A hardwired EV charger installation allows for higher amperage Level 2 EV charging, with the maximum amperage for a Level 2 hardwired EV charger reaching up to 80 amps.
Hardwired EV charger installation provides faster charging speeds compared to plug-in EV chargers, which are typically limited to 40 amps on a 50-amp circuit breaker. The increased amperage capacity of a hardwired EV charger ensures quicker recharging, making it especially useful when you return from a trip and need to charge quickly before heading out again.
For a hardwired EV charger installation, you’ll need a licensed electrician to ensure everything is done correctly and safely. They will:
- Determine the appropriate dedicated EV charger circuit breaker amperage for your EV charger.
- Select the appropriate wire sizes for the hot and ground conductors, rated for 75°C with copper wiring, while considering the distance to the point of use to minimize voltage drop.
- Choose the right conduit size to protect the feeder wires from the electrical panel and the junction box.
- Install and connect the wiring from the electrical panel to the junction box.
Connecting the hardwired EV charger to the junction box requires specific precautions and a solid understanding of electrical hazards, so professional installation is essential.
This guide simplifies the hardwired EV charger installation process. We provide detailed hardwired EV charger wiring diagrams for 12 Amp to 80 Amp Level 2 chargers available today, tailored to various amperage levels. Our diagrams illustrate:
- Wiring the circuit breaker in a single-phase 120/240V electrical panel (common in most U.S. homes).
- Proper wire sizing for hot and ground conductors, rated for 75°C with copper wiring.
- Conduit sizing for feeder wires between the electrical panel and the junction box.
Table of Contents
- Best Hardwired EV Chargers
- Hardwired EV Charger Installation: Conductors, Breaker, and Conduit Guide
- 12 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 16 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 20 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 24 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 28 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 32 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 36 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 40 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 48 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 56 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 64 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 72 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- 80 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
- Why Install a Hardwired EV Charger Over a Plug-in EV Charger?
- When to Choose a Plug-in EV Charger Instead
Best Hardwired EV Chargers
After extensively testing several home EV chargers on the market, we identified the best hardwired EV chargers based on their smart features, ease of installation, safety features, certifications, and overall performance. Below, you’ll find our top recommendations for hardwired EV chargers that stood out during our evaluation.
It’s worth noting that all the chargers listed above are fully compatible with the installation instructions provided in this guide. These chargers were tested using the same circuits outlined in our amperage-specific wiring diagrams, ensuring seamless integration, code compliance, and optimal performance for your hardwired EV charger setup.
Whether you’re looking for reliability, smart features, or future-proofing your permanent home EV charger installation, these chargers offer excellent value for your investment.
Hardwired EV Charger Installation: Conductors, Breaker, and Conduit Guide
The table below summarizes and provides essential guidelines for selecting the correct wire gauge, breaker size, and conduit for a hardwired EV charger installation. It takes into account the 80/20 rule for breaker sizing, proper wire gauge for continuous loads, grounding conductor requirements, and recommended conduit sizes based on the number of conductors and wire size used.
| Hardwired EV Charger Rating (Continuous Loads) | EV Charger Dedicated Breaker Size (20/80 Rule) | Hot Wire Gauge (AWG) | Grounding Conductor Gauge (Copper) | Conduit Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 Amp | 15 Amp | 14 | 14 AWG | 1/2 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 16 Amp | 20 Amp | 12 | 12 AWG | 1/2 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 20 Amp | 25 Amp | 10 | 10 AWG | 3/4 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 24 Amp | 30 Amp | 10 | 10 AWG | 3/4 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 28 Amp | 35 Amp | 8 | 10 AWG | 3/4 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 32 Amp | 40 Amp | 8 | 10 AWG | 3/4 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 36 Amp | 45 Amp | 6 | 10 AWG | 1 Inch schedule 40 |
| 40 Amp | 50 Amp | 6 | 10 AWG | 1 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 48 Amp | 60 Amp | 4 | 10 AWG | 1 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 56 Amp | 70 Amp | 4 | 8 AWG | 1 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 64 Amp | 80 Amp | 3 | 8 AWG | 1 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 72 Amp | 90 Amp | 2 | 8 AWG | 1 Inch Schedule 40 |
| 80 Amp | 100 Amp | 2 | 8 AWG | 1 Inch Schedule 40 |
Expert Electric Vehicle Charger Hardwire Installation Notes:
- EV Charger Dedicated Breaker Size (80/20 Rule): The breaker size is determined using the 80/20 rule, which means the breaker should be rated at 125% of the charger’s maximum amperage to account for continuous loads.
- Hot Wire Gauge (AWG): For hot conductors (L1, L2), solid copper wire, rated for 75°C, is recommended. The appropriate gauge is determined by the amperage rating of the circuit and the load requirements of the EV charger.
- Grounding Conductor Gauge (Copper): The grounding conductor size must comply with NEC standards and is typically determined based on the size of the circuit breaker. In most cases, the grounding conductor is smaller than the hot wire, but it must still be sufficient to ensure safe operation and protect the circuit against faults.
- Conduit Size: The conduit size is determined based on the number of conductors (three: L1, L2, and Ground) and the wire gauge used. This ensures sufficient space for safe wire installation, accounting for heat dissipation and ease of pulling the wires.
12 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 12 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger typically provides a charging rate of up to 2.88 kW, making it suitable for users with moderate charging needs.
