EV charger cable pliability issues include tangling and knotting, reduced maneuverability, increased connector stress, cold weather performance, and negative user experience when charging their electric vehicles (EVs).
According to a recent J.D. Power report approximately 20.8 percent of electric vehicle (EV) users encountered charging disruptions or equipment issues while charging their electric vehicles, some of the issues that faced included station connectivity, internal station faults or errors, charging connector or cable issues, credit card reader and display issues as highlighted in the chart below:
EV charger cable pliability issues can be solved by first choosing the right EV charging cable and the best EV home charger. The key lies in unlocking the secret of EV charger cable pliability.
We’ll delve into the science of pliability, exploring how materials, temperatures, and even cable length can impact your charging experience. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to choose the right EV charging cable and EV charger cable for your climate, whether braving sub-zero chills or scorching summer heat.
Plus, we’ll share expert tips on handling and storing your cable like a pro, ensuring it remains your loyal charging companion, not a frozen foe.
Table of Contents
- Understanding EV Charging Cable Pliability
- EV Charging Cables Pliability Tests
- Factors Affecting EV Charging Cable Flexibility
- EV Charging Cable Material Composition
- EV Charging Cable Diameter
- EV Charging Cable Construction and Design
- Temperature Effects
- EV Charger Cable Construction Materials
- Demystifying Charging Levels and Cable Gauges
- EV Charger Cable Length
- How Does Temperature Affect EV Charging Cables?
- Choosing a Pliable EV Charger Cable
- Best Practices for Home EV Charger Cable Management
- EV Charger Cable Standards
- Conclusions
Understanding EV Charging Cable Pliability
EV charging cable pliability refers to an EV charger cable’s ability to flex, bend, and coil without sustaining permanent deformation or compromising EV charging performance.
High-quality EV charger cables are engineered with advanced materials that allow for smooth maneuverability, effortless coiling, and consistent operation even under challenging conditions—such as extreme cold or confined installation spaces.
EV charger cable pliability is crucial not only for ease of use but also for maintaining the cable’s structural integrity over repeated cycles of bending and storage, ensuring a long service life and reliable performance in various environments.
EV Charging Cables Pliability Tests
There are two major tests that EV charger cables undergo by the manufacturer: materials quality tests and functional tests. The materials quality tests are performed first—both in-house and through third-party approval—to assess the durability and build quality of the cable. Following these, functional tests are conducted. The initial functional test is the IEC 62196 cable test, which evaluates temperature effects, cable pull, torque, and flexing.
The complete process of EV charging tests is shown in the flowchart below:
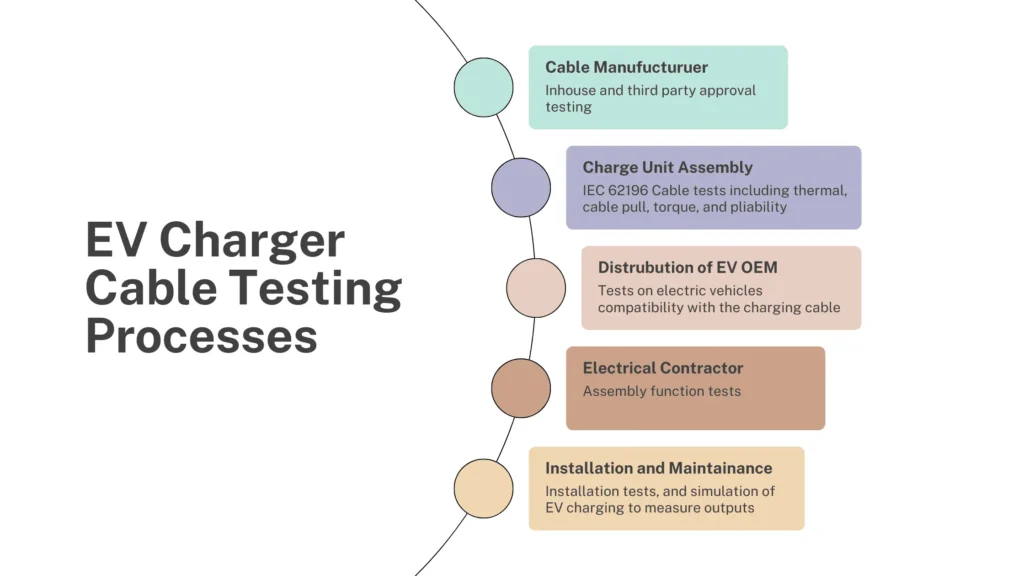
Similar to other wires and cables, bend testing for EV charging cables evaluates their flexibility, durability, and safety. This rigorous process ensures they meet industry standards and perform reliably over their lifespan.
