Supported by you via insider access, and when you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. See our Affiliate Disclosure.
1.44 kW EV Charger Reviews
Use the “Compare” button on each product to select multiple chargers, then click the ⚖️ scale icon to see a full side-by-side comparison.
1.44 kW EV Charger Reviews 2025
Discover the safest and most reliable 1.44 kW EV chargers with our expert-rated reviews. Each charger is scored 1–10 on features, real-world performance, materials, durability, craftsmanship, design, value, and brand reputation, making it easy to find the perfect overnight or low-mileage charging solution.
Quickly narrow your search using our custom 1.44 kW EV charger filters: brand, connector type, power input, charging level, voltage, cable length, safety certifications, and smart features.
For full details, click a charger image or title to read the complete review. Comparing multiple chargers? Use the “Compare” button below the charger, then click the ⚖️ scale icon on the side to view a side-by-side comparison of specifications and detailed expert ratings, so you can make a confident, informed choice.
What is a 1.44 kW EV Charger?
A 1.44 kW EV charger is the standard entry point for home EV charging, commonly known as Level 1 charging. It operates on a 120V household circuit and delivers a continuous load of 12 amps, providing about 3–5 miles of range per hour of charging. Ideal for PHEVs or small EV batteries, it requires no special installation.
A 1.44 kW EV charger (Level 1 EV Charger) is a simple and cost-effective way to charge an electric vehicle, using a standard residential outlet while keeping device purchase and installation costs low compared to Level 2 chargers. It provides reliable overnight or low-mileage charging without requiring a major electrical upgrade, making it ideal for most American homes’ electrical systems.
How to Install a 1.44 kW EV Charger
Installing a 1.44 kW EV charger requires more than just plugging into an outlet. To ensure safe operation, the circuit must be designed and installed properly, following both NEC and local code. Below, we explain the key requirements step by step.
1.44 kW EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
The following diagram shows the recommended wiring configuration for a 1.44 kW Level 1 EV charger. It uses a 120V split-phase supply, protected by a dedicated EV charger 15A single-pole GFCI breaker, with 14 AWG copper conductors terminating at a NEMA 5-15 receptacle.
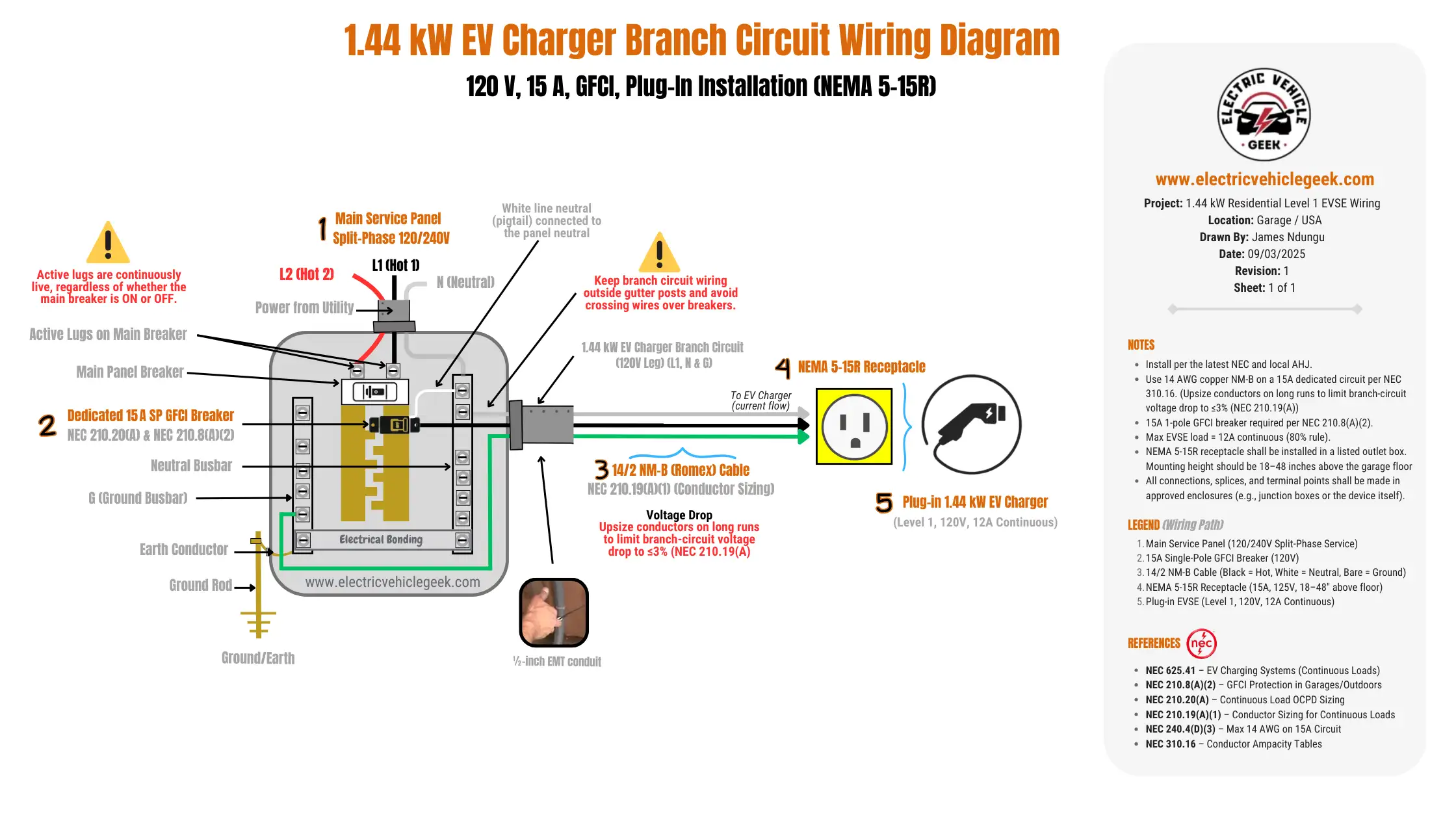
For safe operation, the branch circuit must be protected by a dedicated 15A single-pole GFCI breaker, in accordance with NEC 210.20(A), which requires overcurrent devices to be rated for continuous loads. GFCI protection is also required by NEC 210.8(A)(2) in garages and outdoor locations. This breaker configuration ensures both safety and code compliance for a 1.44 kW Level 1 EV charger installation.
