Level 1 EV charging is often overlooked in the flashy world of high-powered options such as Level 2 charging and Level 3 charging, for this reason, EV charging station businesses and electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers have flooded the market with electric vehicles compatible with Level 2 and Level 3 charging stations and entrepreneurs looking for a piece of the pie following suit.
What Is a Level 1 EV Charger?
A Level 1 EV charger uses a standard 120V household outlet and typically operates at 8 to 16 amps, delivering 1.0 to 1.9 kW of power. This provides about 2 to 5 miles of range per hour. It’s the most affordable and accessible charging option, with no specialized branch circuit installation or expensive panel upgrades required.
Level 1 charging is ideal for overnight use at home and works best for light EV users or drivers with short daily commutes. However, due to its slower speed, it’s not suitable for long-distance travel or quick top-ups.
Shop Level 1 EV ChargersLevel 1 EV Charging Set-Up?
Level 1 EV charging operates through a standard 120V outlet, typically using a NEMA 5-15 outlet for 12-amp Level 1 chargers or a NEMA 5-20 outlet for 16-amp Level 1 chargers in residential settings.
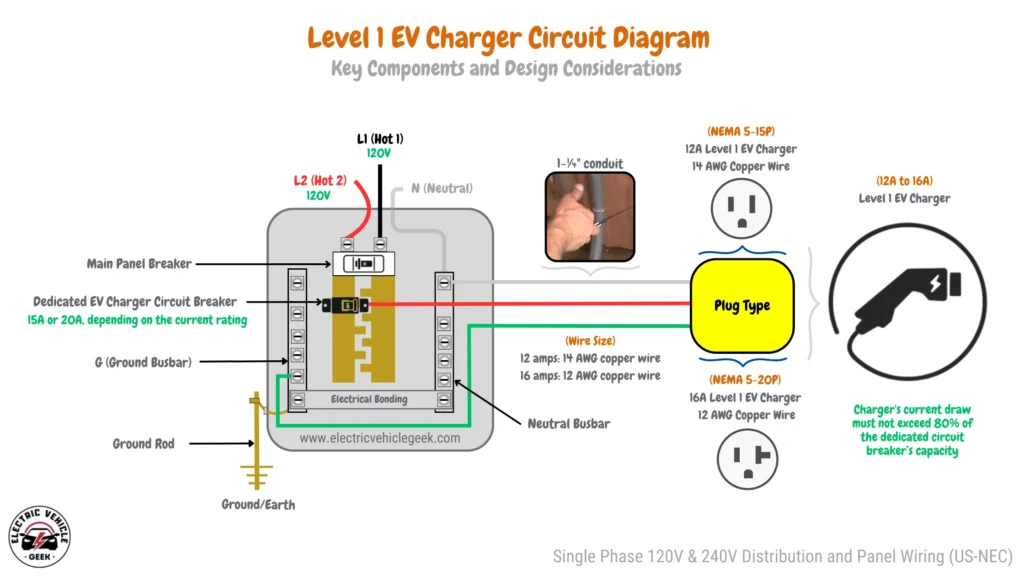
Although Level 1 EV charging is the slowest option, delivering roughly 2 to 5 miles of range per hour, it remains a practical solution for overnight charging, especially for drivers averaging 40 miles per day with small to mid-sized electric vehicles. Depending on battery capacity and available circuit amperage, a full charge typically takes between 6 and 22 hours.