EV Charging Cable Integrity and Durability Testing
EV charger cable integrity and durability testing not only validates compliance with industry standards but also guarantees long-term performance in real-world applications. Two key tests—static and dynamic bend tests—play a crucial role in assessing these attributes.
EV Charging Cable Static Bend Test
This test measures essential material properties, such as stiffness and yield strength, under a constant load. By evaluating how the cable behaves when bent without movement, manufacturers can confirm that it will maintain its structural integrity and resist permanent deformation during prolonged use.
EV Charging Cable Dynamic Bend Test
Simulating real-world conditions, the dynamic bend test subjects the cable to repeated bending cycles. This rigorous assessment evaluates the cable’s fatigue resistance and wear characteristics, providing valuable insights into its long-term durability and performance under everyday charging scenarios.
Why Are EV Charging Cable Pliability Tests Crucial?
Optimized Flexibility
EV charging stations are often installed in confined or irregular spaces, where cables must bend repeatedly during use and storage. Rigorous bend testing confirms that cables retain their flexibility and continue to operate efficiently without suffering internal damage.
Enhanced Durability
Daily cycles of plugging and unplugging, combined with exposure to extreme temperatures and potential physical abrasion, subject EV charging cables to significant stress. Bend testing identifies structural weaknesses early and helps predict a cable’s lifespan, thereby mitigating the risk of unexpected failures.
Guaranteed Safety
A cable that loses its flexibility can overheat or develop faults that lead to sparking and electrical hazards. Comprehensive pliability testing ensures that the cable maintains its integrity under repeated bending, significantly reducing safety risks for both users and equipment.
How We Test EV Charging Cables Pliability
Another test that we do is the Wrap-around Bend Test, which involves wrapping the cable around a specific diameter to inspect for any damage or defects. We also use the Swing Arm Bend Test to assess the cable’s flexibility by bending it over a set radius through a defined motion.
Factors Affecting EV Charging Cable Flexibility
EV charging cable flexibility is determined by several factors: the material used (with advanced elastomers generally offering better pliability than PVC), the cable’s diameter (thicker cables tend to be stiffer), the internal construction (how conductors, insulation, and shielding are arranged), and ambient temperature (colder conditions can reduce flexibility).
EV Charging Cable Material Composition
The intrinsic flexibility of an EV charging cable is largely determined by its material composition. For instance, cables insulated with advanced thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) or rubber-based compounds typically offer superior pliability compared to those using conventional PVC. Selecting the right material involves balancing flexibility with critical factors like durability, thermal stability, and safety.
EV Charging Cable Diameter
The overall diameter of an EV charging cable plays a crucial role in its flexibility. While thicker cables are designed to handle higher current loads, their increased size often reduces bendability. In our reviews, the top-rated EV chargers with pliable and flexible cables—verified through rigorous EV charging cable pliability tests—feature an optimal diameter that ensures efficient power delivery while remaining flexible enough for frequent handling and storage.
