re not ideal for daily charging due to their limited speed.
Level 2 Chargers (Fast Chargers)
These powerful options, also known as SAE J1772 chargers, typically require professional installation and connect to a 240V outlet (think dryer or oven outlet). They offer significantly faster charging, adding 20-30 miles of range per hour, making them ideal for daily use. Popular models include Enphase Smart Level 2 EV Charger, JuiceBox Pro, and ClipperCreek HCS-40.
Level 3 Chargers (DC Fast Chargers)
Often found at public charging stations, these heavyweights deliver direct current, juicing up your EV battery much faster (50-350 kW). While convenient for on-the-go charging, they’re not recommended for regular home use due to their high cost and potential impact on your electrical system.
Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right charger involves more than just EV Charging speed. Here are some crucial factors to also consider:
- Your EV’s Compatibility: Ensure the charger’s connector type matches your EV’s inlet (usually J1772 for most models, but Tesla uses a proprietary connector).
- Charging Needs and Habits: If you drive long distances daily, a Level 2 charger is a must. For occasional use, a Level 1 might suffice. Consider your typical mileage and charging frequency to avoid EV charging anxiety, which is real by the way!
- Budget: Level 1 chargers are the most affordable, while Level 2 and 3 chargers come at a higher price tag. Factor in professional installation costs if opting for Level 2.
- Smart Features: Many chargers offer smart features like scheduling, app control, and energy monitoring, enhancing convenience and potentially lowering costs.
Planning for your Home EV Charger Installation
Now that you’ve chosen your home EV charger, it’s time to map out your installation strategy. This crucial step ensures a smooth process, avoids potential hiccups, and keeps safety at the forefront.
So, let’s dive into the key aspects of planning your home EV charger installation.
Where to Install Home EV Charger
If your garage, carport or diveway is not accessible, convinient and safe, and you are thinking of installing your home EV charger in another location, consider the following:
- Accessibility: Ensure your chosen spot allows easy access to your EV’s charging port, with enough cable length for maneuvering. Consider parking patterns and driveway layouts.
- Safety: Keep the charger away from flammable materials, water sources, and high-traffic areas. Adhere to local building codes and fire safety regulations.
- Weatherproofing: If installing outdoors, choose a weatherproof charger and ensure proper protection from rain, snow, and harsh sunlight.
- EV Charger electrical requirements: Check Electrical Capacity. The electrical requirements for a home EV charger typically include a dedicated circuit with sufficient amperage (32A or 40A for Level 2), compatible voltage (usually 240 volts for Level 2), and proper grounding. check if your home’s electrical panel can support the additional load (usually 100A or 200A) and that the wiring meets local building codes. Consult with a certified electrician for assessment and recommendations.
Do I need a permit to install a home EV Charger
Want to simplify the process?
- Contact Your Local Authority: Reach out to your local building department or electrical inspector to understand specific permit requirements in your area.
- Prepare for the permit application Process: Gather necessary documentation, including charger specifications, installation plans, and electrical diagrams, and submit them for review and approval.
- Seek professional Assistance: Hiring a licensed electrician often streamlines the permitting process, as they are familiar with local regulations and can handle the paperwork on your behalf.
DIY Home EV Charger Installation Guide
This section provides a general overview of how we install our EV chargers, but remember we are professionals, if you intend to install your home EV charger yourself safety is paramount. Proceed with caution, ensure you possess the necessary skills and knowledge and strictly adhere to safety regulations and the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Tools Required for Home EV Charger Installation.
Before embarking on your DIY journey, assemble the necessary tools and materials:
- Safety Gear: Invest in personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves, safety glasses, and arc flash suits for added protection.
- Electrical Tools: Ensure you have appropriate tools like wire strippers, crimpers, a voltage tester, and potentially a drill and saw depending on your installation complexity.
- Charger-Specific Kit: Most Level 2 charger manufacturers offer DIY installation kits containing necessary cables, brackets, and hardware specific to their model.
