We recommend the installation of a NEMA 14-50 GFCI outlet for EV charging when you intend to install a Level 2 plug-in EV charger in a list of places that require GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters) protection such as garages, outdoor parking lots, etc.
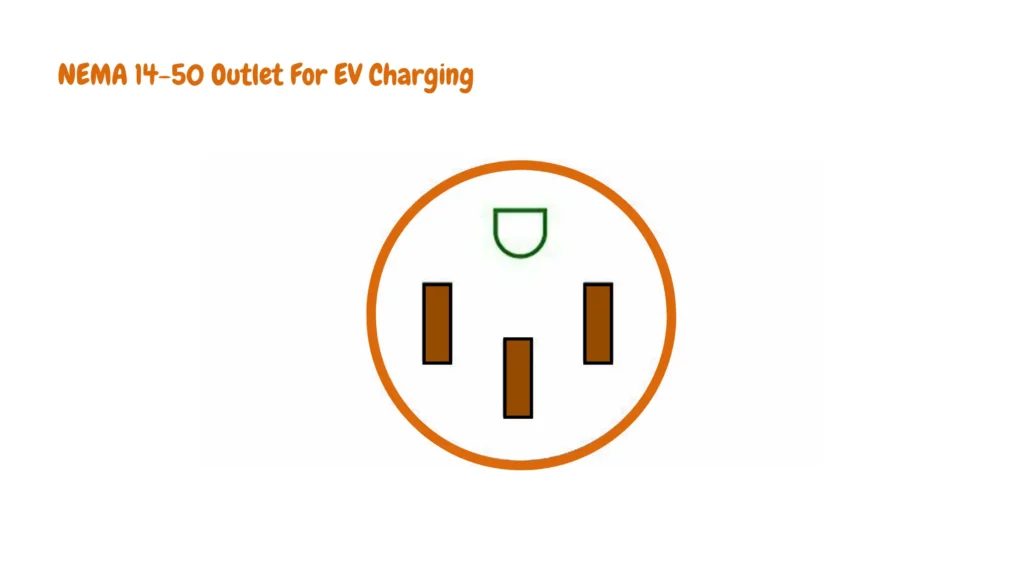
Electric vehicle owners who opt for a plug-in EV charger should familiarize themselves with GFCI outlets and their function in preventing electric shocks in their electric vehicle branch circuits, this guide will help you familiarize themselves with the significance, functionality, and locations where NEMA 14-50 GFCI outlet for an EV charger are required.
Table of Contents
Guide to EV Charging Outlets
Our guide to car charger outlets details the types of EV charging outlets and their installation. It includes visuals and step-by-step instructions for wiring each outlet type. You will learn to connect NEMA outlet terminals and set up a complete branch circuit for a plug-in EV charger or portable EV charger installation.
What is a NEMA 14-50 GFCI Outlet?
A NEMA 14-50 GFCI outlet is a vital component of a Level 2 EV charger electrical vehicle branch circuit that protects you from electrical shocks caused by the Level 2 EV charger, they come equipped with a safety device (GFCI) built into the outlet itself or used in conjunction with GFCI breakers to detect differences in the current flow (indicating a potential leak to ground), the GFCI quickly trips and cuts off power.
A NEMA 14-50 GFCI outlet helps prevent electrical shock hazards, particularly in areas prone to moisture, like garages, and outdoor EV charger installations, its safety features monitor input and output currents on the outlet itself and detect discrepancies, as low as a few milliamps, once a fault is detected the GFCI breaker cuts off the power supply to the NEMA 14-50 GFCI Outlet within 30 milliseconds reducing the risk of electrical shocks.
Installing a NEMA 14-50 GFCI Outlet For EV Charging.
