Level 2 EV charging has emerged as the dominant choice for EV charging with the growing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing need for reliable charging infrastructure.
While Level 3 chargers, also known as DC Fast Chargers (DCFC), often make headlines for their ability to add 100+ miles of range in under 30 minutes, they’re typically reserved for commercial and highway corridor use due to high power requirements and infrastructure costs.
In contrast, Level 2 chargers remain the most widely adopted fast charging solution for residential and workplace installations, offering a balance of speed and practicality by delivering 20–40 miles of range per hour, well-suited for daily fast charging at home.
Shop Level 2 EV ChargersAccording to the U.S. Department of Energy’s Alternative Fuels Data Center, Level 2 chargers account for 79.5% of all EV charger installations in the United States, followed by Level 3 (DC Fast Chargers) at 18.5%, and Level 1 chargers at just 2%, as illustrated in the pie chart below.
The infographic below compares the key differences between Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 (DC Fast Charging) systems.
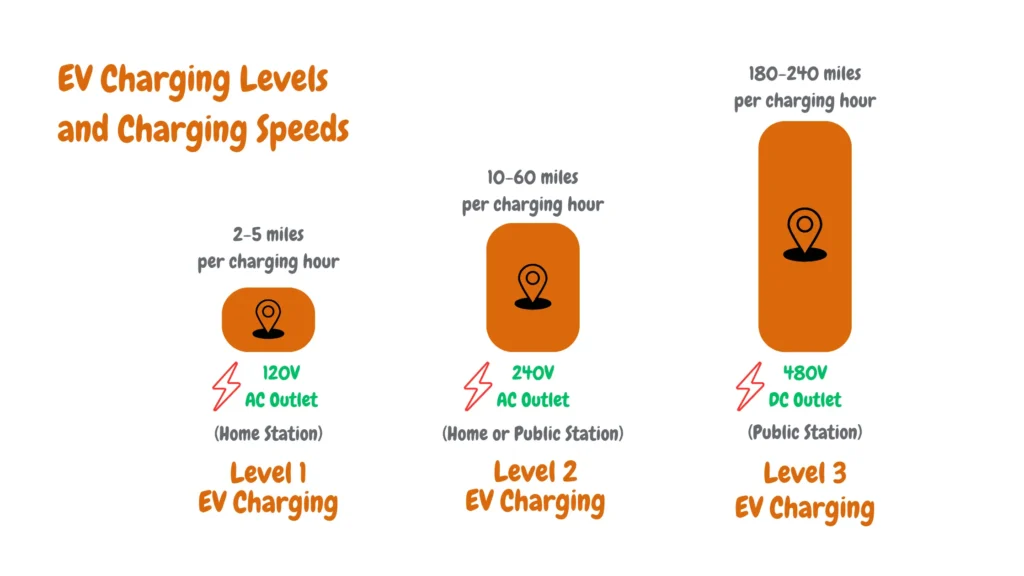
Level 1 chargers operate on a standard 120V AC household outlet, making them the most accessible but slowest option. Level 2 chargers use a 240V single-phase supply, commonly found in residential and commercial settings, and offer significantly faster charging rates. In contrast, DC Fast Chargers (Level 3) require a 480V three-phase electrical supply, specialized equipment, and often additional permitting due to higher infrastructure demands.
Compared to other EV charging levels, Level 2 chargers dominate installations in the United States primarily because of their versatility and compatibility with a wide range of locations, including homes, workplaces, and public destinations.
With charging speeds between 10 and 60 miles of range per hour, Level 2 infrastructure aligns closely with the average U.S. daily driving distance of 37 miles, according to the Department of Transportation, making it an ideal solution for both residential and commercial applications.
Overall, Level 2 EV charging offers a good balance between speed, convenience, and cost, making it a popular choice for home and commercial charging.
There is a high demand for EV chargers, as we expect 26.4 million EVs on the US roads by 2030; it’s estimated that more than 30 million EV chargers will be needed by then to support the steady growth of EV adoption in the US. To meet the demand, businesses and EV owners opt for Level 2 EV chargers since they may already have the electrical infrastructure needed to install a Level 2 charger, making EV chargers’ connection to the grid even more cost-effective.
What is EV Level 2 Charging?