How to Install Your Home EV Charger
Highlighted below are the general steps we take when installing home EV chargers, and specific steps may vary based on your chosen charger and electrical setup. Always consult your specific EV charger installation instructions and relevant safety guidelines.
Here are the generalized steps we take when installing a home EV Charger:
Prepare the Installation Site
Choose a suitable location, considering accessibility, safety, and weatherproofing (if applicable). Mark the mounting points and cable route.
Electric Car Charger Home Wiring Diagram
To help you plan your EV charger electrical processes, here are electric car charger home wiring diagrams for both plug-in and hardwired Level 2 EV charger installations, along with explanations for each component.
Plug-in EV Charger Wiring Diagram
The plug-in EV charger wiring diagram below illustrates how we install plug-in EV chargers.
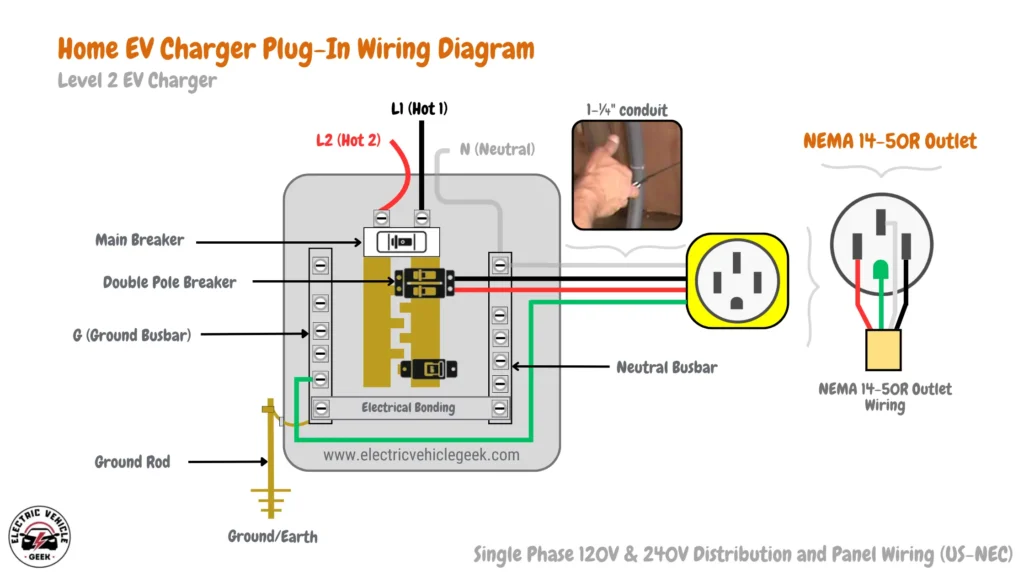
Plug-in EV Charger Installation Components:
Highlighted below are the components of a plug-in charger installation as shown in the plug-in EV charger wiring diagram above:
- Single Phase Panel: Your residential electrical panel, typically operates on a single phase with voltage ranging from 120 to 240 volts.
- Main Breaker: The primary circuit breaker in your home’s electrical panel.
- Dedicated Dual-Pole Breaker (Non-GFCI Two-Pole Circuit Breaker): A separate breaker dedicated solely to the EV charger circuit.
- Ground Bus: A central point where all grounding wires connect.
- NEMA 14-50R Receptacle Outlet: The standard outlet for plug-in EV chargers, providing 240 VAC.
- P1, P2, Ground/Earth: Terminals on the NEMA 14-50R outlet corresponding to hot (P1 & P2) and ground connections.
- 1-¼” Conduit: Conduit pipe protecting the wiring from physical damage and environmental factors.
How to Install a Plug-in EV Charger
As shown in the plug-in EV charger wiring diagram above:
- A dedicated dual-pole breaker is installed in your breaker panel, connected to the main breaker.
- The breaker connects to the ground bus with a grounding wire.
- A 1-¼” conduit runs from the breaker panel to the chosen location for the NEMA 14-50R outlet.
- Inside the conduit, three wires are routed: two hot wires (P1 & P2) and a ground wire.