EV Charging Cable Construction and Design
The flexibility and durability of an EV charging cable depend on both its internal architecture and the quality of its materials. The number and arrangement of conductors, insulation layers, and shielding all play a crucial role in performance. A multi-strand conductor design enhances electrical efficiency while improving mechanical resilience, allowing the cable to endure repeated bending and flexing without degradation.
In cold conditions, insulation quality is equally important. Advanced insulation materials that remain pliable at low temperatures prevent stiffness, cracking, and reduced performance. By combining flexible insulation with a robust internal structure, a well-designed EV charging cable ensures reliable operation across various environmental conditions.
Temperature Effects
Environmental conditions, particularly temperature, can drastically affect cable flexibility. In colder climates, many insulation materials become stiffer, reducing the cable’s ability to bend and coil properly. Comprehensive testing across a range of temperatures is essential to ensure that the cable maintains its performance and structural integrity, even in extreme conditions.
EV Charger Cable Construction Materials
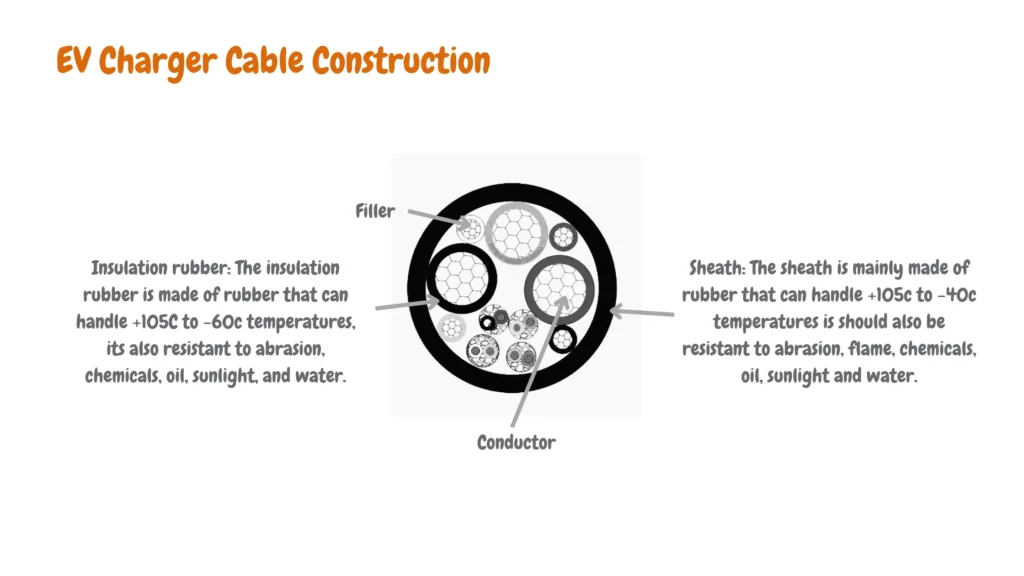
The type of material your cable is made of significantly impacts its flexibility. The most common options are:
- Rubber: Affordable and durable, but stiffens in cold temperatures, making it less ideal for harsh winters.
- PVC: More flexible than rubber, but prone to overheating and degradation in extreme heat.
- TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer): TPE offers excellent flexibility across a wide temperature range, making it a top choice for year-round use.
Demystifying Charging Levels and Cable Gauges
To determine what size cable you need for your EV charger, you will first need to know how much power your vehicle can accept. This information can usually be found in your car’s manual or by contacting the manufacturer. In this case, a 2.5 mm² or 4 mm² cable would be suitable. While thicker cables (lower gauge number) offer higher power output, they tend to be less flexible.
Level 1 Charger Cable Gauges
Level 1 charging operates using a standard 120-volt car charger outlet, akin to the outlets commonly found in households for powering various appliances. This type of charging method delivers up to 1.4 kW (kilowatts) of power and utilizes a current of 12 amps. While convenient for charging at home, Level 1 charging typically involves longer charging times due to its lower power output compared to higher-level charging options.