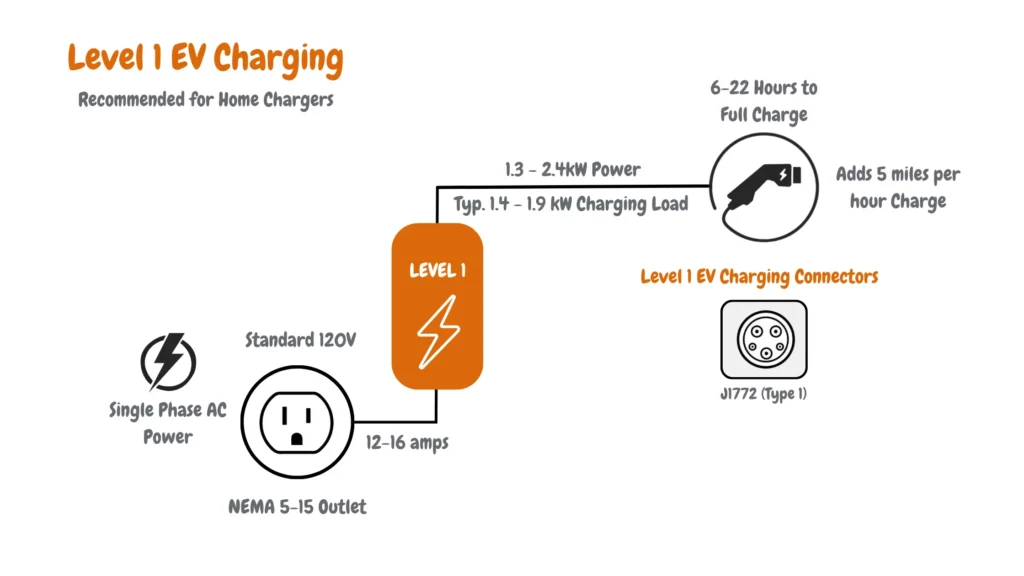
Level 1 EV chargers typically deliver between 1.3 and 2.4 kilowatts (kW) of power via 120-volt, single-phase AC. They draw a continuous load of 12 to 16 amps, depending on the unit and circuit capacity, and use either the SAE J1772 (Type 1) connector or the newer NACS standard, both widely compatible with residential electrical systems and most EVs in North America.
This type of charging is a practical, low-cost solution for budget-conscious drivers, especially for home use. Since it requires no dedicated circuits, panel upgrades, or hardwired installation, setup is as simple as plugging into a standard outlet. Hardware, installation, and energy costs are minimal compared to Level 2 systems, making Level 1 ideal for overnight charging, short daily commutes, and long-term affordability.
Comparing Level 1 EV Charging With Other EV Charging Levels.
Now, compared to its flashier cousins, Level 2 and DC fast charging, Level 1 might seem like a snail compared to a cheetah, as shown in the table below:
| Feature | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charging Time | 6-22 hours | 2-8 hours | 30 minutes |
| Charging Speed | Adds 3-5 miles/hour | Adds 20-60 miles/hour | Adds 100-300 miles/hour |
| Power Requirements | Standard 120V Single Phase AC Power | 208-240V Single Phase AC Power | 480V, Three Phase AC Power |
| Power Output | 1.3 – 2.4 kW | 3 – 19.2 kW | 50 kW – 400 kW |
| Connector Types | J1772 (Type 1) | Mennekes (Type 2), Tesla, GB/T (AC) | CCS1, CCS2, CHAdeMO, GB/T (DC), Tesla |
| Amps | 12-16 amps | 12-80 amps | <125 amps |
| Charging Load | 1.4 – 1.9 kW | Typ. 7-10 kW | Typ. 50-150 kW |
| Application | Home | Home & Commercial | 480V, Three-Phase AC Power |
While Level 2 chargers typically deliver 240V, offering significantly faster charging speeds, Level 1 operates at a lower voltage, as shown in the Level 1 and Level 2 EV chargers wiring diagram below:
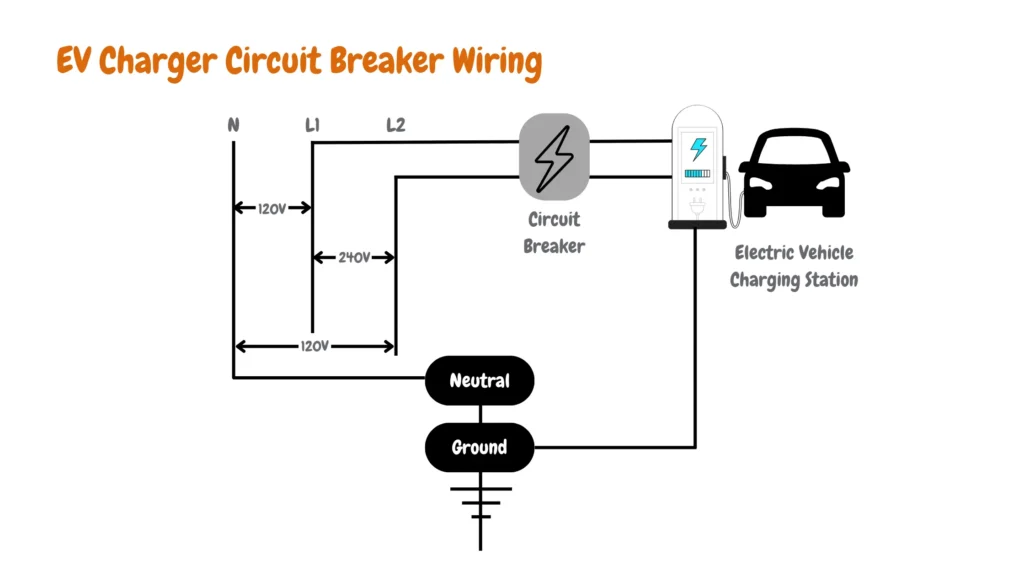
The low voltage of a level 1 charger translates to slower charging rates. For instance, while a Level 2 charger might add 20-30 miles of range per hour, a Level 1 might only manage 3-5 miles in the same timeframe. That means a fully depleted battery could take 8 to 24 hours to recharge – marathon, not sprint, as we mentioned earlier.
