While understanding EV charging levels is key, confusion around them can hamper the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, which could hinder our progress toward a more eco-friendly transportation industry.
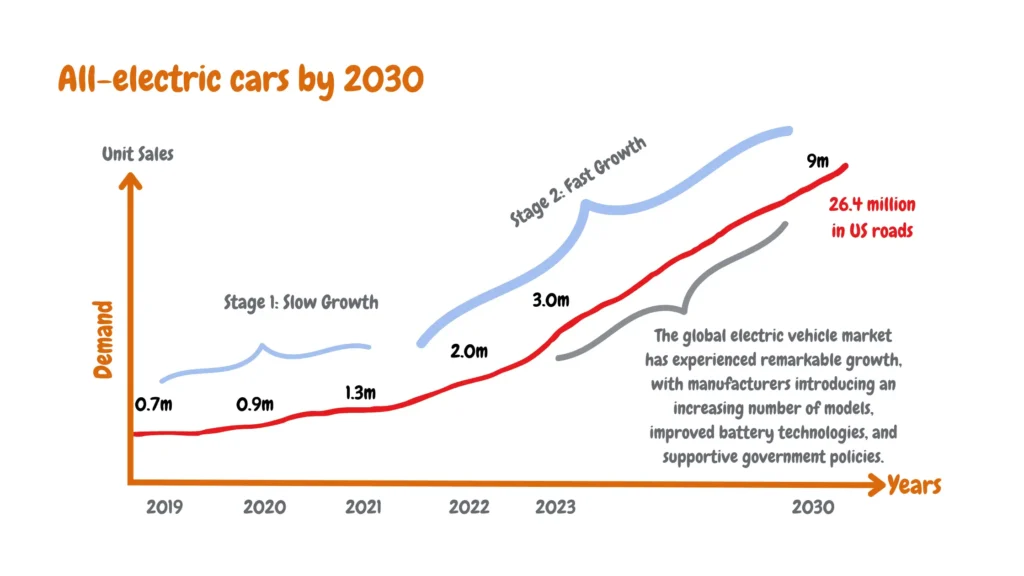
The landscape of electric vehicles (EVs) is transforming rapidly, with it, the ease of charging. In the United States alone, the number of EVs on the road is skyrocketing, projected to reach 26.4 million by 2030, as shown in the image below: 2019-2030 electric car growth in the United States.
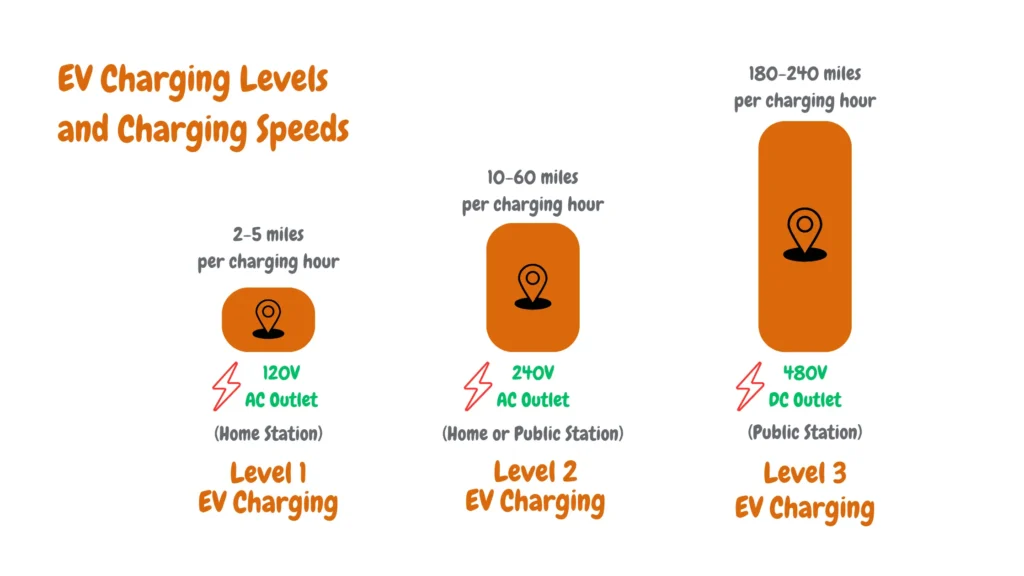
As we strive to reach the forecasted figures for green transportation, readily available and efficient charging solutions are crucial. This guide helps eliminate that roadblock by demystifying the three EV charging levels (Level 1 charging, Level 2 charging, and Level 3 charging) and empowering you to make informed choices.