Level 2 EV charging is a step from the basic Level 1 charging that uses a standard household outlet. It offers significantly faster charging speeds, making it ideal for home and commercial use.
To quickly explain Level 2 EV charging, we have created descriptive infographics that highlight crucial Level 2 EV charging features such as power, speed, installation, and use, as shown below:

Here’s a breakdown of the EV Level 2 Charging critical features highlighted in the infographics.
EV Level 2 Charging Power and Speed
- EV Level 2 Charging Voltage: Operates at 208-240 volts, compared to Level 1’s 120 volts. This higher voltage translates to more power being delivered to your EV.
- EV Level 2 Charging Current: Delivers 12-80 amps, with 32 amps typical. Higher amperage means faster charging.
- EV Level 2 Charging Power Output: Ranges from 3 kW to 19.2 kW, with most common chargers being around 7-10 kW. This translates to adding 20-60 miles of range per hour of charging, significantly faster than Level 1’s 4 miles per hour.
- EV Level 2 Charging Time: Depending on your battery size and power, a Level 2 charger can fully charge your EV in 2-8 hours, much faster than Level 1’s 11-20 hours.
EV Level 2 Charging Installation and Use
EV Level 2 Charging Outlet
Typically, plug-in Level 2 chargers use a 240V industrial-grade outlet, which can be either a three-prong or four-prong type. Common three-prong outlets include NEMA 6-30, NEMA 6-50, NEMA 10-30, and NEMA 10-50, each featuring two hot wires and a ground. Four-prong outlets, such as NEMA 14-30 and NEMA 14-50, are also widely used. In addition to these plug-in options, Level 2 chargers can be hardwired for a more permanent installation.
For detailed wiring diagrams and electrical requirements for both plug-in and hardwired Level 2 EV chargers, check out our comprehensive guide section: What Are the Electrical Requirements for a Level 2 EV Charger?
EV Level 2 Charging Connectors
Connector standards vary by region and vehicle manufacturer, with common types including Mennekes (Type 2), Tesla/NACS, and GB/T (AC). It is essential to verify compatibility between your Level 2 EV charger connector and your vehicle’s charging inlet before purchasing to ensure seamless and reliable charging.
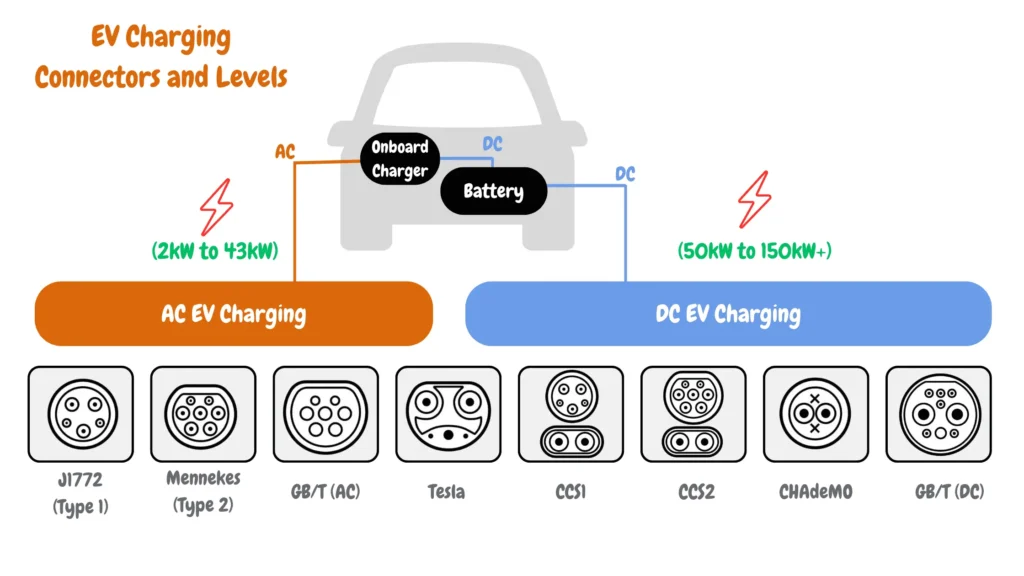
Comparing Level 2 EV Charging With Other EV Charging Levels.