12 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
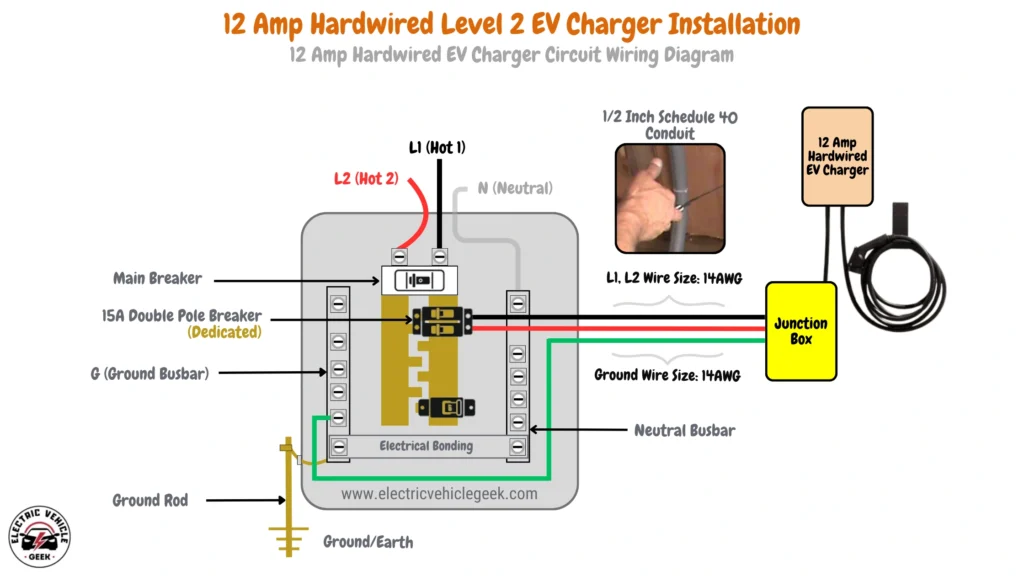
12 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 15 Amp dedicated breaker, as per the 80/20 rule, ensuring safe operation for continuous loads. The wiring includes 14 AWG wires for the hot conductors (L1 and L2) and a 14 AWG copper grounding conductor. For conduit, a 1/2-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended to accommodate the wires comfortably.
16 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 16 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger offers a charging rate of up to 3.84 kW, making it ideal for users who need a moderate charging speed.
16 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
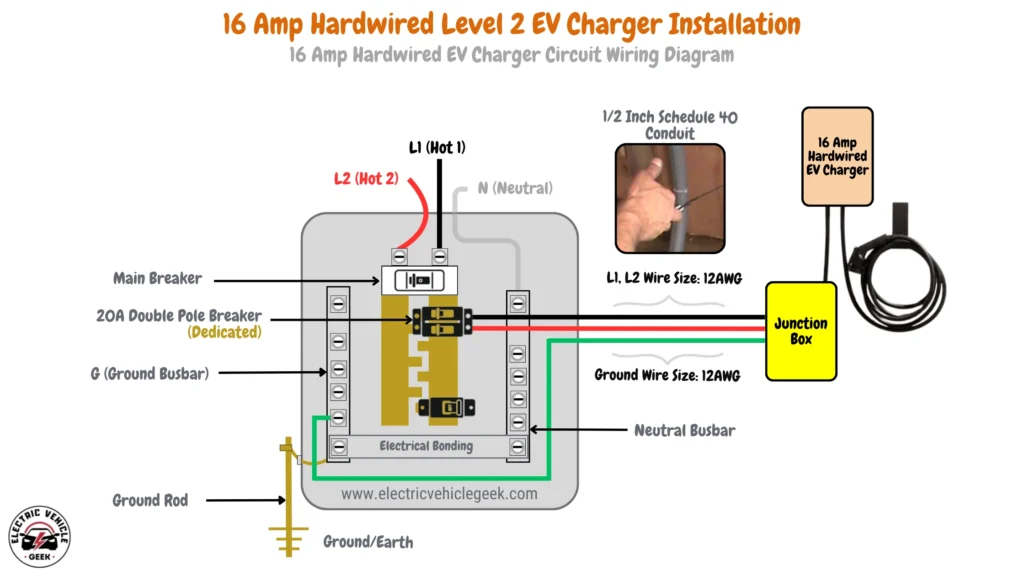
16 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 20 Amp dedicated breaker, following the 80/20 rule for safe operation with continuous loads. The installation uses 12 AWG wire for the hot conductors (L1 and L2) and a 12 AWG copper grounding conductor. For conduit, a 1/2-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended to ensure proper wire placement and heat dissipation.
20 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 20 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger typically provides 4.8 kW of charging power.
20 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
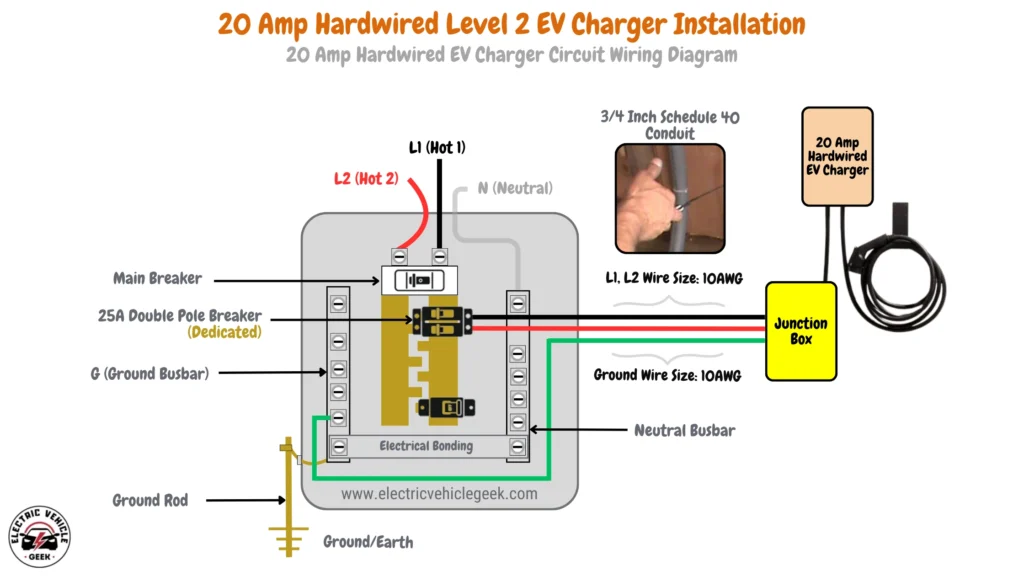
The diagram illustrates the installation of a 20 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger, showcasing a 25A double-pole dedicated breaker within the electrical panel, connected to the charger via a junction box. It specifies the use of 10 AWG wire for both the hot conductors (L1 and L2) and a 10 AWG copper grounding conductor.