But before you dismiss Level 1 as a relic of the past, consider its hidden strengths. Level 1 charging boasts plug-and-play simplicity, unlike its high-powered counterparts, which often require professional installation. No fancy equipment, no permits, just your trusty car charger outlet and the charging cable that usually comes with your EV (think of it as your EV’s portable gas pump!).
This translates to significant cost savings, making it a budget-friendly choice for many drivers. Plus, with its widespread availability, you can charge anywhere with access to a standard outlet – think your home, workplace, or even a friend’s garage. Remember, convenience has its perks!
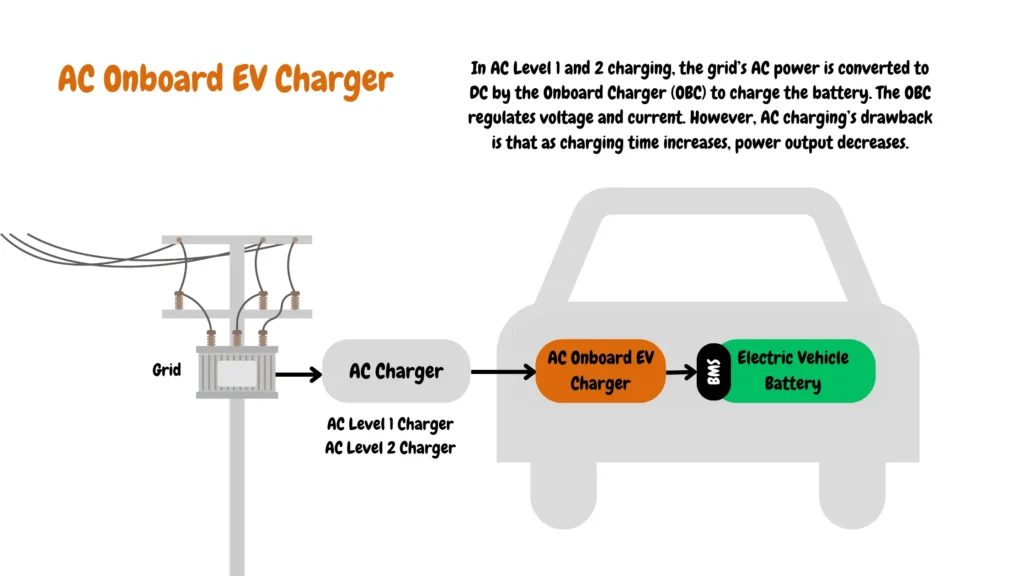
Level 1 charging AC/DC conversion.
As shown in the image below, Level 1 AC chargers rely on the electric vehicle’s onboard charger to convert alternating current AC to direct current DC to charge your electric vehicle (AC EV charging).