What are the 3 Levels of EV Charging?
The charging speed and power requirements increase with each level, with higher levels delivering more power to the vehicle as shown in the chart below, thereby shortening the charging time.
Level 1 EV Charging
The diagram below provides a detailed breakdown of Level 1 EV charging, the most basic method of charging electric vehicles.
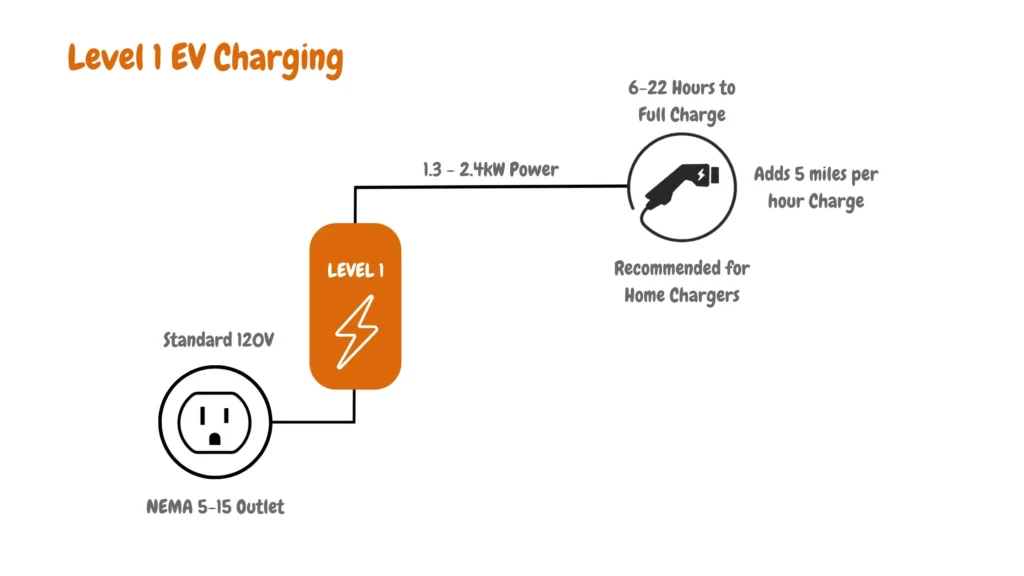
The diagram above highlights Level 1 EV charging power sources, charging speeds, and applicability with more detailed information contained in the diagram explained below:
Level 1 EV Charging Power Outlet and Power Requirements
- NEMA 5-15 Outlet: The standard three-prong plug in most rooms. No fancy equipment is needed!
- Standard 120V: Level 1 EV charger charges through a 120-volt (120V) single-phase AC plug (a typical wall outlet) at 12-16 amps, the same voltage that powers your home lights. It’s readily available, but limited power to the EV charger means limited EV charging speed.
Level 1 EV Charging Charging Speed
- 6-22 Hours to Full Charge: Be prepared for patience. Fully charging your EV with Level 1 can take a long time, depending on its battery size. Think overnight top-ups, not quick pit stops.
- Adds 5 miles per hour Charge: The good news is, that even slow charging adds range. Level 1 delivers around 5 miles of range for every hour your EV is plugged in. It might not be much, but it helps for short commutes or energizes your battery while parked.
Level 1 EV Charging Power Output Suitability
- 1.3 – 2.4kW Output Power: Level 1 offers readily available power. However, this comes with a lower power output of 1.3 – 2.4kW compared to other levels, hence the slower charging speeds.
- Recommended for Home Chargers: It’s easy and convenient to plug your EV directly into your house. But remember, this is mainly for overnight charging or topping off.