The conductors from the electrical panel to the junction box are housed in a 3/4-inch Schedule 40 conduit, providing protection and ease of installation. Additionally, the neutral wire is properly connected to the neutral busbar, ensuring correct circuit configuration and safety.
24 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 24 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger delivers a charging rate of up to 5.76 kW, making it suitable for users who need faster charging times.
24 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
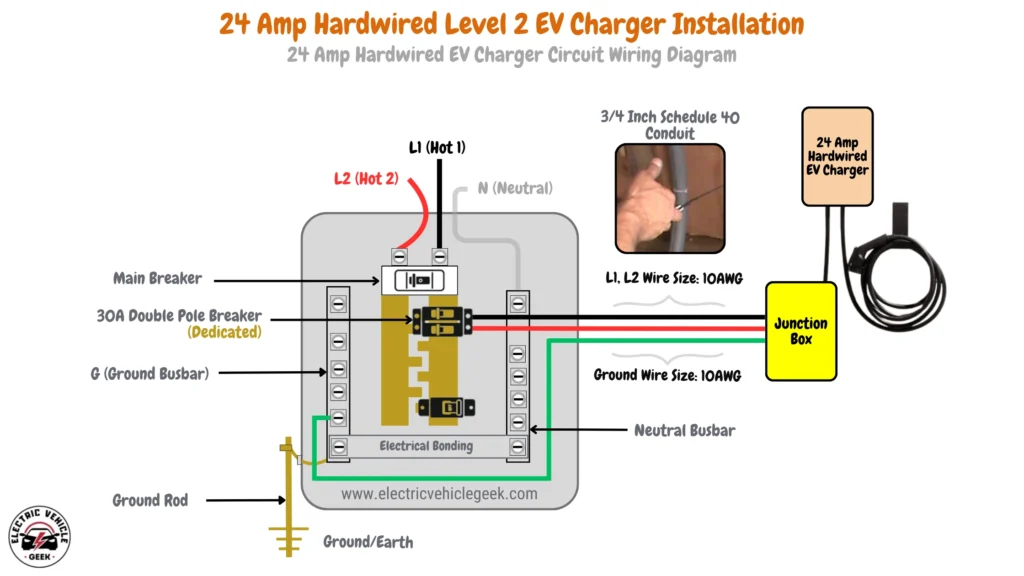
24 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 30 Amp dedicated breaker, following the 80/20 rule for handling continuous loads safely. The installation uses 10 AWG wire for both the hot conductors (L1 and L2) and a 10 AWG copper grounding conductor. For conduit, a 3/4-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended to accommodate the wires and ensure proper ventilation.
28 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 28 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger provides up to 6.72 kW of charging power, perfect for users looking for a balance between speed and efficiency.
28 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
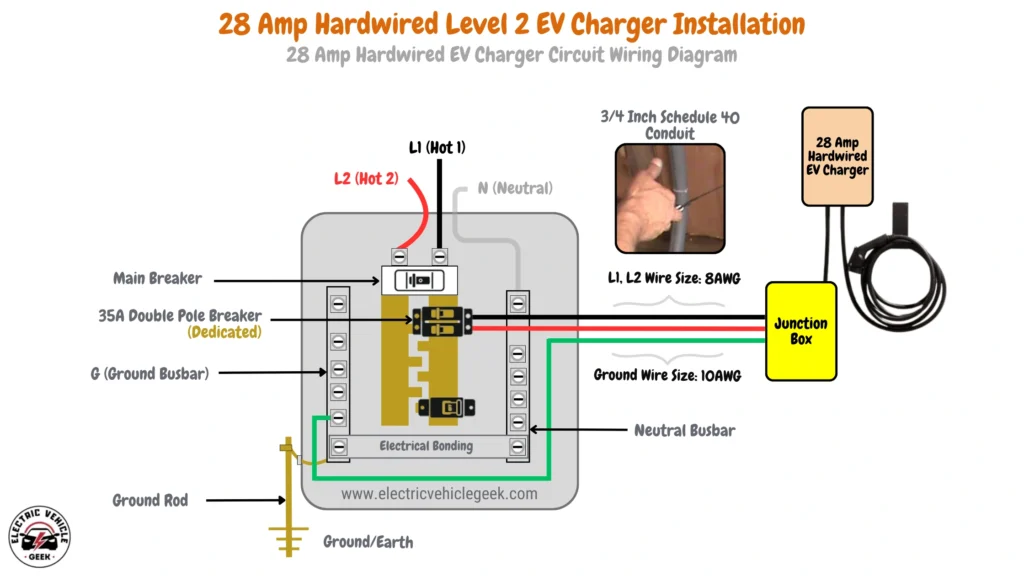
28 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 35 Amp dedicated breaker, adhering to the 80/20 rule for safety. The installation uses 8 AWG wire for both the hot conductors (L1 and L2) and a 10 AWG copper grounding conductor. A 3/4-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended to safely house the wires and maintain proper heat dissipation.
32 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 32 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger offers up to 7.68 kW of charging power, making it ideal for faster home charging.