DC Level 2 and DC Level 2 chargers come equipped with an offboard charger that converts AC to DC, allowing the DC charger to bypass the vehicle’s onboard charger for fast DC EV charging, as shown in the image below:
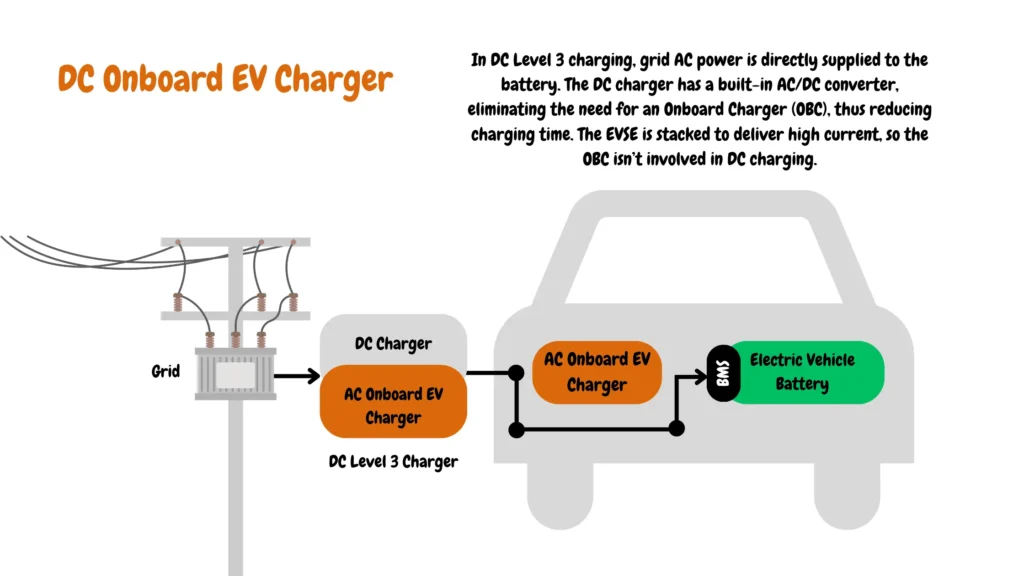
Why Would Anyone Buy a Level 1 Charger?
Level 1 chargers are the least expensive way to charge an electric vehicle (EV) at home compared to level 2 and 3 chargers. They’re also easy to use, don’t require any special setup, and are available to most homeowners.
Yes, it’s the “slow and steady wins the race” approach – think marathon, not sprint. But it’s a perfectly viable solution for many, especially first-timers or budget-conscious buyers.
Intrigued? Buckle up, and let’s explore the world of Level 1 charging–from its lightning-fast affordability to its potential pit stops, so you can decide if it’s the right fit for your electric adventure.
Get Expert Advice on Level 1 EV charging.
Level 1 charging is budget-friendly, simple, and perfect for home charging. But is it right for you? Get matched with the ideal charger for your EV & lifestyle with our expert consultation.
Find Your Perfect ChargerBook today & shop for your EV charger confidently!
Pros and Cons of Level 1 EV Charging
Level 1 EV charging has both pros and cons:
| What are the advantages of a Level 1 charger? | What are the disadvantages of a Level 1 charger? |
|---|---|
| Cost-effective: Free or inexpensive home charging compared to pricier alternatives. | Simple setup: No complex installations or permits are required; just plug and play. |
| Convenient: Easily charge at home, work, or a friend’s place without hunting for stations | Circuit concerns: Watch out for overloaded circuits, which can trip breakers or pose safety risks. |
| Simple setup: No complex installations or permits are required; just plug and play. | Limited range: Short trips are fine, but longer commutes or road trips might be challenging. |
Level 1 Slow Charging.
As you can see from the pie chart below, level 1 charging stations occupy only 2% of the entire electric vehicle charging station distribution in the United States.
Slow charging, synonymous with Level 1 chargers, is the major factor contributing to the poor adoption of Level 1 charging stations and why potential EV owners avoid purchasing Level 1-compatible electric vehicles.
Despite Level 1 chargers being cheaper and compatible with standard 120-volt outlets, unlike Level 2 chargers that need slight electrical panel modifications and a 240v outlet, and Level 3 chargers requiring 480V power and three-phase DC power with additional permitting, customers still prefer Level 2 and Level 3 charging despite their high electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) costs, and installation costs due to complex installation and more advanced hardware components.
How Long Does a Level 1 Charger Take to Charge?