Level 2 Charger Cable Gauges
Level 2 charger cables step up the power and speed compared to Level 1 charging. It requires a 240-volt outlet, akin to what is commonly used for household electric dryers or ovens. This higher voltage enables Level 2 charging stations to deliver up to 19.2 kW (kilowatts) of power and can handle currents of up to 80 amps.
One notable aspect of Level 2 charger cables is the variation in cable gauge requirements, depending on the amperage. For instance:
- For 16 amps, a 14-gauge cable is sufficient.
- For 24 amps, a 12-gauge cable is recommended.
- For 32 amps, a 10-gauge cable is needed.
- For 40 amps, an 8-gauge cable is required.
- For 48 amps, a 6-gauge cable is necessary, though it often requires hardwiring.
These varying cable gauge requirements ensure safe and efficient power transmission during Level 2 charging sessions, catering to the diverse needs of electric vehicle owners.
Level 3 Charger Cable Gauges
Level 3 (DC Fast Charging) charger cables operate with high-voltage DC power, exceeding 350 kW and hundreds of amps. This necessitates special cables and connectors, not typically available for home use.
EV Charger Cable Length
Cable length and pliability are closely linked when it comes to EV charger cables, especially considering the 25-foot limit. As The National Electrical Code® (NEC) Section 625.17 (B) outlines, the cable connecting the electric vehicle to the charger must be a flexible cable of EV, EVJ, EVE, EVJE, EVT, or EVJT. The total usable length should not exceed 25 feet unless equipped with a cable management system integrated into the listed electric vehicle supply equipment (as per Section 625.17 (C)).
How Cable Length Affects Pliability
Longer cables are inherently less pliable: The 25-foot limit addresses concerns about heat dissipation and voltage drop. However, longer cables, especially those required for handling higher currents (which typically have lower gauges), tend to be less flexible by nature.
Increased handling challenges: Longer, less pliable cables present practical challenges during connection and disconnection processes. They are more cumbersome to maneuver and are susceptible to tangling, kinking, storage problems, and damage, thereby increasing the risk of tripping hazards.
How Does Temperature Affect EV Charging Cables?
Extreme temperatures—both hot and cold—can negatively impact the pliability and performance of EV charging cables.
Cold Weather Effects On EV Charging Cables
In low temperatures, cables stiffen, making them more prone to damage from bending. To mitigate this:
- Choose cables with low-temperature flexibility ratings and materials like TPE to maintain suppleness in freezing conditions.
- Store cables indoors or in insulated spaces to prevent stiffness and cracking.
One emerging EV charging cable pliability control technology we are closely following tackles a common issue for EV owners in cold climates: stiffening charging cables. As temperatures drop, cables become more difficult to maneuver, creating challenges for individuals with limited strength or older users.
To solve this, new pliability control systems may be introduced. These systems could detect when a user is struggling with a stiff cable. If the system senses this, it will assess the ambient temperature and, if needed, activate a nearby charger to warm the cable. This would make the cable easier to handle when the EV driver arrives.
This technology could become a valuable solution as the number of EVs and chargers continues to grow.
Hot Weather Effects On EV Charging Cables
Excessive heat can soften and degrade cables. To protect against this:
- Opt for cables made from heat-resistant materials like heat-stabilized TPE or XLPE to withstand high temperatures.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, and let cables cool down after use to prevent damage.
Choosing a Pliable EV Charger Cable
When selecting an EV charger cable, consider your climate. Choose cables made from suitable materials and with proper ratings. Regular maintenance will help ensure the cable lasts and remains safe. Check the NEMA rating to confirm the cable’s suitability for outdoor use in different weather conditions.
Our Cold Weather Tests for EV Chargers
We conduct at least three cold weather tests to evaluate charger durability in extreme conditions. These tests involve freezing the charger to the temperatures specified by the manufacturer for over 24 hours. For each EV charger, we ensure the temperatures align with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
For example, our recent top performer, the Battery Tender eCharge EV Charger, was tested at -22°F. This helps us assess the cable’s pliability and its ability to bend easily in cold temperatures for improved management.