- Not ideal for Long Journeys: With such slow speeds, Level 1 isn’t practical for replenishing your electric vehicle battery for long trips. Plan accordingly!
Level 2 EV Charging
The diagram below provides a detailed explanation of the Level 2 EV charging level, highlighting the functionalities of Level 2 EV charging, a significant upgrade from the previously explained Level 1.
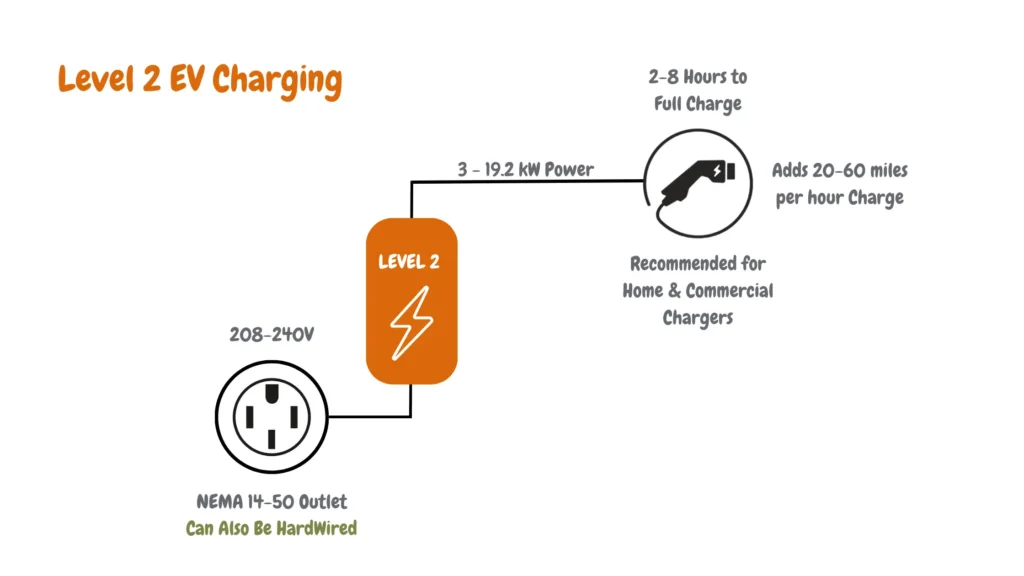
Here’s a breakdown of level 2 EV Charging as shown in the diagram above:
Level 2 EV Charging Outlet and Power Requirements
- NEMA 14-50 Outlet: Unlike Level 1’s standard outlet, Level 2 requires a dedicated 240-volt outlet delivered through a single-phase AC power at 12-80 amps (Typ. 32 amps), commonly identified by four prongs in an “L” shape.
- Can Also Be Hardwired: This signifies that Level 2 chargers can be directly wired into your electrical panel besides using a specialized outlet for a permanent and potentially more efficient setup.
Level 2 EV Charging Charging Speed
- 2-8 Hours to Full Charge: Compared to Level 1’s lengthy charging time, Level 2 can significantly recharge your EV battery in 2-8 hours, depending on its capacity and the charger’s output.
- Adds 20-60 miles per hour Charge: This translates to much faster replenishment, offering 20-60 miles of range for every hour your EV is plugged in, a vast improvement over Level 1.
Level 2 EV Charging Power Output and Suitability
- 3 – 19.2 kW Output Power: Level 2 operates with higher power output (3-19.2 kW) than Level 1 (1.3-2.4 kW), enabling faster charging speeds.
- Recommended for Home & Commercial Chargers: While Level 1 primarily serves home charging, Level 2’s speed and convenience make it suitable for home installations and public charging stations.
Level 3 EV Charging
The diagram below showcases the ultimate speed demon of the EV charging world: Level 3 charging, also known as DC Fast Charging. Buckle up, because things are about to get electrifyingly fast!

The diagram above shows features of Level 3 EV charging such as power requirements, charging speeds, and power output and suitability, explained in more detail below:
Level 3 EV Charging Power Requirements
- 480V: Level 3 operates on a mighty 480 volts, delivered through three-phase power at <125 amps (Typ. 60 amps) like industrial applications.