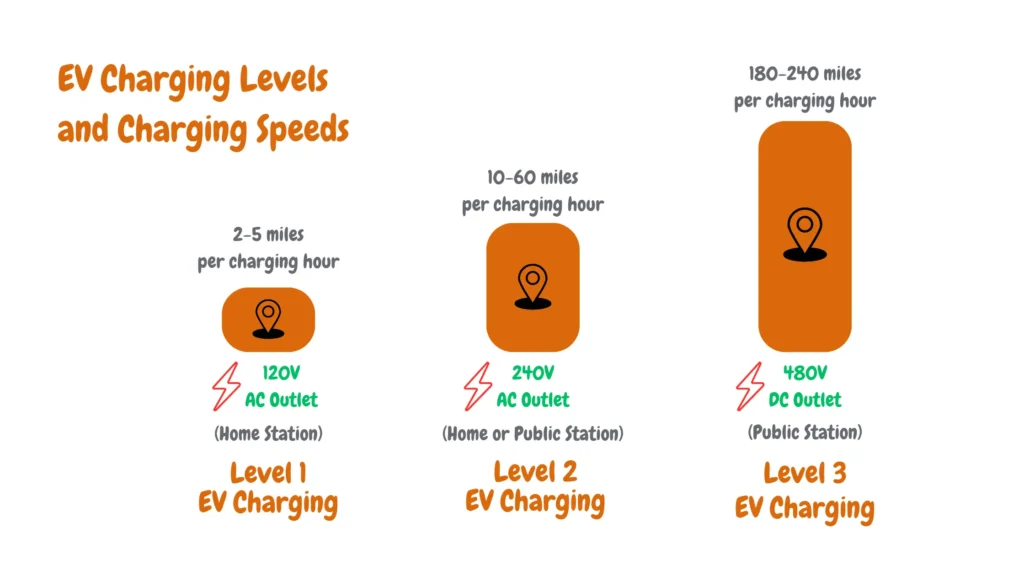
Level 1 charging, the slowest option, typically adds 3-5 miles of range per hour, requiring 6-22 hours for a full charge based on battery size.
In contrast, Level 2 charging is moderately faster; adding 20-30 miles of range per hour takes 4-8 hours for a full charge. Level 3 charging, known as DC Fast Charging, is the quickest, typically adding 100-200 miles of range in 30-60 minutes, with an 80% charge achieved in 20-45 minutes before slowing down for battery protection.
| EV Charging Feature | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charging Time | 6-22 hours | 2-8 hours | 30 minutes |
| Charging Speed | Adds 3-5 miles/hour | Adds 20-60 miles/hour | Adds 100-300 miles/hour |
Level 1 slow charging speeds are ideal for overnight home EV charging; however, most electric vehicle owners would prefer an EV charge ideal for quick top-ups on the go, daily charging, and longer trips, which Level 2 and Level 3 chargers offer.
According to a recent McKinsey Survey, 42 percent of electric vehicle owners consider charging speed the most important factor, with 60% preferring high-performance levels that facilitate quick top-ups at 30 minutes or less.
As it turns out, 70% of the respondents don’t mind paying a premium to enjoy convenient, fast charging to in-home chargers bundled with other green solutions favoring Level 2 and 3 chargers.
Why Aren’t Level 1 Chargers Common in Public EV Stations?
Level 1 charging stations are not common, as we discovered in the introduction of this EV Level 1 charging guide, only 2% of EV charging stations are equipped with Level 1 charging capabilities, and the answer simply lies in customer preferences and market trends which dictates charging equipment companies, EV charging stations investors and government agencies are willing to set-up.
EV charging station investors want traffic flowing into their EV charging business to get an ROI on their investment. When comparing EV charging levels, Level 3 and Level 2 are the most attractive to investors, respectively, as they allow them to serve as many customers. per day, their daily revenue streams increase due to their fast charging capabilities.
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charging Time | 6-22 hours | 2-8 hours | 30 minutes |
| Potential Customer Served Per Day (Assumpt: 100% occupancy) | 1-4 clients | 3-12 clients | 48 clients |
| Revenue Per Day (Assumed cost to charge a 60 kWh battery is $19.5 at a public station) | $19.5 – $78 | $58.5 to $234 | Approx $936 |
As shown in the chart below, EV owners also have special preferences when it comes to choosing their EV charging stations:
Based on the user’s preferences mentioned above (Customer is King), Investors might not invest in Level 1 charging due to the following:
Charging Speed
With Level 1 offering the slowest charging speed (3-5 miles per hour), it falls short of the 42% priority on fast charging times. This might deter limited-time clients, especially those on long trips or needing quick top-ups.