- The conduit terminates at the NEMA 14-50R outlet, where the wires are connected to the corresponding P1, P2, and Ground/Earth terminals.
- The EV charger plugs directly into the NEMA 14-50R outlet, receiving 240 VAC for charging.
- We recommend installing the NEMA 14-50R outlet 20-26 inches from the ground for accessibility.
Plug-in EV Charger Safety Measures.
EV charging involves high-voltage electricity, increasing the potential for leakage and the risk of shock. RCDs provide crucial protection against this danger. Additionally, plug-in home EV chargers are often expensive and susceptible to damage from voltage spikes. SPDs offer an extra layer of security, ensuring the longevity and safety of your charging equipment.
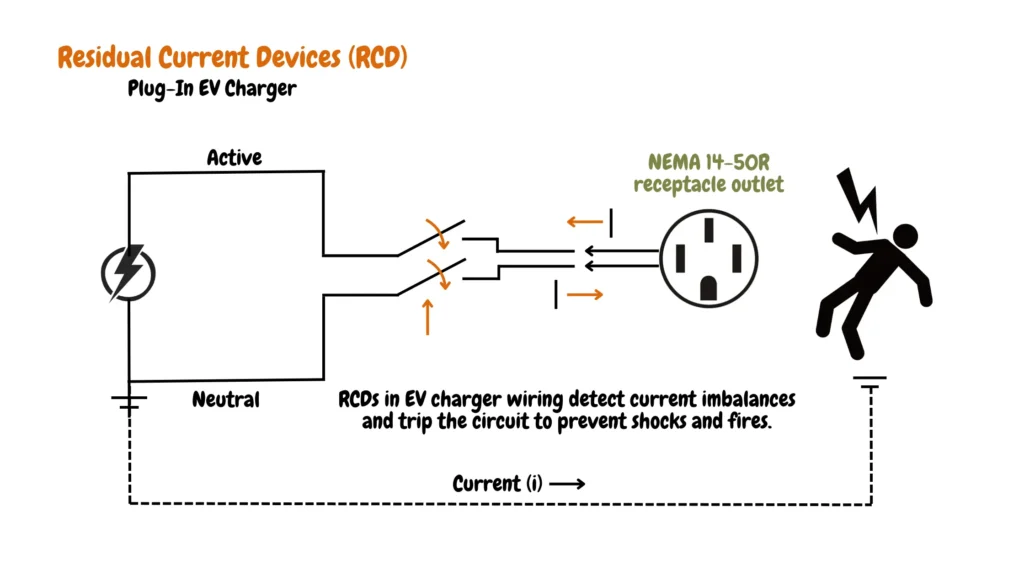
Residual Current Device (RCD) in Plug-in EV Charger Installation.
As shown in the Residual Current Devices (RCD) wiring diagram for EV chargers shown below, the RCD Detects imbalances in electrical current, and the RCD swiftly cuts power if a leak or shock hazard is detected, preventing potential injuries. Required for EV charging circuits, RCDs mitigate risks associated with high-voltage systems.