32 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
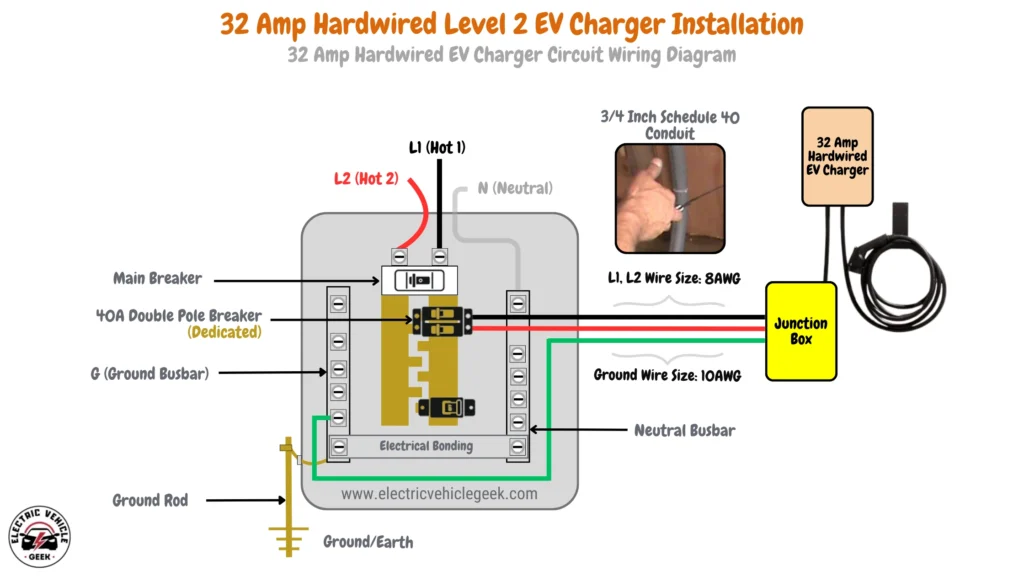
32 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 40 Amp dedicated breaker, according to the 80/20 rule, to accommodate continuous loads. The system uses 8 AWG wire for both hot conductors (L1 and L2), with a 10 AWG copper grounding conductor. A 3/4-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended for proper wire fit and heat management.
36 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 36 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger provides up to 8.64 kW of charging power, suitable for users who require a quicker charge for their electric vehicles.
36 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
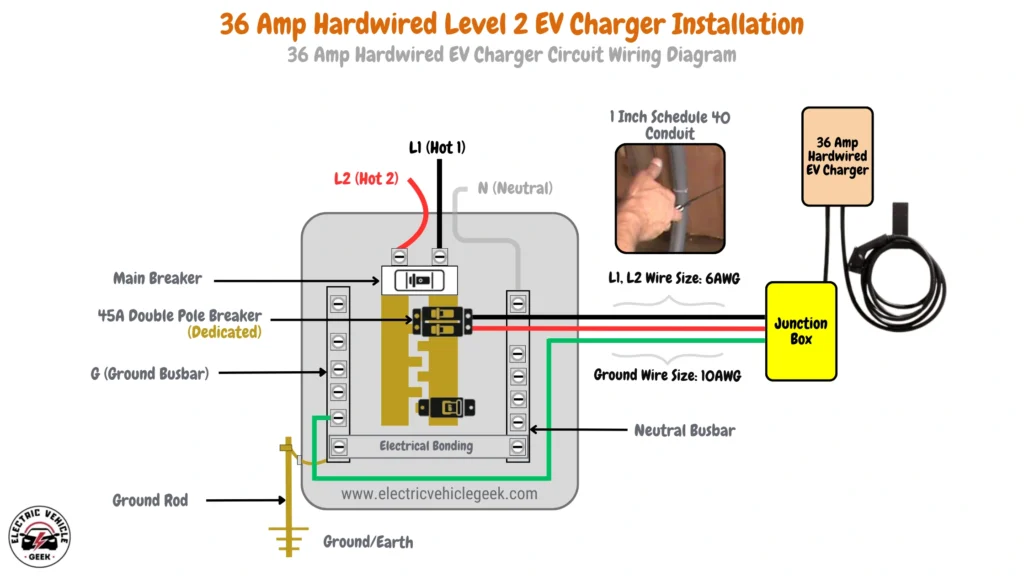
36 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 45 Amp dedicated breaker, following the 80/20 rule for handling continuous loads safely. The installation uses 6 AWG wires for the hot conductors (L1 and L2) and a 10 AWG copper grounding conductor. A 1-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended to allow ample space for the wires and ensure proper ventilation.
40 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 40 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger offers up to 9.6 kW of charging capacity, making it an excellent choice for users seeking fast charging at home.
40 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
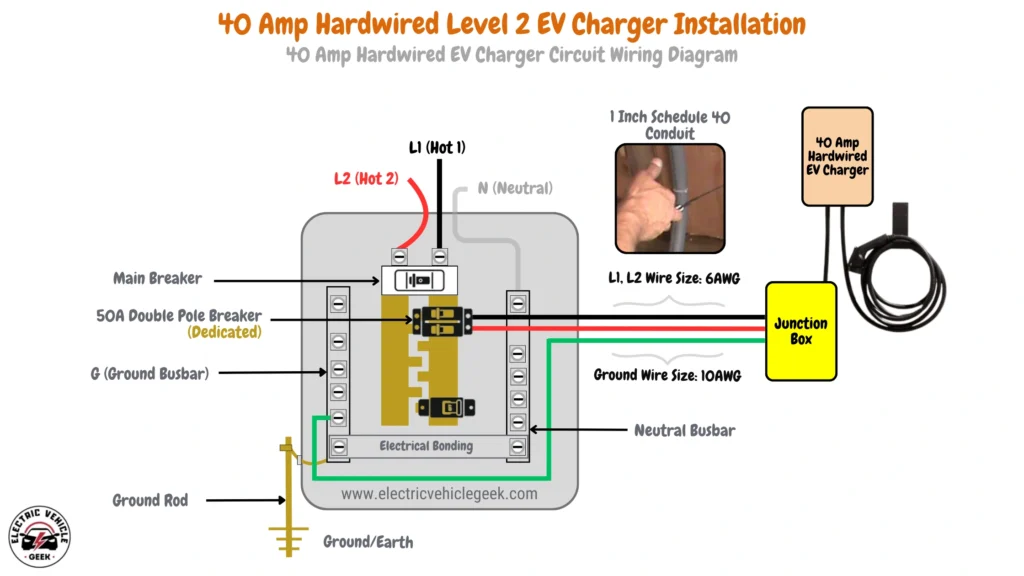
40 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 50 Amp dedicated breaker, adhering to the 80/20 rule for continuous load safety. The system uses 6 AWG wires for the hot conductors (L1 and L2) and a 10 AWG copper grounding conductor. For conduit, a 1-inch Schedule 40 size is ideal to ensure a safe, organized installation.