Affordability
While Level 1 is generally the cheapest option, the 35% emphasis on charging costs requires consideration. If the business charges per kWh, the slow speed of Level 1 might not offer competitive rates compared to faster Level 2 or DC fast chargers.
Availability of Free Spots
17% value availability of free spots, which might not be a major concern. However, Level 1 chargers are often single units and slow charging, limiting availability for multiple clients needing simultaneous charging. This could lead to congestion and frustration.
Smart EV Charging Features
Smart charging empowers businesses to attract clients, optimize operations, and contribute to a greener future. Level 1 charging offers limited to no smart charging features, while level 2 and level 3 charging offer smart charging capabilities, as shown in the image below, making them attractive to entrepreneurs looking to offer optimized business operations.
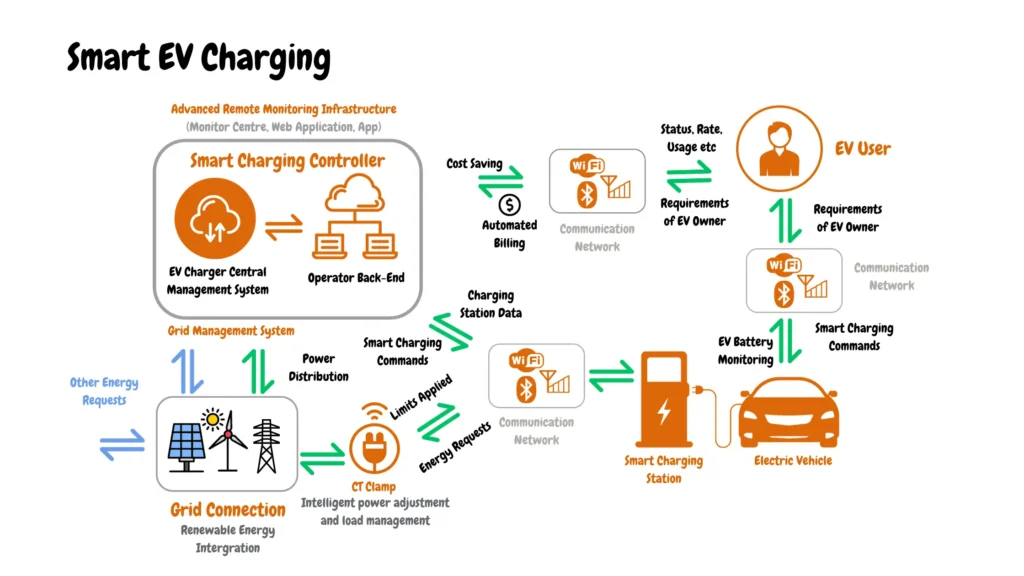
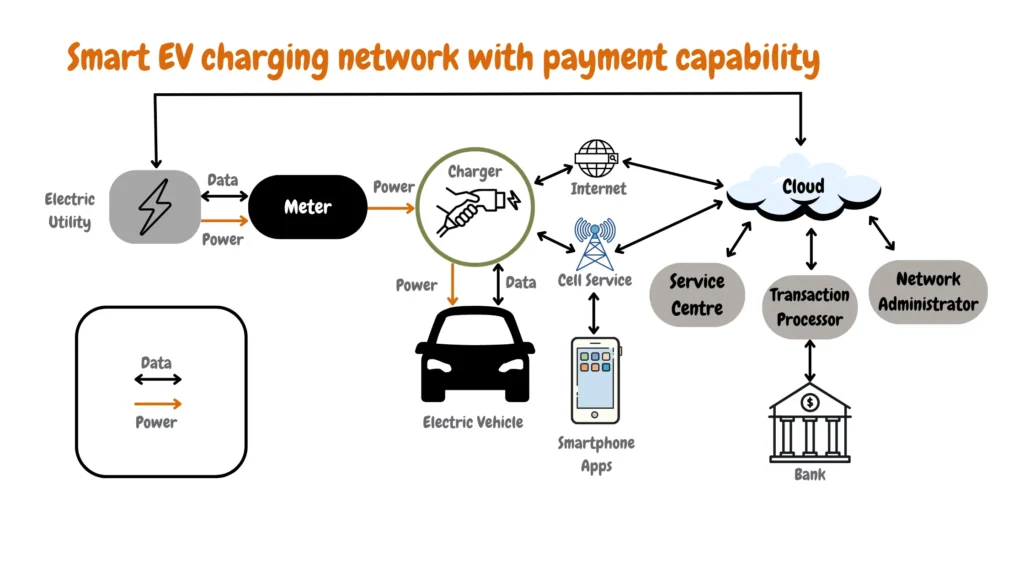
The lack of smart charging features on Level 1 charging might also affect a business service delivery due to few options for integrating payment options; 17% of clients prioritize charging stations that integrate different payment options which can easily be integrated into Level 2 and Level 3 charging stations as shown in the diagram below that shows payment integration into a smart EV charging network.