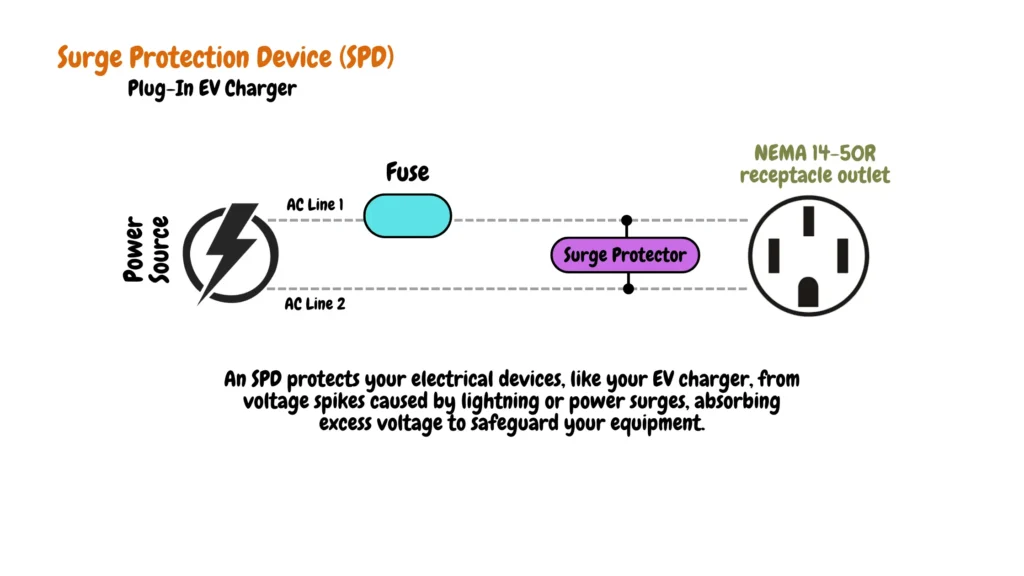
Surge Protection Device (SPD) in Plug-in EV Charger Installation.
We also recommend installing a surge protection device on your EV charger as shown in the illustrative image below to shield your EV charger and other electrical equipment from voltage spikes triggered by lightning or power surges, the SPD absorbs excess voltage, safeguarding sensitive electronics from damage.
Hardwired EV Charger Wiring Diagram
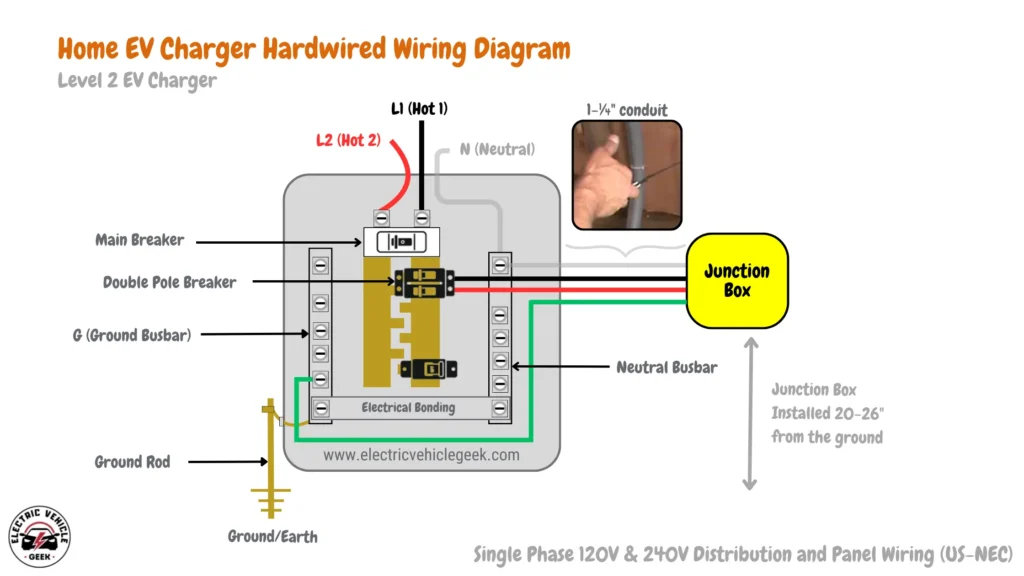
Hardwired EV Charger Wiring Components
- Single Phase Panel: Your home’s electrical panel, typically single-phase 120v/240v for residential use
- Main Breaker: The main circuit breaker in your home’s electrical panel.
- Dedicated Dual-Pole Breaker (Non-GFCI Two-Pole Circuit Breaker): A separate breaker dedicated solely to the EV charger circuit.
- Ground Bus: A central point where all grounding wires connect.
- Home EV Charger Terminal Block: The internal connection point for the charger’s wiring where P1, P2, Ground/Earth High-gauge wire (6 AWG Wire) suitable for handling the EV charger’s current, we recommend purchasing 90° C+ capable of handling heat generated typically wires that can handle 90° C+.