48 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 48 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger delivers up to 11.52 kW of charging power, providing one of the faster home charging options.
48 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
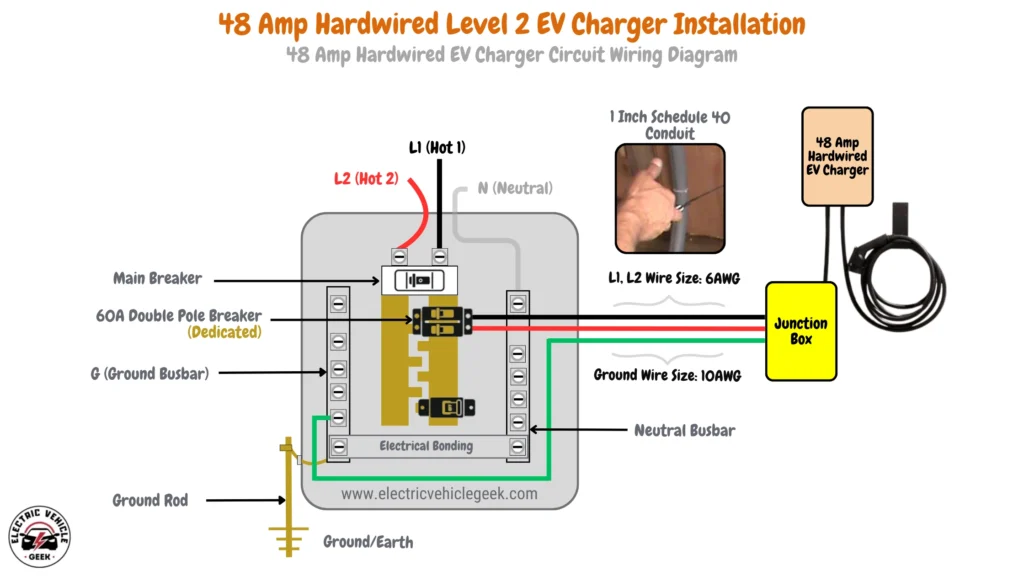
48 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 60 Amp dedicated breaker, following the 80/20 rule for optimal safety with continuous loads. The installation uses 4 AWG wires for the hot conductors (L1 and L2), paired with a 10 AWG copper grounding conductor. A 1-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended for proper wire routing and ventilation.
Can I Use 6 AWG Wire for a 48A EV Charger Installation?
Yes, you can use 6 AWG copper wire for a 48A EV charger if it’s allowed by the manufacturer’s installation manual and you’re using the correct wire type and installation method.
Some 48A hardwired EV chargers such as the Hardwired Emporia EV Charger are designed with terminals that exclusively accept 6 AWG (American Wire Gauge) copper wire and cannot directly accommodate larger 4 AWG wires.
EMPORIA Level 2 EV Charger Review
Our Experience in the Field: Real-World 48A Hardwired EV Charger Installations
We’ve encountered situations where an older 48A hardwired EV charger was installed using 4 AWG wires, but the replacement unit – such as the Emporia Level 2 charger – terminals only accept 6 AWG wire connections which even the manufacturer recommends.
Instead of replacing the entire circuit, we used a UL-listed reducing splice connector to transition from 4 AWG to 6 AWG. These connectors are approved for 75°C-rated terminations and maintain a safe, code-compliant installation.
In other cases, we’ve made the same 4 AWG to 6 AWG transition using mechanical connectors such as lugs, split bolts, or wire nuts, as well as compression connectors or terminal blocks/barrier strips.
These transitions are typically made inside a hardwired EV charger junction box, and all components must be UL-listed, support the conductor sizes involved, and be rated for 75°C or higher as shown in the circuit wiring below:
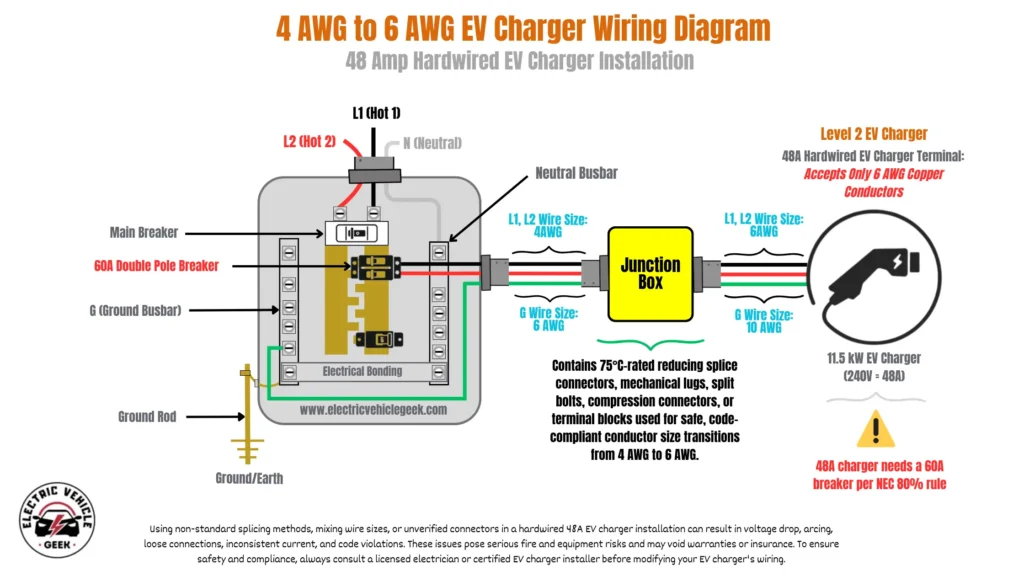
We use these methods to safely replace 48A hardwired EV chargers installed with 4 AWG circuits when upgrading to newer chargers that only accept 6 AWG wires, without the cost or complexity of replacing the entire branch circuit.