The correct conductor size for this installation is 14 AWG solid copper, as specified in NEC 210.19(A)(1). For concealed indoor runs, 14/2 NM-B (Romex) cable is suitable. Where wiring is exposed, the preferred method is THHN copper conductors in ½-inch EMT conduit, which offers superior mechanical protection and long-term durability.
The length and gauge of EV charger installation conductors directly affect charging performance, especially when using a Level 1 EV charger extension cord to extend the reach of your 1.44 kW Level 1 EV charger. Excessive distance increases voltage drop, which reduces efficiency and can increase the risk of overheating. The NEC recommends limiting voltage drop to 3% on branch circuits.
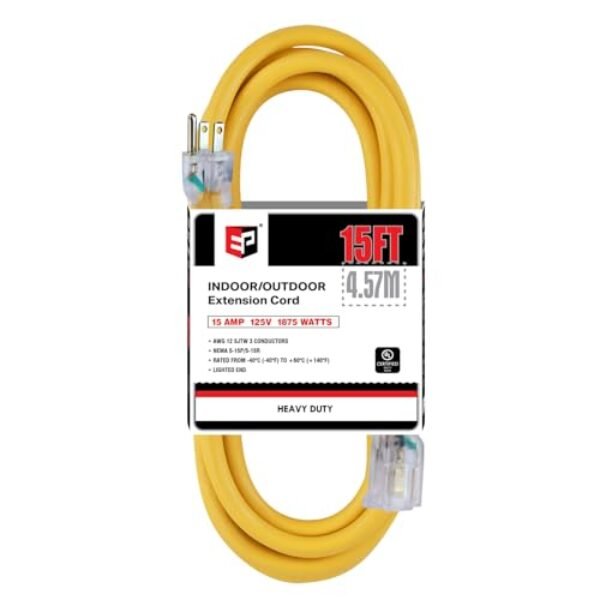
For a 1.44 kW Level 1 EV charger extension, we recommend the EP Level 1 EV Charger Extension Cord, a heavy-duty cord designed to safely extend your charger’s reach while maintaining efficient power delivery.
Voltage drop occurs when cords are too long or too thin, reducing the power delivered to the charger and slowing the charging process. Poor connections can also contribute. The EP extension cord, featuring 12-gauge wire and secure connectors, minimizes voltage drop, ensuring reliable and efficient charging even when your 1.44 kW Level 1 EV charger is relocated.
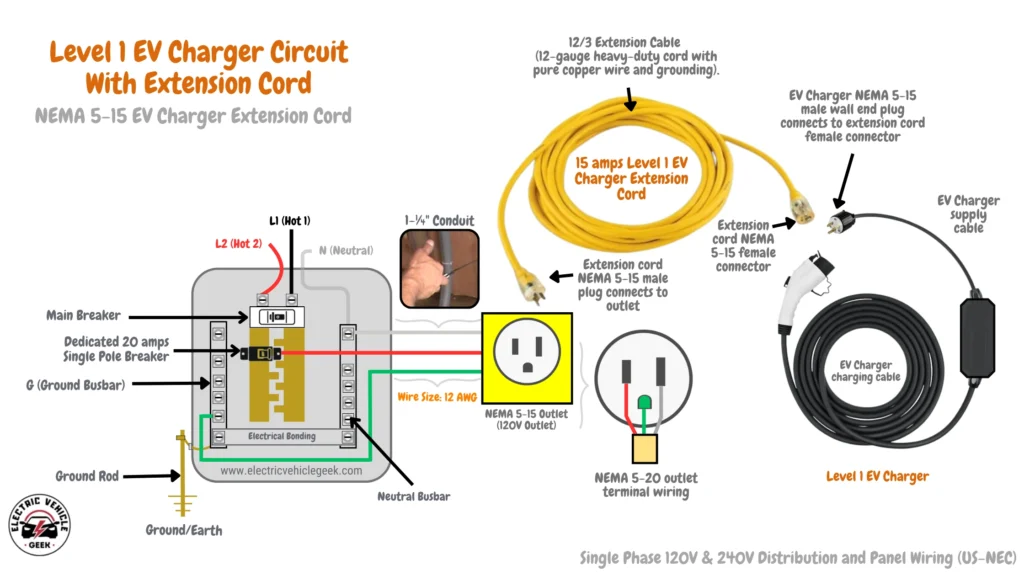
Our recommendations are as follows: at 50 feet, 14 AWG copper results in about a 2.5% drop, which is acceptable. At 100 feet, 14 AWG causes a nearly 5% drop, which is too high for EV charging. To maintain efficiency and safety, we recommend upsizing to 10 AWG copper for any run approaching 100 feet, as this keeps voltage drop closer to 2% and ensures reliable charging performance.