We also perform frozen connector drop tests, where we drop the connector at least five times to check for any damage. Finally, we power up the charger while it’s frozen to ensure it delivers full power. The results of these cold weather tests are included in our Durability Over Time ratings under each EV charger review.
Best Practices for Home EV Charger Cable Management
Your EV charging cable is more than just a conduit for power—it’s an essential component for a safe, efficient, and reliable charging experience. Proper care and management not only extend its service life but also enhance its performance. Here are expert strategies to ensure your cable remains in optimal condition:
EV Charging Cable Handling
- Avoid excessive bending, kinking, or twisting to prevent internal damage.
- Be mindful of cable weight and refrain from dragging it, which can lead to premature wear and tear.
EV Charging Cable Storage Practices
- Coil the cable loosely to avoid creating tight bends that can stress the internal conductors.
- Store the cable indoors or in a controlled environment to shield it from environmental hazards.
- Regularly clean the cable to remove dirt, dust, and contaminants that could degrade insulation over time.
- In cold weather, bring the cable indoors to maintain flexibility and prevent stiffening.
- In hot climates, avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and high temperatures to minimize thermal degradation.
Efficient EV Charging Cable Management Solutions
- Utilize cable organizers, holders, ties, or clips to keep cables neatly coiled and accessible.
- Consider installing a retractable reel system for effortless extension and retraction during daily use.
- For setups with multiple or dual chargers, label cables clearly for quick identification and streamlined operation.
- Designate specific storage spaces for EV charging cables to prevent damage and reduce clutter.
- Enhance security by mounting cables along walls or ceilings and, where appropriate, using padlocks or secure anchoring systems.
- For an extra layer of protection, integrate an EV charger lock box to safeguard both the cable and charging equipment from theft or unauthorized use.
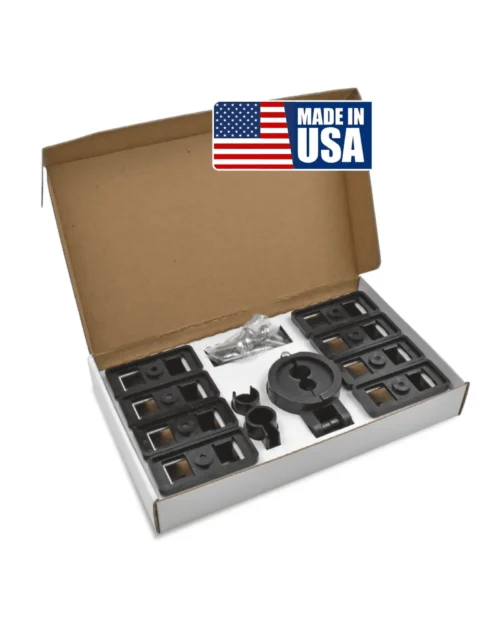
EV Charger Cable Management Kits
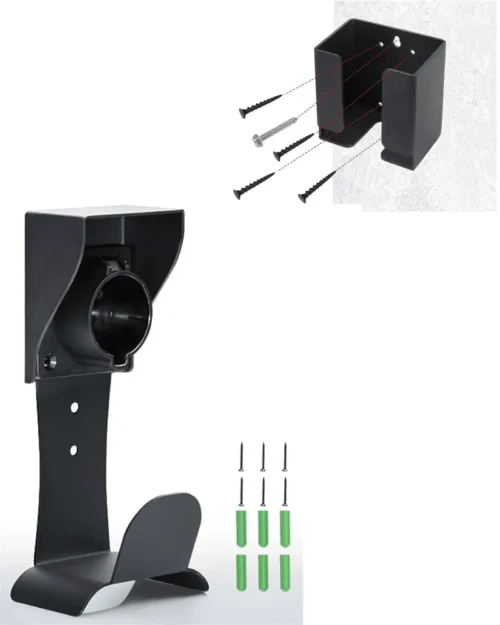
We recommend two EV Charger Cable Management Kits: the Alpha Rider EV Charger Holder and the voCharge Home Cable Management Kit.