Here’s a table comparison of Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 EV charging:
| Feature | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charging Time | 6-22 hours | 2-8 hours | 30 minutes |
| Charging Speed | Adds 3-5 miles/hour | Adds 20-60 miles/hour | Adds 100-300 miles/hour |
| Power Requirements | Standard 120V Single Phase AC Power | 208-240V Single Phase AC Power | 480V, Three Phase AC Power |
| Power Output | 1.3 – 2.4 kW | 3 – 19.2 kW | 50 kW – 400 kW |
| Connector Types | J1772 (Type 1) | Mennekes (Type 2), Tesla, GB/T (AC) | CCS1, CCS2, CHAdeMO, GB/T (DC), Tesla |
| Amps | 12-16 amps | 12-80 amps | <125 amps |
| Charging Load | 1.4 – 1.9 kW | Typ. 7-10 kW | Typ. 50-150 kW |
| Application | Home | Home & Commercial | 480V, Three-Phase AC Power |
Level 2 strikes the perfect balance between speed, convenience, and cost. It’s powerful enough for most daily needs, readily available at homes and public stations, and won’t break the bank compared to DC fast-charging.
There is also a difference in EV charging processes when you compare Level 2 and Level 3 charging. For starters, Level 2 AC occurs on the electric vehicle’s onboard charger, which means a Level 2 charger is a simple charger compared to a Level 3 charger, which includes an onboard charger in the charger itself that converts AC to DC. It’s able to transfer the DC directly to the vehicle’s battery, as shown in the infographic image below:

Level 2 Smart EV Charging Features
To illustrate Level 2 smart charging features, we have made an infographic that shows the concept of Level 2 smart features for EV charging in detail, including central hubs, communication networks, Grid connection, and Monitoring Features, and how they all connect to form one Smart EV charging environment.
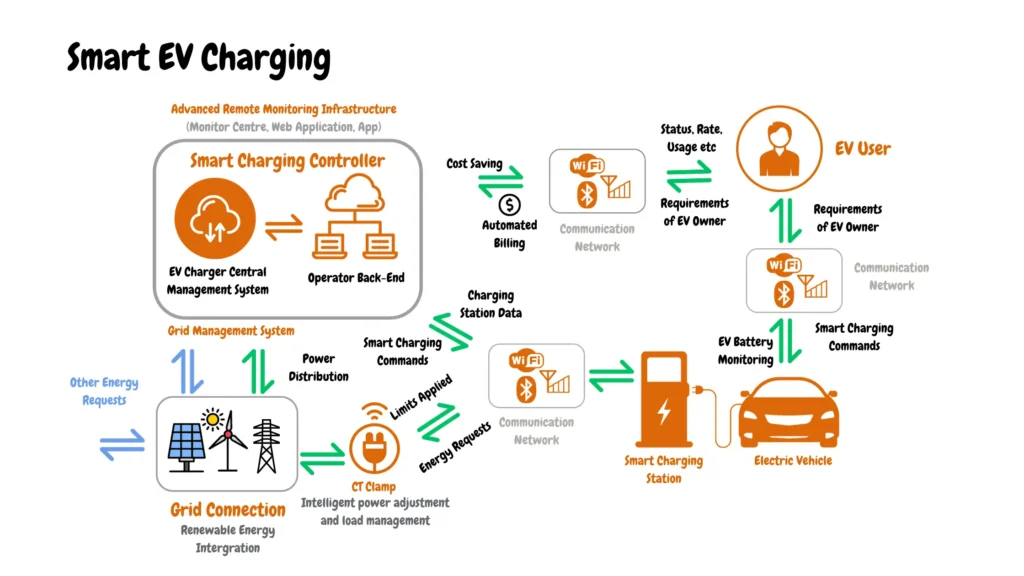
The specific features and functionalities of Level 2 smart charging systems can vary depending on the manufacturer and model. The infographic image above shows the main features and functionalities of high-end Level 2 EV chargers.
Specific features and functionalities of the Level 2 smart charging system:
Level 2 Smart EV Charging Central Hub
As shown in the infographic image above, the central hub of a smart level 2 EV charger consists of a smart charging controller, operator backends, and an EV charger central management system, which acts as the headquarters of a smart EV charging system.
- Smart Charging Controller: This brain controls the operation, managing charging based on various factors.
- Operator Back-End: Connects to the controller for remote management and data collection.
- EV Charger Central Management System: Oversees multiple charging stations and optimizes their performance.