Level 3 EV Charging Speed
- Adds 60-100 miles per hour Charge: Gone are the days of waiting for hours. Level 3 can add a whopping 60-100 miles of range to your EV’s battery in just one hour, depending on the charger’s power and your car’s capabilities.
- Full charge in approximately 30 minutes: Ready for this? In as little as 30 minutes, you can go from near-empty to almost full. Now, that’s what we call convenience on the go! Level 3 truly redefines “fast charging.”
Level 3 EV Charging Power Output and Suitability:
- 50 kW – 400 kW Output Power: Brace yourself for pure power! Compared to Level 2’s 3-19.2 kW, Level 3 chargers boast a massive output range of 50 to 400 kW. That’s a game-changing leap in charging speed.
- Recommended for Commercial Chargers: Level 3 isn’t currently suitable for home installations due to its high power requirements. You’ll primarily find it at public charging stations like highway rest stops, shopping malls, and dedicated charging hubs. With its growing accessibility, having a Level 3 EV charger in your home might be in the future!
EV Compatibility
Understanding your electric vehicle’s (EV) compatibility with different charging levels (Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3) is crucial for efficient charging. Just as superheroes have unique powers, each EV model has specific charging capacity limitations and EV charging connector types.
A Guide to EV Charging Connectors and Levels
Here’s an infographic displaying various EV charging connectors categorized on how they work based on current delivery (AC Charging & DC Charging), indicated below the connector name is their respective charger output power.
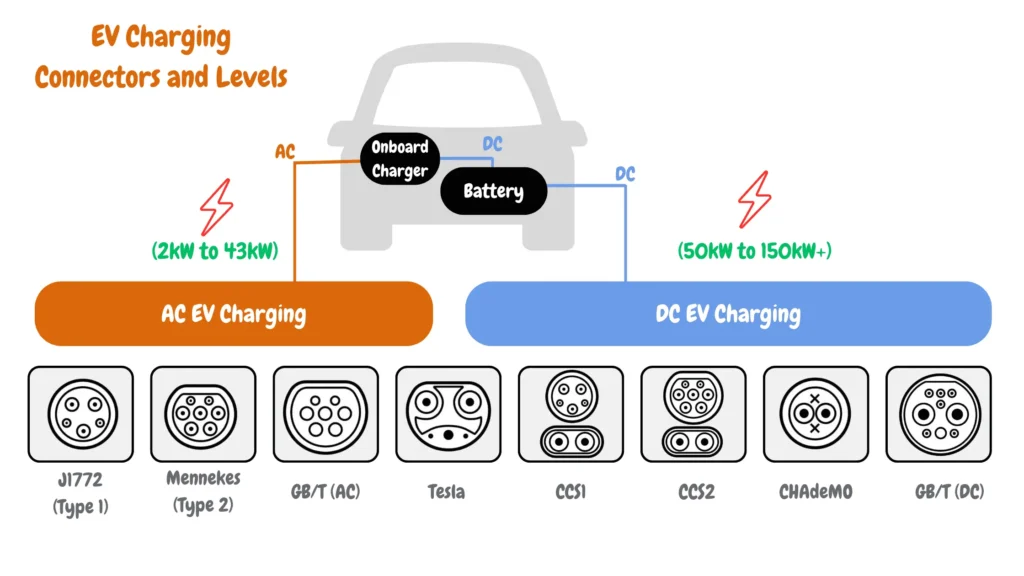
AC Charging Connectors (First Section)
This section focuses on connectors exclusively used for AC charging, highlighted in the first column of the diagram. The first diagram illustrates that AC charging involves converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by the electric vehicle’s onboard charger. The range of 2kW to 43kW represents the power output of various AC chargers.
J1772 (Type 1) Connectors
- Region: Primarily North America and Japan.
- Levels: Supports Level 1 (home outlet) and Level 2 (240V) AC charging.
- Identification: Look for the five prongs arranged in a J-shape.
- Compatibility: Most EVs in these regions have a J1772 inlet, making it widely compatible with charging stations offering AC charging.
