Supported by you via insider access, and when you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. See our Affiliate Disclosure.
Solar Inverters for EV Charging
A solar inverter for EV charging converts solar energy into the AC power your electric vehicle charger needs. It manages high power demands while balancing solar, grid, and home energy. Advanced models enable bidirectional flow (V2G), letting your EV serve as a home backup battery.
Solar Inverters for EV Charging Guide
Charging your EV directly from solar panels is the ultimate goal for sustainable driving, literally powering your electric vehicle on sunshine. The technology today has evolved into smart, integrated systems that optimize efficiency, safety, and convenience.
This guide answers your pressing questions and helps you choose the right solar inverter for solar EV charging, emphasizing proper sizing and compliance for optimal performance and longevity.
Can You Charge an EV with a Solar Inverter?
Yes, absolutely. To be technically compliant and safe, your inverter’s output rating (and the circuit it sits on) must be 125% of the continuous load you plan to pull. Conversely, the load must not exceed 80% of the inverter’s continuous rating.
What Size Inverter Do I Need to Charge an EV?
To comply with electrical code requirements, ensure safety, and maintain reliability, your inverter should be sized at least 125% of your EV charger’s continuous load rating.
For instance, if you have a 7.6 kW Level 2 charger, a 9.6 kW inverter is appropriate. For a 9.6 kW charger, an 11.4 kW inverter is recommended. For larger EV chargers with loads of 11.5 kW, consider inverters rated at 15 kW or greater.
Proper sizing helps avoid inverter overheating, extends equipment lifespan, and prevents energy clipping when your solar array produces more power than the inverter’s capacity.
Expert Note: Integrated inverter-charger units are typically engineered with built-in oversizing and advanced thermal management systems. As a result, manual oversizing of the inverter is generally not required, ensuring optimal performance and longevity without additional complexity.
Why Oversize the Inverter?
The Thermal Reality
Inverters generate heat when running continuously at high capacity, such as during a typical 5 to 8-hour EV charging session. If the inverter is rated exactly at your EV charger’s draw, it will likely thermal derate, slowing down to protect internal components. Oversizing allows the inverter to operate in a “comfort zone,” improving efficiency and extending hardware lifespan.
Matching Inverter to Charge Speed
Your inverter’s continuous AC output must match the desired EV charging rate with a 25% safety buffer for heat and simultaneous home loads.
For example, if your desired charge rate is 7.6 kW (32A), a recommended inverter continuous output is 9.6 kW (40A), which provides a 20% safety margin for thermal and load headroom. For 9.6 kW (40A) charging, an 11.4 kW (50A) inverter is optimal, often referred to as the “Goldilocks” zone for most home solar charging needs. For larger EVs requiring 11.5 kW (48A) or more, inverters rated 15 kW or higher are needed to avoid bottlenecks.
Whether you’re upgrading an existing system or starting fresh, choosing a charger matched to your inverter’s capacity ensures you get the best performance without compromise.
Inverter Versus Circuit Breaker Sizing
Both the inverter rating and the circuit breaker size must respect the 125% continuous load rule. Additionally, the wiring gauge must be selected accordingly, using thicker wiring such as 6 AWG instead of 8 AWG, to safely carry the current without overheating or voltage drop.
Can I Charge My EV Directly from Solar Panels?
In principle, yes, but practically, an inverter is almost always required. Solar panels output DC voltage at variable levels, which is unsuitable for directly charging EV batteries that require stable AC power input. The inverter converts the DC power from your solar panels into AC power for use by Level 2 EV chargers.
Some advanced DC fast chargers have built-in inverter functionality, allowing more direct solar-to-EV charging. However, these setups are uncommon in residential environments due to complexity and cost.
How Much Solar Do I Need for EV Charging?
Sizing your solar array depends on several factors. First, calculate your daily EV energy use by multiplying your average daily driving miles by your EV’s energy consumption in kilowatt-hours per mile. Next, consider the average daily sunlight hours at your location, known as peak sun hours.
Then, account for system efficiency losses, which typically amount to about 10 to 15 percent due to inverter, wiring, and battery inefficiencies. Finally, include a safety buffer by oversizing your solar array by approximately 25 percent to cover variability in weather and future energy needs.