Level 2 and Level 3 chargers address these factors, offering faster speeds, dynamic pricing options, and smart features like reservation systems and load balancing. Smart charging enhances data insights, user experience, and grid stability, making it a win-win for businesses and clients.
Business Management.
While Level 1 chargers might fall short on client priorities like speed, cost, and convenience, smart charging elevates Level 2 and 3 options, offering dynamic pricing, reservations, and remote business management.
However, the benefits go beyond client satisfaction. Smart EV charging allows EV charging station businesses to remotely monitor usage, schedule charging, and troubleshoot issues (17% of EV owners prefer fast technical support in case of problems), saving time and resources.
Businesses using smart EV charging can leverage data insights and integrate them with renewable energy as shown in the image below, solidifying their commitment to sustainability and reducing the cost of charging an EV, offering them a competitive advantage, as 35% of EV owners consider charge costs to be a determining factor in the selection of charging stations.
Get Your Profitable EV Station Business Plan
Are you ready to tap into the booming EV market with your charging station? But unsure which level to choose. Don’t get stuck in the slow lane! Our EV charging station business plan writing services provide expert insights and strategic recommendations to help you navigate the market and maximize your return on investment.
Get Your EV Charging Station Business Plan Now!Start Your EV Charging Station Business Today
Level 1 EV Charger Installation Safety.
While Level 1 charging is generally safe, a few key points deserve your attention:
- Dedicated Outlet Installation: If you lack a conveniently located 120V outlet or need a higher-capacity one, consider hiring an electrician to install a dedicated outlet specifically for your EV charging needs.
- Complex Wiring and Upgrades: If your electrical system requires complex upgrades to accommodate Level 1 charging safely, consulting a qualified electrician is crucial to ensure code compliance and optimal performance.
- Ground Control: Make sure the outlet you’re using is properly grounded. Look for the three-prong plug configuration for grounded outlets. Ungrounded outlets pose a safety hazard and should not be used for EV charging.
- Circuit Check: Don’t overload your circuits! A level 1 charger cable uses a standard connection of 120V and a 20-amp circuit. Check the outlet’s capacity (usually listed in amps) and ensure your EV’s charging requirements don’t exceed it. Using a higher-amp circuit, like the one powering your dryer, might be tempting, but exceeding its capacity can trip breakers or worse, cause electrical fires. Consult an electrician if unsure about your circuit’s capabilities.
- Weather Woes: If charging outdoors, invest in a weatherproof Level 1 EV charger, specifically designed for outdoor EV charging. Regular extension cords aren’t meant for the elements and pose safety risks.
Frequently Asked Questions.
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions about Level 1 charging, answered for your convenience:
How much does it cost to charge an EV using Level 1 charging?
The cost per mile varies depending on your electricity rate In the US, the average electricity rate is around 14.96 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Assuming a Level 1 charger delivers 3 miles per kWh, the cost per mile would be around 5 cents. However, depending on your specific electricity rate, your actual cost may be higher or lower.
Is it safe to use a regular extension cord for Level 1 charging?
No, a regular extension cord for Level 1 charging is not recommended. They might not be rated for the sustained load and could overheat, posing a fire hazard. Always use a properly rated charging cable designed for EV charging and ensure the outlet is grounded and in good condition.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.