Mennekes (Type 2) Connectors
- Region: Dominant in Europe, gaining traction globally.
- Levels: Supports Level 1, 2, and 3 (AC only) charging.
- Identification: Recognized by its seven pins in a round configuration.
- Versatility: This connector’s increasing prevalence makes it a future-proof option for AC charging compatibility.
GB/T (AC) Connectors
- Region: Specific to China.
- Levels: Used for Level 1 and 2 AC charging.
- Identification: Similar to the Mennekes connector with seven pins but a different layout.
- Relevance: Primarily relevant for EVs sold or used within China.
Tesla Connectors
Note: While Tesla utilizes AC charging through its proprietary connector, it’s important to acknowledge that it’s not directly compatible with other AC charging networks due to its unique design.
DC Charging Connectors (Second Section)
Moving into the realm of DC fast charging, the diagram presents a range of power outputs (50kW to 150kW+) and connectors associated with this high-speed charging method.
Compared to AC charging, DC delivers direct current directly to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger and resulting in significantly faster charging speeds.
Tesla DC Charging Connectors
Tesla utilizes its proprietary connector primarily for their Supercharger network, offering DC fast charging exceeding 100kW in some locations. While convenient for Tesla owners, it’s incompatible with other EV models unless an adapter is used.
CCS1 & CCS2 DC Charging Connectors
These represent the Combined Charging System connectors that dominate North America and Europe. CCS2 is the newer, universal standard gaining global adoption. Both enable 50kW to 350kW+ DC fast charging, ensuring compatibility with a broader range of EVs.
CHAdeMO DC Charging Connectors
Popular for DC fast charging in Japan and parts of Asia, offering speeds comparable to CCS. However, its presence outside its core region is limited, impacting compatibility for travelers or EVs primarily used outside these areas.
GB/T DC Charging Connectors
Specific to China, it is used for DC fast charging with a similar power range to CCS and CHAdeMO. Its relevance primarily extends to EVs sold or used within China.
Knowing your EV’s charging specifications across different levels is essential for choosing the right charger and avoiding potential damage. Attempting to charge your EV at a higher rate than it can handle can stress the battery and shorten its lifespan. Therefore, before plugging in, ensure you understand your electric vehicle’s unique charging capabilities to make informed decisions.
Choosing the Right EV and Charger for You based on EV Charging Levels.
Below, we have outlined some of the critical factors to consider when choosing an EV and its ideal charging partner, based on the different EV charging levels:
EV Charging Speed Requirments.
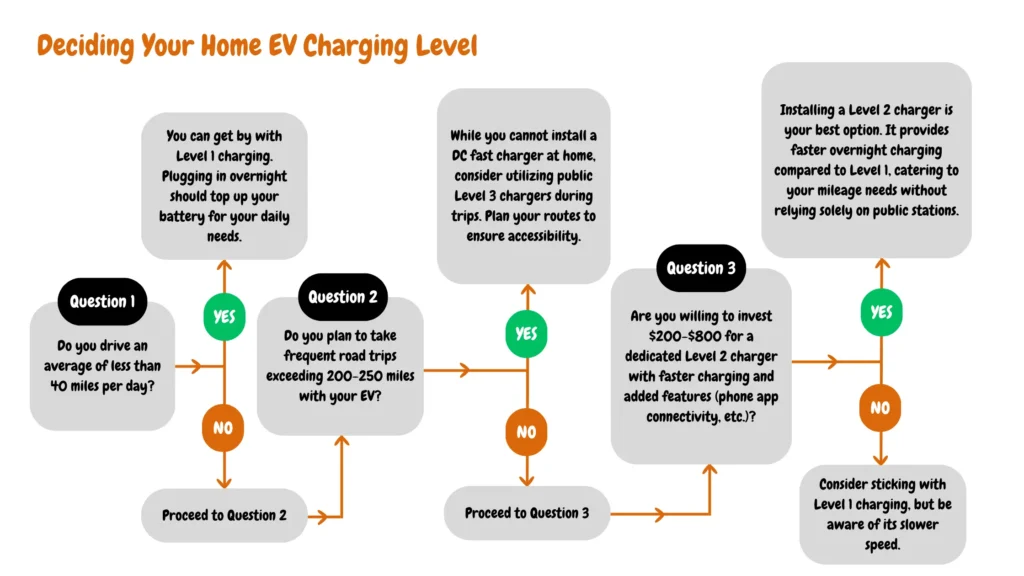
When considering EV charging speed requirements, Level 1 charging is akin to overnight phone charging—suitable for topping up at home but not ideal for quick getaways.