For example, if you drive 40 miles a day and your EV consumes 0.3 kWh per mile, your daily energy need would be 12 kWh. Assuming you get 5 peak sun hours per day, the base solar array size would be 2.4 kW (calculated as 12 divided by 5). Adding a 25% safety buffer increases this to about 3.0 kW. Therefore, a 3 kW solar array would reliably cover your daily EV charging requirements under these conditions.
Integrated Versus Separate Solar Inverter Setup
When selecting your setup, you have two main options: an integrated inverter/charger or a separate smart charger paired with an inverter.
Integrated units are ideal for new solar and EV installations because they offer the highest efficiency with less DC-to-AC conversion loss. These systems tend to be less complex, often coming as a single unit controlled via a unified app. Examples include the SolarEdge Home Hub and Tesla Powerwall 3.
Separate setups are better suited for retrofitting existing solar arrays. Although they have more complexity, requiring multiple devices to communicate with each other, the modularity can offer flexibility. A common example is the combination of a Lectron Level 1/2 EV charger with an Enphase IQ inverter.
Integrated units often come with built-in oversizing and thermal management, so manual oversizing of the inverter is usually unnecessary.
Features To Look For When Shopping for Solar Inverters for EV Charging
Modern solar inverters for EV charging come packed with advanced features that optimize performance and user experience. Solar Boost Mode allows you to combine grid power with solar energy for faster charging sessions.
Dynamic Load Balancing helps prevent breaker trips by throttling EV charging based on your home’s overall load at any given time. Green-Only Mode enables your EV to charge solely using surplus solar energy, maximizing renewable usage.
Pure sine wave output ensures clean, stable AC power delivery that is fully compatible with sensitive EV charging electronics, reducing heat buildup, electrical noise, and long-term component stress.
Bidirectional flow, Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) support lets you use your EV’s battery for home backup power or even feed energy back to the grid when conditions are favorable.
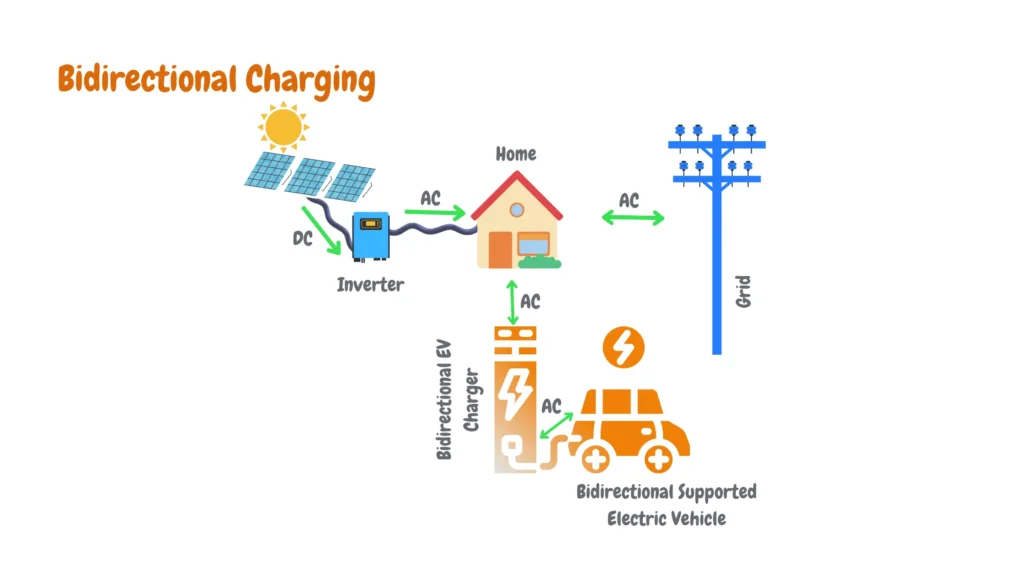
Advanced monitoring and smart home integration provide remote management capabilities and detailed data tracking for energy usage and system performance.
Grid compatibility is also crucial; your inverter should support the standard 60 Hz frequency and meet certifications like UL1741 and IEEE1547 to ensure safety and reliability.
Power oversizing capability prevents inverter clipping by allowing the inverter to accept higher DC input than its AC output rating (DC-to-AC ratio > 1). This ensures peak solar production is fully utilized without wasting energy, maximizing overall system efficiency, or damaging your solar EV charging system.
Proper inverter sizing following the 125% rule and correct breaker and wiring compliance remain fundamental for safety and system longevity.