Most 1.44 kW Level 1 EV chargers are also called NEMA 5-15 Level 1 chargers because they plug into a standard home NEMA 5-15 outlet. For garages and outdoor areas, a GFCI-protected NEMA 5-15 outlet is required by NEC 210.8(A)(2). Using the correct outlet ensures safe and reliable charging every time.
For the best results, we recommend the top-rated NEMA 5-15 outlets we’ve reviewed. These outlets feature durable construction, reliable GFCI protection, and long-lasting performance, giving you peace of mind while charging your EV. Pairing your charger with a high-quality outlet helps prevent electrical hazards, ensures consistent power delivery, and keeps your home charging setup safe and efficient.
Outlet Placement
1.44 kW Level 1 EV charger outlet placement is critical for usability and safety. The outlet should be:
Placed within convenient reach of the vehicle’s charging port for reliable use, reducing strain on the cable and ensuring safe, consistent connections every time
Positioned close to the electrical service panel to reduce wire distance, minimize voltage drop, and ensure safe, efficient power delivery
Mounted 18 to 48 inches above the garage floor, which balances accessibility, protection from moisture, and user convenience
We recommend labeling the outlet “For Electric Vehicle Charging Only”. This practice prevents accidental misuse of the receptacle, ensures clarity for inspectors, and reinforces that the circuit is dedicated to continuous EV charging.
Permits and Code Compliance
Most jurisdictions require a permit and inspection for EV charger installation, and this step should never be skipped. Always confirm requirements with your Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) before starting work.
This guide follows the principles of the National Electrical Code (NEC), but local amendments may add further requirements. Compliance with both NEC and local codes is mandatory for a safe and approved installation.
Expert Help Selecting Your 1.44 kW Charger
Perfect for low-mileage EVs, a 1.44 kW charger keeps overnight charging simple and safe. Our experts guide you to the most compatible models while helping you save up to 20% on the charger and reduce overall project costs.Looking for chargers with different power outputs? Check out these common options, ranging from entry-level 1.44 kW Level 1 chargers to high-output 19.2 kW Level 2 EV chargers.
Level 1, 120 V / 12 A
Entry-level chargers for small batteries and overnight home charging
(~52 h for 75 kWh)
Level 1, 120 V / 13.75 A
Slightly faster chargers for small EVs and light daily commuting
(~45 h for 75 kWh)
Level 1, 120 V / 16 A
High-output chargers for small batteries and overnight top-ups
(~39 h for 75 kWh)
Level 1 / Light Level 2
Faster 120 V / 16.7 A or low-end 240 V / 16.7 A EV chargers for short daily trips
(~37.5 h for 75 kWh)
Level 2, 240 V / 15.8 A
Low-end chargers for typical home charging of medium batteries
(~19.7 h for 75 kWh)
Level 2, 240 V / 32 A
Mid-range chargers for home use with faster overnight charging
(~9.7 h for 75 kWh)
Level 2, 240 V / 40 A
Higher-power chargers for larger batteries or multiple daily users
(~7.8 h for 75 kWh)
Level 2, 240 V / 41.6 A
Balanced Level 2, fast charging without stressing electrical panels
(~7.5 h for 75 kWh)
Level 2, 240 V / 48 A
Standard home or small commercial chargers
(~6.5 h for 75 kWh)
Level 2, 240 V / 50 A
High-output chargers for EVs with large batteries
(~6.25 h for 75 kWh)
Level 2, 240 V / 80 A
Max-power residential or commercial AC fast charging
(~3.9 h for 75 kWh)
Learn how EV charger kW impacts charging speed and explore our full reviews from 1.44 kW to 19.2 kW.
Tip: Use this table to quickly see how charging speed, type, and usage vary across kW ratings. Browse EV chargers by kW to explore how charging speed, type, and usage vary – Access all reviews from 1.44 kW to 19.2 kW on our EV Charger kW Ratings & Reviews hub page.