Level 2 charging is a mid-range option, delivering a charging speed 6-8 times faster than Level 1, making it suitable for home and public charging. Meanwhile, Level 3 (DC Fast Charging) offers a rapid energy boost, zipping you up in minutes, perfect for road trips or busy schedules. Your choice should align with your daily driving habits and the urgency of charging needs.
EV Charging Costs.
Charging at home presents significant cost savings, particularly with Level 1 or 2 chargers at 19.9-30 cents per kWh, as they typically leverage lower electricity rates than public stations. However, convenience at public stations comes with a price for instance, in California, it is 40 cents per kW; however, you will find varying rates, sometimes with time-of-use options to save during off-peak hours.
To determine the most cost-effective solution, it’s essential to consider your usual charging locations and usage patterns and crunch the numbers accordingly.
EV Charging Infrastructure Near You.
When assessing the EV charging infrastructure available in your area using our EV charging map, you will note that cities are becoming increasingly EV-friendly, with charging stations proliferating across various locations.
It’s crucial to verify the availability and types of charging stations in your vicinity. Additionally, ensure these stations offer charging levels compatible with your EV model. Accessibility is also critical, primarily if you heavily rely on public charging. Prioritize stations with convenient locations and operating hours to accommodate your charging needs effectively.
EV Charger Installation.
Regarding installation requirements for different EV charging levels, Level 1 charging is typically straightforward, involving plug-and-play functionality with a standard outlet. However, Level 2 charging may require dedicated outlets or professional installation for optimal charging speeds.
Before opting for a Level 2 charger, carefully assess your home’s electrical system and potential installation costs. This evaluation ensures compatibility and helps avoid unexpected expenses associated with installing a Level 2 charger.
EV Charging Installation Requirements
Regarding EV charging installation requirements, Level 1 and Level 2 chargers typically utilize standard 120V or 240V outlets, which may already be available in your home. However, Level 3 charging, also known as DC Fast Charging, necessitates specific high-voltage connections different from standard household outlets.
Before installing any level of charger, it’s crucial to check your home’s electrical panel to ensure it can handle the increased load, especially for higher-level chargers. Overloading the electrical panel can lead to safety hazards and damage to your home’s electrical system. Therefore, conducting a thorough assessment of your electrical infrastructure is essential to ensure safe and efficient charging for your electric vehicle.
EV Charger Battery Requirements
When considering EV charger battery requirements, it’s important to recognize that larger battery packs demand higher charging capacity for efficient charging. Therefore, understanding your EV’s specifications is crucial. By checking your EV’s capabilities, you can ensure that the chosen charger aligns with its charging needs, preventing any potential issues or inefficiencies.
Future Trends in EV Charging
In contemplating future trends in EV charging, it’s vital to recognize the evolving landscape of EV technology, such as wireless EV Charging and bi-directional EV charging.