- 1-¼” Conduit: Same as the plug-in diagram.
- : Same as the plug-in diagram.
How to Install a Hardwired EV Charger
To install a hardwired EV charger as shown in the hardwired EV charger wiring diagram above, start by running a 1-¼” conduit from the breaker panel to your chosen location for the charger.
Inside the conduit, route three 6 AWG wires: two hot wires (P1 & P2) and a ground wire, all rated for 90°C or higher. Then, terminate the conduit at the EV charger’s terminal block, connecting the wires to the corresponding P1, P2, and Ground/Earth terminals.
Since it’s hardwired, the EV charger is directly connected to the circuit, bypassing the need for an outlet.
Hardwired EV Charger Safety Measures
When it comes to ensuring safety in hardwired EV charger installations, two critical components stand out: the Residual Current Device (RCD) and the Surge Protection Device (SPD).
Residual Current Device (RCD) in Hardwired EV Charger Installations
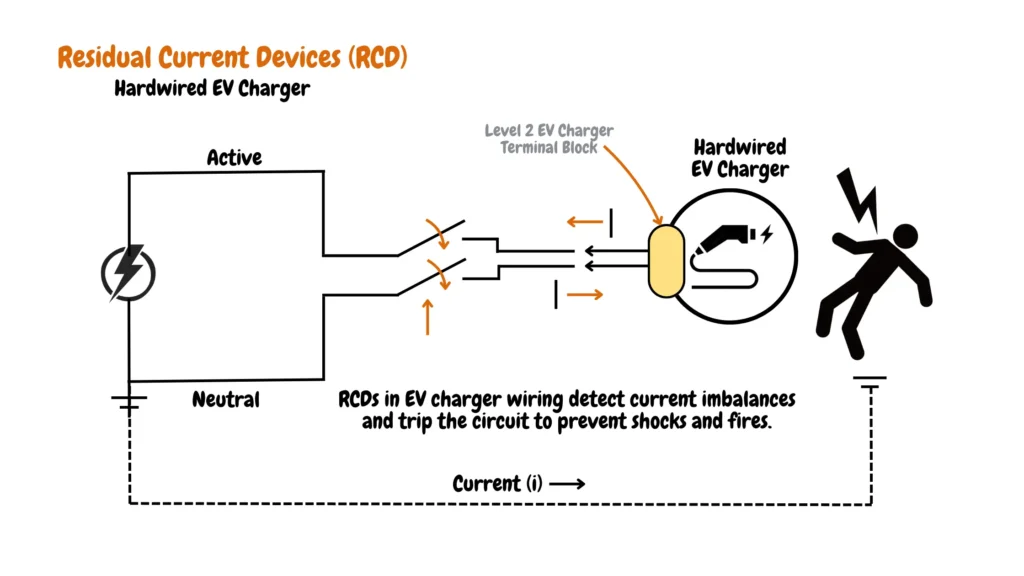
The RCD plays a pivotal role in detecting minute imbalances in electrical current, promptly shutting off power to prevent potential leakage or shock hazards. With its rapid response time measured in milliseconds, the RCD acts as a crucial safeguard against serious injuries or fatalities. Its installation is mandatory for hardwired EV chargers due to the inherent risks associated with high-voltage systems.