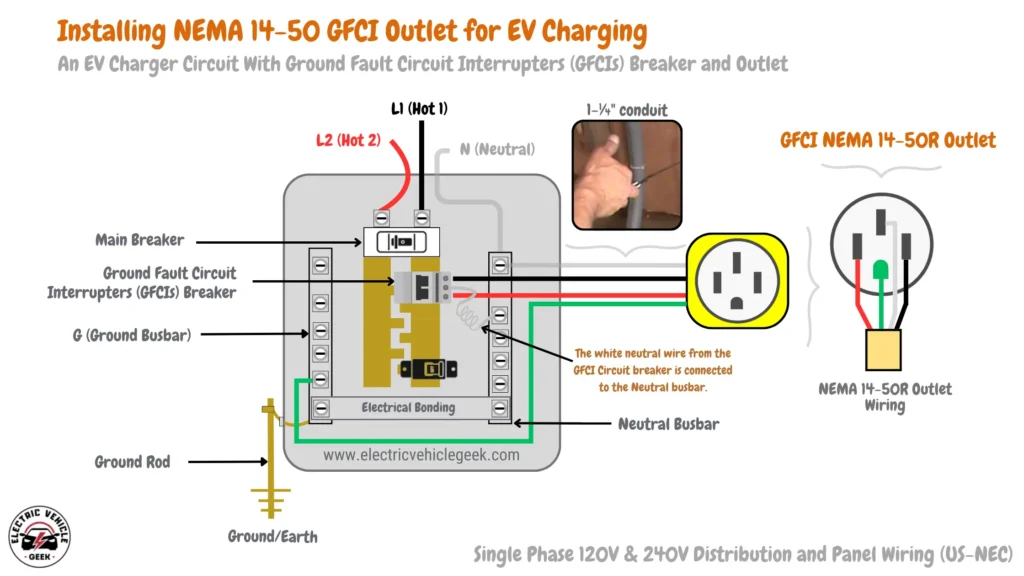
If you intend on purchasing or have purchased a Level 2 EV charger you will need a NEMA 14-50 outlet that is protected by a GFCI breaker, some of the outlets that we install for GFCI protection include:
Siemens QF250A GFCI Breaker and ENERLITES 50 Amp 125/250V NEMA 14-50R Power Outlet
We use the Siemens QF250A GFCI Breaker and ENERLITES 50 Amp 125/250V NEMA 14-50R Power Outlet when installing Level 2 EV chargers in locations requiring GFCI protection to comply with electrical safety standards such as garages, and outdoor EV chargers installations.
To understand the NEMA 14-50 GFCI Outlet wiring, envision it like this:
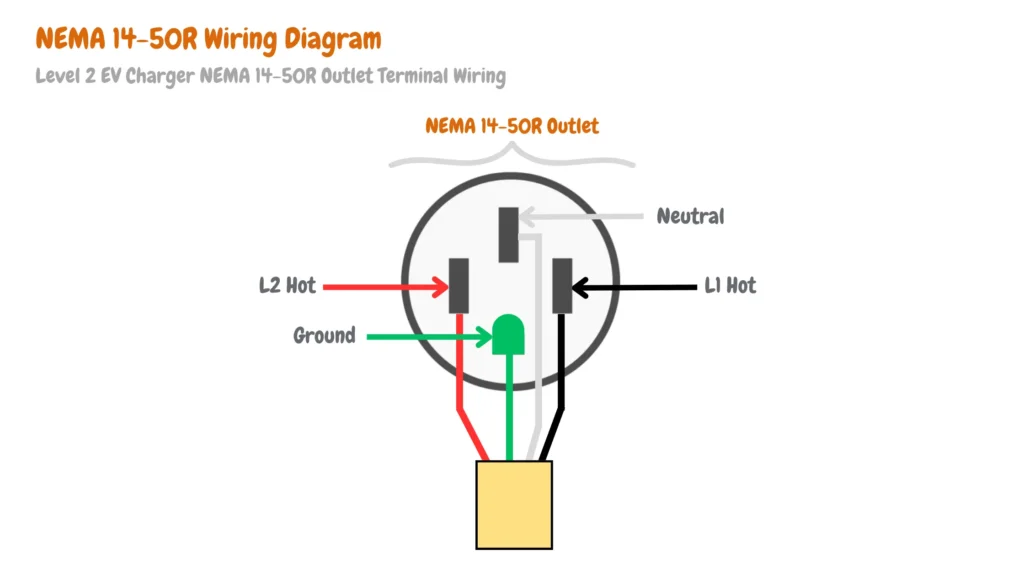
- The half-round or U-shaped connection represents the ground.