Our Recommendation
For all new 48A hardwired EV charger installations, always follow the manufacturer’s installation manual.
While 4 AWG copper conductors are often recommended for 48A Hardwired EV charger installation, if the EV charger manufacturer (e.g., Emporia) specifies 6 AWG copper wire, it is best to run the entire circuit using 6 AWG THHN/THWN or SEU/SER cable and protected with a 60A dedicated circuit breaker, as shown in the 48A hardwired EV charger with 6 AWG circuit wiring diagram below:
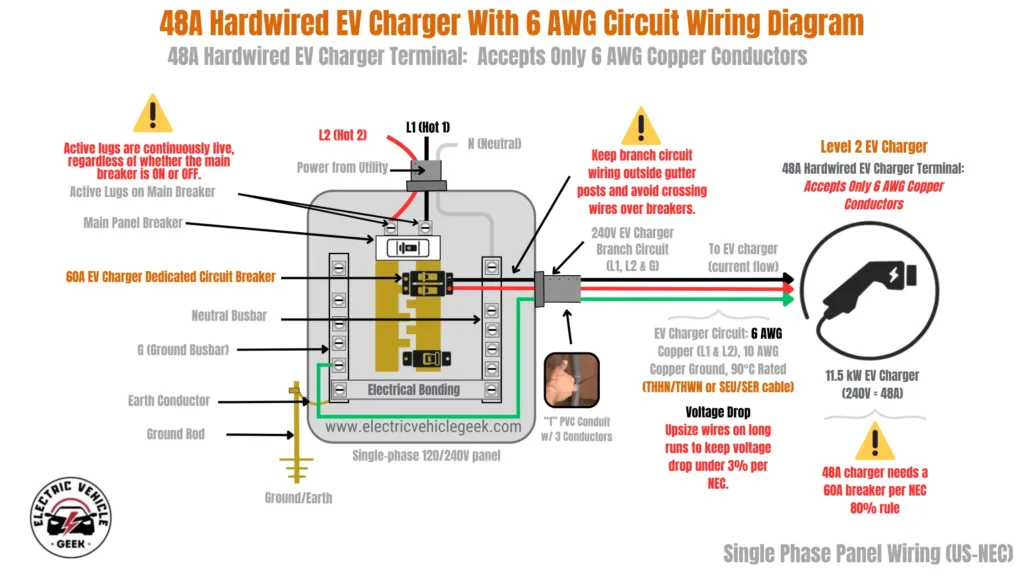
Using electrical tools such as reducing splice connectors, mechanical connectors (including lugs, split bolts, and wire nuts), compression connectors, or terminal blocks/barrier strips in high-load hardwired EV charger installations is one of the more complex hardwired EV charger installations that we don’t recommend for DIY installations.
If you encounter a situation requiring wire adaptation or have any doubts about the installation process, we recommend consulting a licensed electrician or certified EV charger installer. They can assess your specific requirements, ensure compliance with local electrical codes, and perform the installation safely and effectively.
56 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 56 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger provides up to 13.44 kW of power, suitable for those who need fast, efficient home charging.
56 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
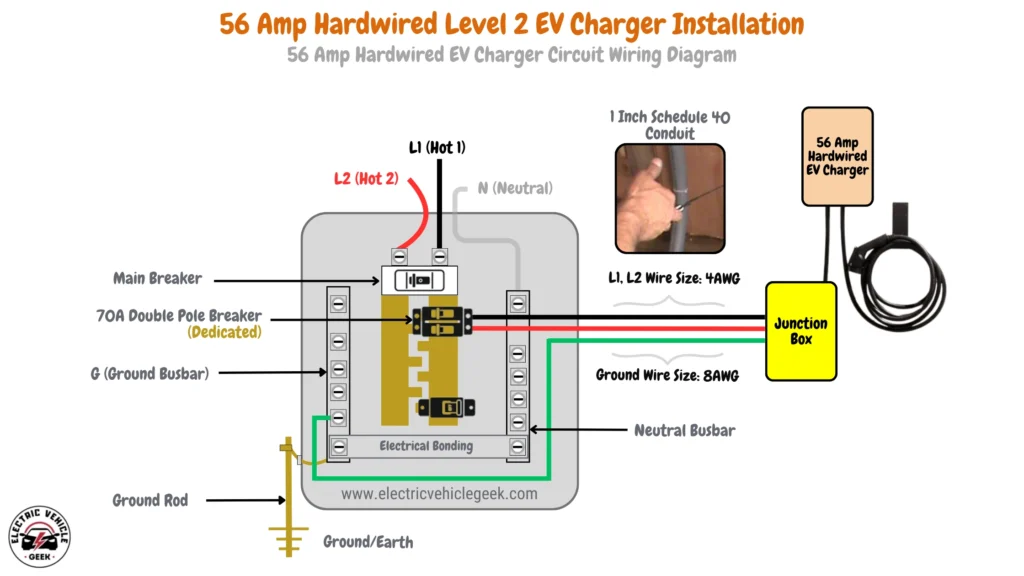
56 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 70 Amp dedicated breaker, following the 80/20 rule to safely accommodate continuous loads. The installation uses 4 AWG wires for the hot conductors (L1 and L2), with an 8 AWG copper grounding conductor. A 1-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended to ensure proper spacing and heat management.
