When planning to install a home EV charger, understanding the conduit requirements is essential for ensuring a safe and compliant setup. Conduits protect electrical wiring from physical damage, environmental factors, and interference, particularly in indoor and outdoor installations where wiring is exposed to elements.
Table of Contents
Types of Conduit for EV Charger Installation
| Type of Conduit | Characteristics | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC (polyvinyl chloride) Conduit (Schedule 40) (Popular Choice) | – Rigid structure providing robust protection. – Excellent moisture, chemical, and corrosion resistance. – Lightweight and easy to handle. | – Cost-effective compared to metal conduits. – Suitable for both aboveground and underground installations. – UV resistant, ideal for outdoor applications. | – Non-conductive, providing safety against electrical hazards. – Ideal for residential and commercial installations with variable environmental conditions. |
| Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) | – Flexible, corrugated structure that bends easily by hand. – Smooth interior for easy wire pulling. | – Lightweight and easy to handle. – Resistant to moisture and corrosion, suitable for concealed applications behind walls or in concrete slabs. | Lower impact resistance than rigid conduits, not recommended for areas prone to physical damage. |
| Liquidtight Flexible Non-Metallic Conduit (LFNC) | Waterproof and dustproof, designed for wet locations | – Provides strain relief and protection against moisture and oils. – Flexible and easy to install, suitable for outdoor applications. | Best for environments with high exposure to liquids or where moisture is a concern. |
| Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC) | – Heavy-duty, galvanized steel or stainless steel construction. – Provides excellent mechanical protection. | – Ideal for industrial and commercial settings needing high protection. – Offers grounding for electrical systems and protection against electromagnetic interference | Heavier and more challenging to handle, requiring specialized tools for installation. |
| Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) | Lightweight and thin-walled metal conduit made of galvanized steel. | – Cost-effective and suitable for residential applications. – Provides good protection against physical damage, easier to install than RMC. | Limited resistance to corrosion and humidity, which may be a concern in certain environments. |
Among the various options above, the PVC conduit pipe is a popular choice for both indoor and outdoor home EV charger installations due to its durability, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand moisture.
EV Charger Installation PVC Conduit Size (Schedule 40)
The term “Schedule 40” pertains to the wall thickness of the PVC conduit, which directly impacts its pressure rating and overall durability. Schedule 40 PVC conduits have thicker walls compared to other types, allowing them to withstand various environmental stresses while providing reliable protection for the electrical wiring of your EV charger installation.
| Nominal Size (NOM) | Outside Diameter (O.D.) | Inside Diameter (I.D.) | Wall Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 inch | 0.840 inches | 0.622 inches | 0.109 inches |
| 3/4 inch | 1.050 inches | 0.824 inches | 0.113 inches |
| 1 inch | 1.315 inches | 1.049 inches | 0.133 inches |
| 1-1/4 inch | 1.660 inches | 1.380 inches | 0.140 inches |
| 1-1/2 inch | 1.900 inches | 1.500 inches | 0.145 inches |
| 2 inch | 2.375 inches | 2.203 inches | 0.154 inches |
| 2-1/2 inch | 2.875 inches | 2.609 inches | 0.203 inches |
| 3 inch | 3.500 inches | 3.250 inches | 0.216 inches |
| 3-1/2 inch | 4.000 inches | 3.500 inches | 0.226 inches |
| 4 inch | 4.500 inches | 4.026 inches | 0.237 inches |
| 5 inch | 5.563 inches | 5.047 inches | 0.258 inches |
| 6 inch | 6.625 inches | 6.034 inches | 0.280 inches |
When selecting conduit sizes for Level 1 and Level 2 EV chargers, the optimal choices typically fall within the 3/4-inch and 1-inch categories of schedule 40 PVC conduit.
EV Charger Installation 3/4 inch Conduit
With an outside diameter of 1.050 inches and an inside diameter of 0.824 inches, the 3/4 inch conduit strikes a balance between capacity and ease of installation of level 1 and Level 2 EV chargers which have 3 to 4 feeder wires from the dedicated circuit breaker to the NEMA outlet, or hardwired wallbox. Its wall thickness of 0.113 inches provides adequate protection for wiring while maintaining flexibility for various installation scenarios.