Level 2 Smart EV Charging Communication Network
The infographics show that a Level 2 Smart EV Charging Communication Network has two main features: a network and EV smart charging data.
- Communication Network: A network (Wi-Fi, cellular, etc.) links the components for data exchange.
- Charging Station Data: Provides information on status, usage, power distribution, etc.
- Other energy requests: Integrates with smart home systems for energy management.
- Status, Rate, Usage, etc.: Provides detailed information on the charging process.
Level 2 Smart EV Charging Advanced Monitoring
There are two features shown related to the monitoring and management of charging stations, including:
- Monitor Centre, Web Application, App: Allow remote monitoring and management of charging stations.
- EV Battery Monitoring: Tracks battery health and optimizes charging for longevity.
- Intelligent power adjustment and load management: Automatically adjusts charging based on available grid capacity.
Benefits of Level 2 Smart EV Charging
We recommend upgrading to a level 2 supported EV Charger, such as the Enphase Smart EV Charger, which offers benefits such as smart EV charging, cost savings, renewable energy integration, and automated billing.
Smart Grid Integration
- Grid optimization: Smart chargers can communicate with the grid to optimize charging based on various factors such as grid conditions, user preferences, and the availability of renewable energy. For example, they can adjust charging rates to avoid overloading the grid during peak hours or high electricity demand.
- User preferences: These chargers allow users to set preferences regarding charging times, ensuring that their vehicles are charged when it’s most convenient or cost-effective.
- Renewable energy availability: Smart chargers can prioritize charging when renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are abundant. This helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels and supports the transition to a cleaner energy grid.
Cost Saving
- Off-peak charging: By scheduling charging sessions during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower, smart chargers can significantly reduce charging costs for EV owners.
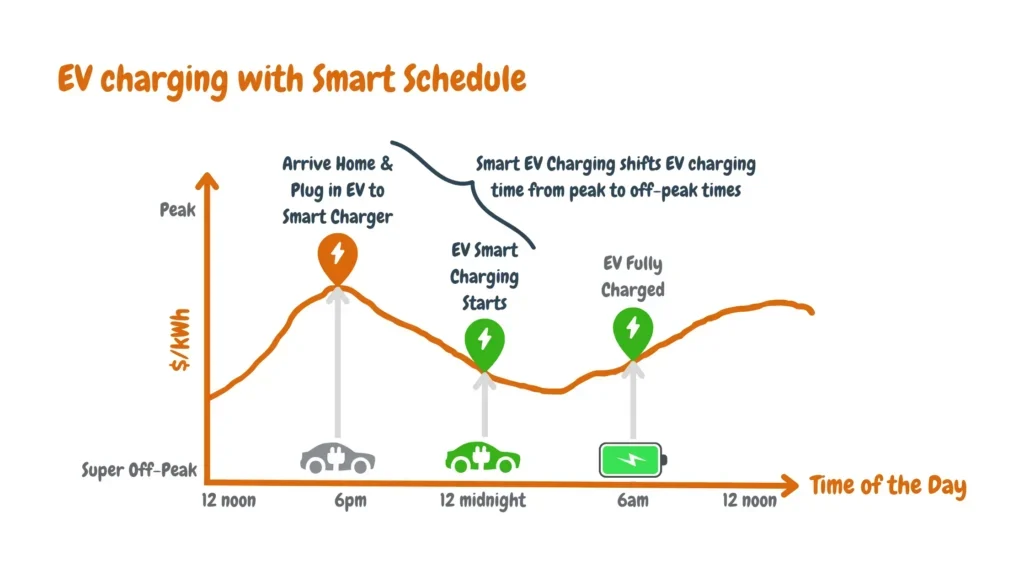
- EV charging load management: Smart chargers can detect when renewable energy sources generate excess power and adjust charging accordingly. Charging during these times often incurs lower or even zero costs, further contributing to cost savings for EV owners.