64 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 64 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger delivers up to 15.36 kW of charging power, ideal for users who need rapid charging for multiple electric vehicles or larger battery capacities.
64 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
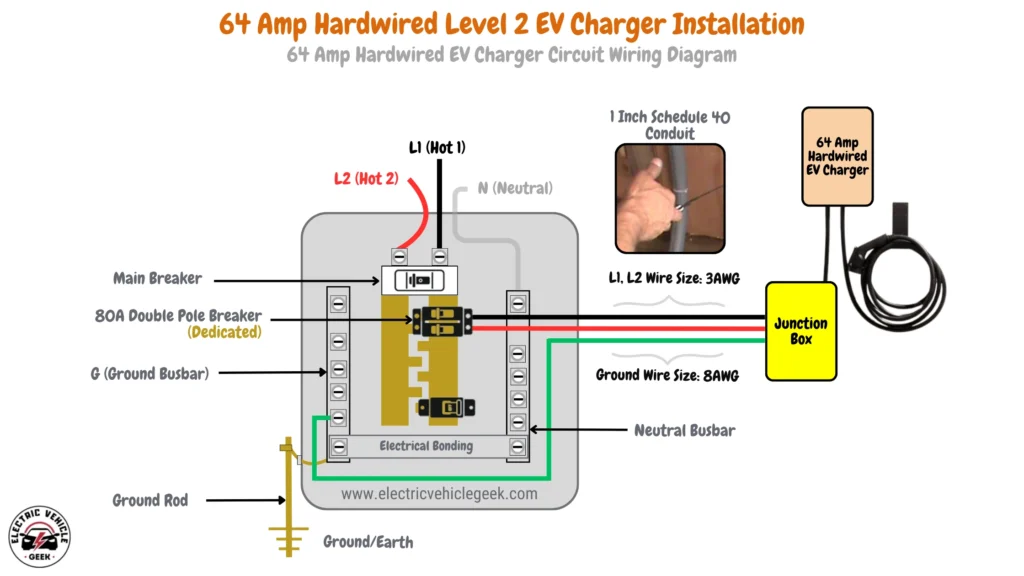
64 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires an 80 Amp dedicated breaker, following the 80/20 rule for safety. The installation uses 3 AWG wires for the hot conductors (L1 and L2), paired with an 8 AWG copper grounding conductor. A 1-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended to accommodate the larger wires and ensure proper ventilation.
72 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
A 72 Amp hardwired Level 2 EV charger offers up to 17.28 kW of charging power, making it one of the fastest options for home installations.
72 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
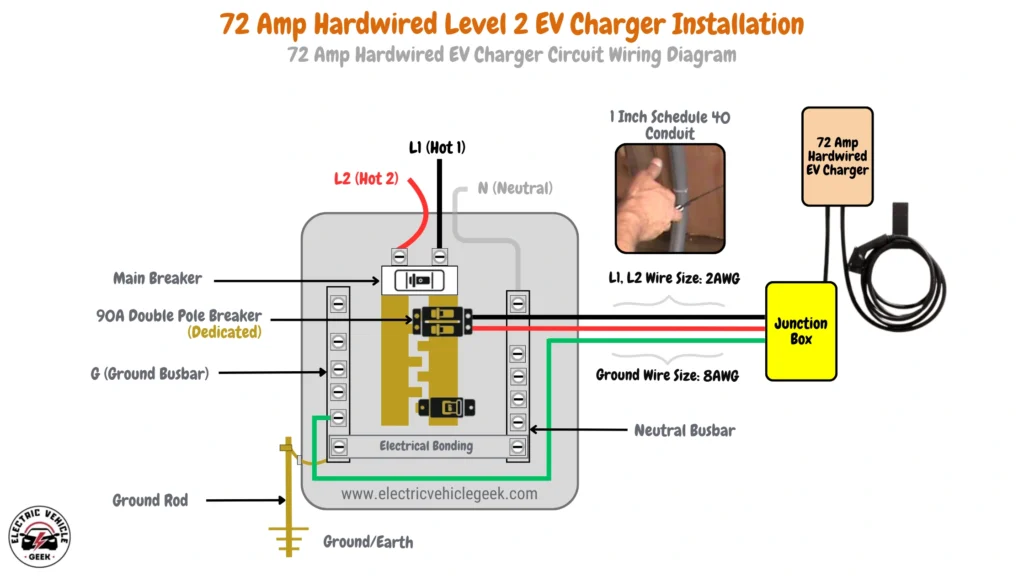
72 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 90 Amp dedicated breaker, according to the 80/20 rule, for safe continuous load handling. The installation uses 2 AWG wires for the hot conductors (L1 and L2), with an 8 AWG copper grounding conductor. A 1-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended for proper wire placement and to avoid overheating.
80 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Installation
An 80 Amp Level 2 hardwired EV charger delivers up to 19.2 kW of power, providing one of the fastest charging rates for residential applications.