A 34-inch conduit accommodating a 3-conductor 6 AWG cable assembly for EV charger installation:
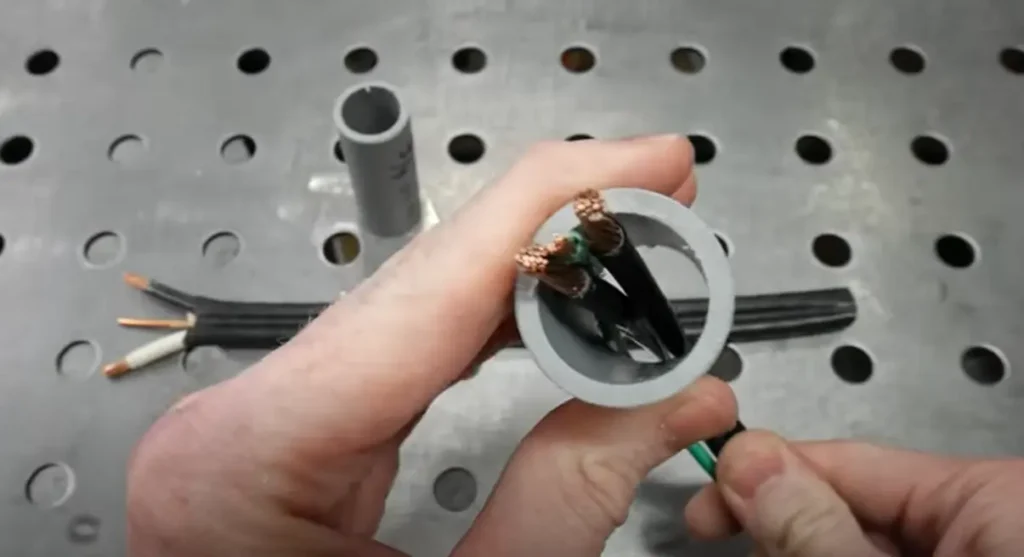
EV Charger Installation 1-inch Conduit
The 1-inch conduit, boasting an outside diameter of 1.315 inches and an inside diameter of 1.049 inches, allows for a larger volume of wiring, making it an excellent option for Level 2 chargers installations that have other EV charger accessories such as wiring smart meters, solar EV charging accessories, etc. With a wall thickness of 0.133 inches, this conduit provides robust mechanical protection, accommodating the increased electrical demands of complex Level 2 installations while still ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Conduit Sizing Based on Wire Size and Quantity for EV Charger Installations
Now that you understand Schedule 40, it is time we dig deeper and understand that the size of conduit to use depends on the number of feeder wires from the circuit breaker to the outlet or EV charger, and the size of the wires used:
| Conduit Size in Inches | 14AWG | 12AWG | 10AWG | 8 AWG | 6 AWG | 4 AWG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 Inch schedule 40 | 11 (2.8 kW EV Chargers) | 8 (3.8 kW EV Chargers) | 5 (5.7 kW EV Chargers) | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 Inch Schedule 40 | 9 (2.8 kW EV Chargers) | 6 (3.8 kW EV Chargers) | 4 (5.7 kW EV Chargers) | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3/4 Inch schedule 40 | 21 | 15 | 9 | 5 (7.6 kW EV Chargers) | 4 (9.6 kW EV Chargers) | 2 |
| 3/4 Inch schedule 80 | 17 | 12 | 7 | 4 (7.6 kW EV Chargers) | 3 (9.6 kW EV Chargers) | 1 |
| 1 Inch Schedule 40 | 34 | 25 | 15 | 9 (7.6 kW EV Chargers) | 6 (9.6 kW EV Chargers) | 4 (11.5 kW EV Chargers) |
| 1 Inch Schedule 80 | 28 | 20 | 13 | 7 | 5 | 3 (11.5 kW EV Chargers) |
| 1 1/4 Inch schedule 40 | 60 | 43 | 27 | 16 | 11 | 7 (11.5 kW EV Chargers) |
| 1 1/4 Inch schedule 80 | 51 | 37 | 23 | 13 | 9 | 6 |
| 1 1/2 Inch schedule 40 | 82 | 59 | 37 | 21 | 15 | 9 |
| 1 1/2 Inch schedule 80 | 70 | 51 | 32 | 18 | 13 | 8 |
| 2 Inch Schedule 40 | 135 | 99 | 62 | 36 | 26 | 16 |
| 2 Inch Schedule 80 | 118 | 86 | 54 | 31 | 22 | 14 |

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.