Alpha Rider EV Charger Holder
Alpha Rider EV Charger Holder
EVoCharge EV Charging Cable Management Kit
EVoCharge EV Charging Cable Management Kit
EV Charger Cable Standards
Several international and European standards are crucial for ensuring EV charger cables’ safety, reliability, and durability.
Here’s a brief overview of some key standards certifications that together offer a complete EV Charger cable assessment:
- IEC 62893 Series: This comprehensive series defines general requirements, dimensions, and testing procedures for EV charger cables. It covers aspects like construction, electrical properties, and mechanical performance.
- EN 50620: This European standard focuses on safety requirements for EV charger cables. It addresses electrical, mechanical, and environmental aspects, including protection against electric shock, fire hazards, and environmental stresses.
- BS EN 50620 Annex F & IEC 62893-2 (Weathering/UV): These sections specifically address the cable’s ability to withstand harsh weather conditions, including sunlight and ultraviolet radiation, ensuring long-lasting performance and safety.
- IEC 62893-2, BS EN 50620 Annex D (Chemicals): These standards assess the cable’s resistance to various chemicals it might encounter, such as fluids, cleaning agents, and fuels, preventing degradation and potential hazards.
- IEC EN 80811 – 404 (Mineral Oil Immersion): This standard tests the cable’s ability to withstand immersion in mineral oil, which is relevant for situations where cables might be exposed to lubricants or fuels.
- IEC EN 60811-503 (Shrinkage) and IEC EN 80811-507 (Hot Set): These standards evaluate the dimensional stability of the cable under various temperature conditions, ensuring proper fit and function.
- IEC 62893-2, EN 50620 Annex C (Cold Impact): This section assesses the cable’s performance at low temperatures, critical for cold climates where cables might become brittle.
- IEC 60811 (Heat Shock): This standard tests the cable’s ability to withstand rapid temperature changes, preventing potential damage.
- ISO 48 for EVI-2, ISO 7619-1, or HD605:S2 for EVI-1 (Shore hardness): This assesses the cable’s material stiffness, influencing flexibility and handling characteristics.
- IEC EN 60332-1-2 (Vertical Frame Propagation): This standard evaluates the cable’s fire resistance, preventing flame spread and ensuring safety in case of fire incidents.
- BS EN 50525-1, and IEC 62821-1 (Assessment of Halogens): These standards limit the use of halogenated materials in the cable, reducing the risk of toxic fumes during fire events.
- IEC EN 60228 (Conductor Resistance): This standard ensures the conductor material has minimal resistance, minimizes energy losses, and maintains efficient power transfer.
- IEC 60245-2, and EN 50395 (Voltage Tests): These standards test the cable’s ability to withstand high voltages, preventing electrical breakdowns and ensuring safety.
Conclusions
Mastering the selection of EV charging cables starts with understanding the interplay between material science, thermal performance, and mechanical resilience. Rigorous tests—such as static and dynamic bend assessments—ensure that cables maintain dielectric integrity and resist fatigue even under harsh environmental conditions.
Advanced materials like TPE provide exceptional flexibility and durability, ensuring that cables perform reliably in sub-zero temperatures as well as high-heat environments. By adopting best practices in cable management—gentle handling, loose coiling, and proper storage—you can minimize microfracture propagation and extend the service life of your EV charging solution.
Ultimately, investing in high-quality, rigorously tested cables is essential for a smooth, efficient, and safe charging experience. We believe that our EV charging cable pliability guide will help you to confidently select the ideal EV charger and maintain its charging cable for long-term reliability.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.