Surge Protection Device (SPD) in Hardwired EV Charger Installations
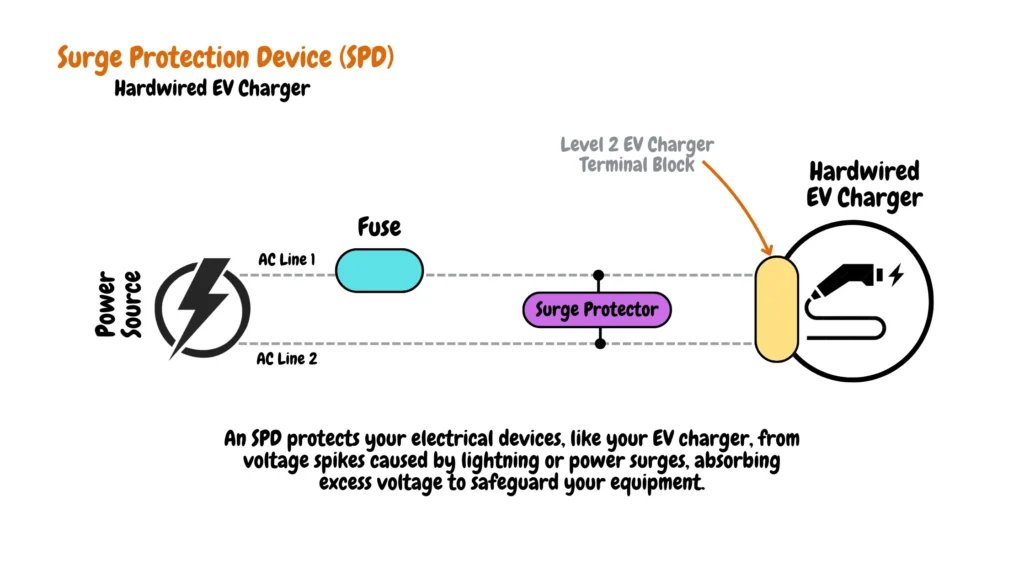
Complementing the RCD, the Surge Protection Device (SPD) provides essential defense against voltage spikes caused by lightning, power surges, or similar events. These spikes pose a significant threat to sensitive electronics, potentially resulting in costly damage or replacement. By serving as a sacrificial barrier and absorbing excess voltage, the SPD shields the EV charger and other valuable equipment, minimizing the risk of harm and ensuring continued operation.
Hiring a Certified Home EV Charger Installer
While the DIY approach can be rewarding for some, partnering with a qualified electrician offers several advantages for your home EV charger installation. This section highlights the benefits of professional installation and guides you on finding the right pro for the job.
Why Choose A Certified Home EV Charger Installation?
Opting for professional installation empowers you to reap the benefits of your home EV charger with complete peace of mind. Here’s why:
- Expertise and Experience: Licensed electricians possess the knowledge, skills, and experience to handle complex electrical work safely and efficiently. They stay updated on the latest regulations and ensure code compliance, minimizing potential risks.
- Safety First: Professional installers prioritize safety throughout the process. They use proper personal protective equipment, follow strict safety protocols, and conduct thorough testing to ensure your electrical system and home remain protected.
- Warranty and Support: Many professional installations come with warranties on both the work and the charger itself, offering valuable protection and peace of mind in case of unforeseen issues. Additionally, you’ll have access to expert support should you need assistance in the future.
- Time-Saving Convenience: Hiring a professional saves you valuable time and effort. They handle all aspects of the installation, from planning and permitting to wiring and final testing, leaving you free to focus on other priorities.
Finding the Right Certified Home EV Charger Installer
Now that you’re convinced of the benefits, it’s time to find the perfect electrician for your project. Here’s how:
- Ask for Recommendations: Seek referrals from friends, family, neighbors, or online communities who have recently installed home EV chargers. Positive word-of-mouth can be a great starting point.
- Check Qualifications and Credentials: Ensure the electrician is licensed and insured in your area. Verify they have experience with EV charger installations and familiarity with your specific charger model.
- Get Multiple Estimates: Compare quotes from different electricians to find one that offers competitive pricing and aligns with your budget and project needs.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions about the electrician’s experience, approach, timeline, and warranty terms. A transparent and communicative professional is key to building trust.
- Check Online Reviews: Look for online reviews and testimonials from past clients to gauge the electrician’s reputation and customer satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions.
Can I install my own EV charger at home?
Can you plug an EV directly into a 220v outlet?
Should I install an EV charger at home?
How does an EV charger connect to your house?
Can a local electrician install an EV charger?
Can I install a fast EV charger at home?
What to consider when installing an EV charger?
How much power does a home EV charger need?
How much does it cost to install an EV charger?
Can I have 2 EV chargers?

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.