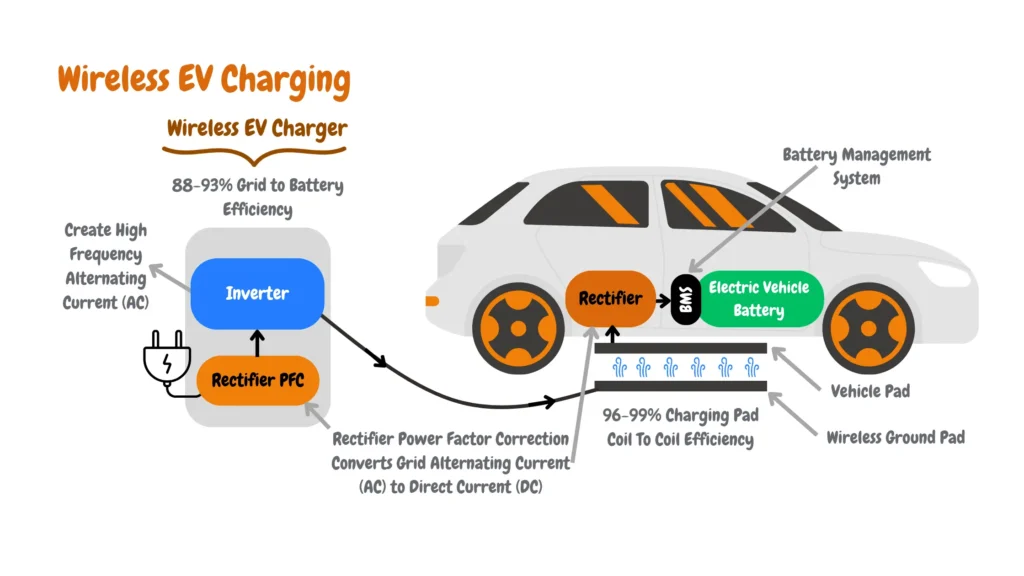
As advancements continue, it’s wise to consider whether you require faster charging or longer-range capabilities. Therefore, adaptability becomes paramount. Selecting a charging solution that can accommodate not only your current needs but also potential future changes ensures that you’ll be prepared to embrace the evolving capabilities of EV technology seamlessly.
People Also Ask
How Long Does It Take to Charge an Electric Car at a Station?
Level 1 charging provides a slow but steady pace, adding 3-5 miles per hour, suitable for overnight top-ups. Level 2 significantly increases, delivering 12-32 miles per hour, ideal for daily commutes and planned road trips. DC Fast Charging, the fastest option, adds 60-200 miles in 30 minutes, perfect for quick top-ups during long journeys.
What Is the Difference Between Level 2 and DC Fast Charging?
Level 2 charging operates on 240V power, commonly accessible at homes and public stations. It offers a cost-effective per-mile charge compared to DC Fast Charging. DC Fast Charging, however, uses direct current (DC) for rapid charging, making it suitable for quick top-ups during long trips, albeit potentially pricier per minute.
How Much Does It Cost to Install a Home EV Charger?
Home EV Charger installation costs vary depending on your electrical setup and chosen charger model. On average, the national installation cost for EV charging stations ranges from $1,000 to $2,500.
Where Can I Find Public Charging Stations for My Electric Car?
Discovering public charging stations for your electric vehicle is easy with our EV Charging Map. Use the EV charging map as your secret weapon, pinpointing nearby stations, filtering by connector type and availability, and displaying real-time usage data. Major networks like Tesla Supercharger and automaker-affiliated options continue to expand their infrastructure, providing additional charging options.
What Are the Future Trends in EV Charging Technology?
Future trends in EV charging technology promise an electrifying journey. New Ultra-fast charging technologies, such as wireless EV Charging, aim for quicker EV charging, while EV charging standardization initiatives ensure network compatibility. Bidirectional charging transforms EVs into mobile batteries, enhancing grid sustainability. Expect advancements in smart grid integration and renewable energy sources, propelling eco-friendly adventures forward.
Conclusions
Thank you for reading our article on EV charging levels! We recommend Level 2 EV Charging due to its speed and convenience for daily use or DC Fast Charging for rapid long-distance journeys.
Don’t overlook Level 1 for occasional top-ups. We also encourage you to understand your EV’s charging capabilities and associated costs over the long run. With this knowledge, we believe you can conquer range anxiety and embark on a thrilling journey towards a sustainable future.

About the Author: James Ndungu
James Ndungu, founder and editor-in-chief of Electric Vehicle Geek, brings over five years of hands-on experience in Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) selection, permitting, and installation. He specializes in assisting businesses and homeowners in the United States with a seamless transition to electric vehicles.
As a certified EV charger installer and holder of advanced certifications, including the EVITP (Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program), Diploma in Electric Vehicle Technology, and Diploma in Engineering Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles, I provide expert guidance and in-depth reviews on the latest EV charging equipment.