80 Amp Hardwired EV Charger Circuit Wiring Diagram
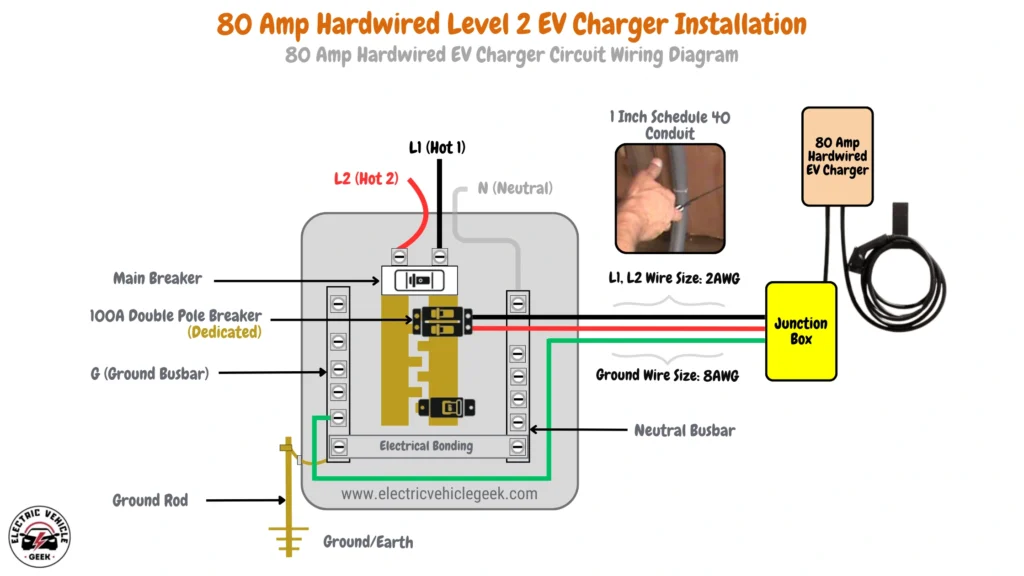
80 Amp hardwired EV charger installation requires a 100 Amp dedicated breaker, following the 80/20 rule for optimal safety. The system uses 2 AWG wires for the hot conductors (L1 and L2), with an 8 AWG copper grounding conductor. A 1-inch Schedule 40 conduit is recommended to accommodate the larger wires and ensure proper ventilation.
Why Install a Hardwired EV Charger Over a Plug-in EV Charger?
A hardwired EV charger offers several key advantages over a plug-in EV charger, making it the preferred choice for many EV owners, particularly in residential and commercial settings where reliability and safety are top priorities.
1. Enhanced Safety
- Eliminates Plug Connections: Hardwired chargers connect directly to your electrical panel, eliminating the risks associated with loose or worn plug connections that can lead to overheating or electrical faults.
- Weatherproof Installation: A hardwired installation is typically sealed and better protected against environmental factors like rain, dust, and debris, making it more suitable for outdoor use.
2. Greater Power Capacity
- Higher Amperage Support: Many hardwired chargers can handle higher amperage, enabling faster charging speeds compared to some plug-in models that are limited by outlet capacity.
- Reduced Risk of Circuit Overload: A direct connection to the electrical system ensures that the charger is adequately supported by the home’s wiring and circuit breakers.
3. Permanent, Code-Compliant Setup
- Meets Electrical Codes: Hardwired installations are often required to meet local building codes and safety standards, ensuring compliance and long-term operational integrity.
- Professional Installation: Hardwiring typically involves licensed electricians, which ensures a properly configured and optimized setup for your specific needs.
4. Clean and Professional Aesthetic
- No Visible Cords or Outlets: Hardwired chargers have a cleaner appearance as there is no need for bulky outlets or visible cords. This is particularly appealing for residential garages or commercial spaces.
- Less Wear and Tear: With no need to repeatedly plug and unplug the charger, hardwired setups minimize wear and tear on both the charger and the outlet.
5. Reduced Risk of Accidental Disconnection
- Permanent Connection: A hardwired charger cannot be unplugged accidentally, ensuring uninterrupted charging, which is especially important for high-demand or fleet environments.
6. Scalability and Future-Proofing
- Supports Future Upgrades: A hardwired installation can often support more powerful chargers or additional units in the future without requiring significant modifications.
- Ideal for Permanent Locations: If the EV charger is intended to remain in the same location long-term, hardwiring provides a robust and reliable solution.
When to Choose a Plug-in EV Charger Instead
While hardwired chargers offer significant advantages, plug-in chargers may still be suitable for renters, those who need portability, or in cases where local electrical codes or infrastructure constraints make hardwiring impractical.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.


















The 48amp connection indicates a #6 in the picture, but a #4 in the description. If using a charge point charger do we have to downsize the conductor (to a #6) in a junction box to fit in the lugs in the charger?
Yes, in a few 48A hardwired EV charger installation cases you will need to transition from #4 AWG to #6 AWG conductors because some EV chargers, including models like Emporia, have terminals designed exclusively for #6 AWG copper wire connections. This downsizing is typically done inside a junction box using UL-listed reducing splice connectors or mechanical connectors to ensure a safe, code-compliant installation without replacing the entire branch circuit.
The junction box houses the connections and protects 75°C-rated components such as reducing splice connectors, mechanical lugs, split bolts, wire nuts, compression connectors, or terminal blocks that are sized appropriately for both conductor sizes. Following the charger manufacturer’s installation manual is critical. If it specifies #6 AWG wire, you must use it either by running the entire circuit with #6 AWG conductors or by safely transitioning from #4 AWG to #6 AWG inside the junction box.
Our updated 48A hardwired EV charger wiring diagrams now clearly illustrate our recommended #4AWG full circuit wiring, and two other scenarios: a full #6 AWG run from the electrical panel to the charger, and a transition from #4 AWG to #6 AWG inside a junction box. Using one wiring type and size without junctions or splices approach helps avoid common risks such as voltage drop, overheating, arcing, or potential warranty and insurance issues caused by improper wiring.