- Opposite the ground, you’ll find the neutral wire (usually white).
- The two remaining black wires are the hot wires, positioned 180 degrees out of phase with each other. These are the 120-volt hot wires that supply power.
The image below shows an electrical circuit diagram of a NEMA 14-50R outlet installed from the 120/240V single-phase electrical panel with a GFCI circuit breaker (NEC-US).
NEMA 14-50R GFCI Outlet EV Charging Cables Sizes.
- For a 25-foot run, choose #8 wire.
- For a 50-foot run, #6 wire is appropriate.
- For longer distances like a 100-foot run, consider using #4 wire.
We love this combination because the ENERLITES 50 Amp 125/250V NEMA 14-50R Power Outlet comes with its compatible Siemens QF250A GFCI Breaker that will allow the comparison of the input current from the hot side with the output current from the neutral side to ensure a balanced current flow,
In case the Siemens QF250A GFCI Breaker detects any difference such as leakage of current or ground faults, the GFCI breaker trips to cut off power to the ENERLITES 50 Amp 125/250V NEMA 14-50R Power Outlet to mitigate the risk of electrical shocks and damage to the EV charger.
We recommend the installation of NEMA 14-50 GFCI outlets and GFCI breakers by licensed electricians and certified EV charger installers who will access your home electrical system electric vehicle branch circuit and recommend a suitable NEMA 14-50 GFCI outlet and a GFCI breaker, to ensure proper integration with the main electrical panel and the electric vehicle branch circuit.
A licensed electrician or certified EV charger installer will ensure your EV charger installation adheres to electrical safety standards and consult with your local building authority to comply with regional regulations.
NEMA 14-50 GFCI Outlet Reliability Concerns
NEMA 14-50 outlets with GFCI protection have become the standard for dedicated EV charging circuits due to their high power capacity (240V, 50A) and built-in safety features. However, for EV charging applications, some reliability concerns require consideration:
Nuisance EV Charger Circuit Breaker Tripping
- The Culprit: Recent code updates mandate GFCI protection for NEMA 14-50 outlets. While most EV chargers possess internal GFCI circuits, the interaction between these two systems can lead to “nuisance tripping.”
- The Problem: This unintended tripping disrupts charging, often occurring unexpectedly and requiring a manual reset. This can be inconvenient and frustrating for EV owners.
Wear and Tear
- Frequent Use vs. Intended Design: NEMA 14-50 outlets are typically used for plug-in EV chargers, which are infrequently plugged and unplugged. EV charging, however, involves more frequent connection and disconnection, potentially leading to:
- Loose Connections: Over time, these connections can loosen, compromising safety and potentially causing overheating or arcing.
- Outlet Wear: Repeated plugging and unplugging of the EV charger can wear out the internal components of the outlet, reducing its lifespan.
Mitigating these Concerns
- Consulting a Qualified Electrician: An electrician can assess your existing electrical system and determine if a dedicated EV charger circuit with a properly sized NEMA 14-50 outlet (without GFCI) is a viable option. This eliminates potential nuisance-tripping issues associated with dual GFCI systems.
- Hardwired EV Chargers: Consider a hardwired EV charger installation instead of a plug-in option. This eliminates the wear and tear concerns associated with frequent plugging and unplugging.
- High-Quality Outlets: If using a NEMA 14-50 outlet, choose a high-quality brand known for durability to minimize wear and tear.
- Careful Use: Practice care when inserting and removing the EV charger to minimize stress on the outlet connection.
By understanding these potential drawbacks and implementing appropriate solutions, you can ensure the safe and reliable operation of your NEMA 14-50 GFCI outlet for EV charging.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.
Last update on 2026-02-19 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API