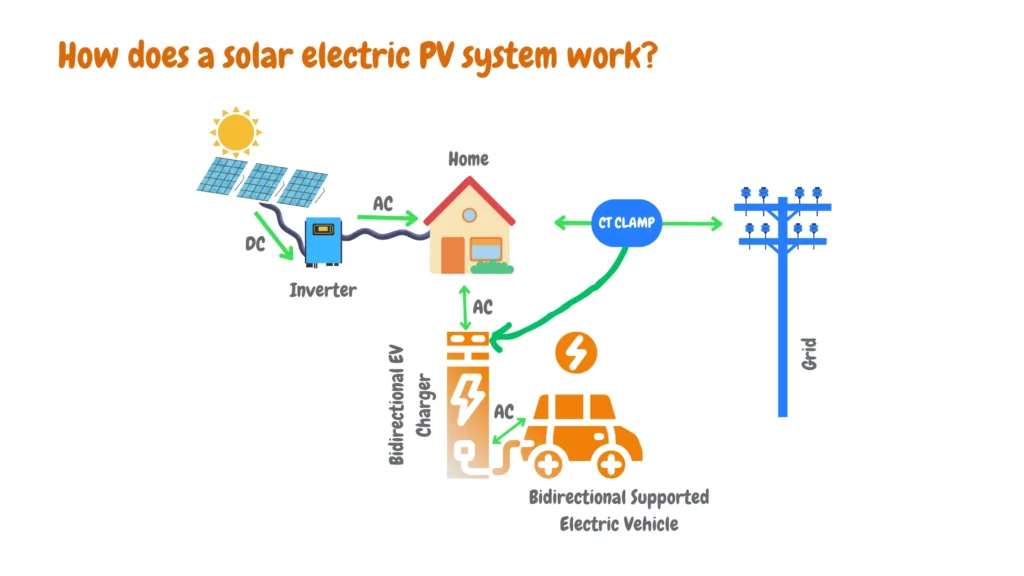
Renewable Energy Integration
Prioritizing renewable energy: Smart chargers can be programmed to prioritize charging using renewable energy whenever available. This reduces carbon emissions associated with EV charging and supports the growth of renewable energy infrastructure.
Automated Billing
Accurate billing: Smart chargers enable automated billing based on energy usage, providing EV owners with precise information about their charging costs. This eliminates the need for manual meter readings or estimations, ensuring fair and transparent billing practices.
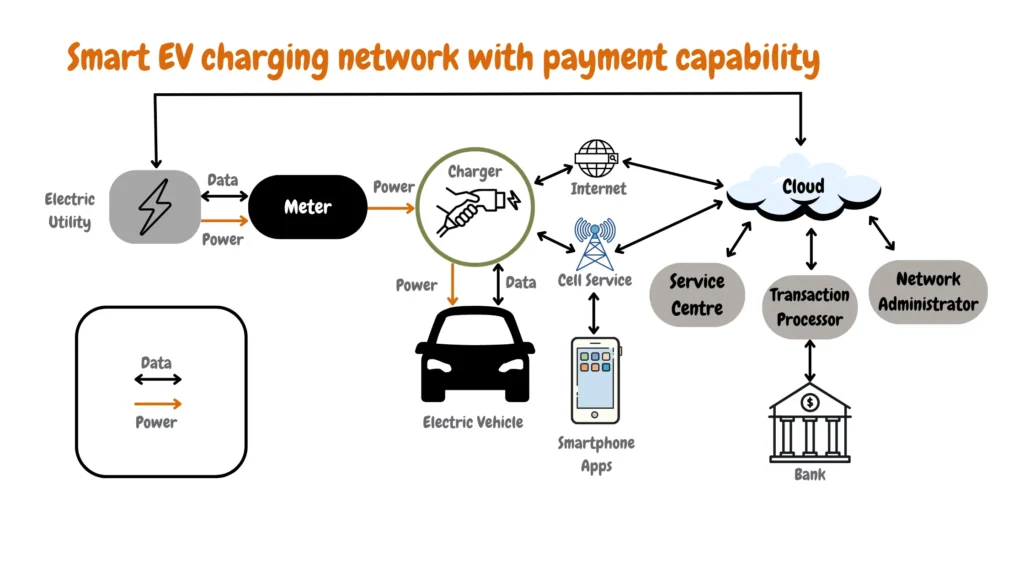
Installing Your Level 2 Charger
Ready to enhance your home with a Level 2 charger? Here’s how to make it happen efficiently and safely.
Choosing the Right Level 2 EV Charger
Begin by selecting a Level 2 EV charger that is fully compatible with your vehicle and aligned with your specific charging requirements. Consider your car’s recommended charging rate and compatible EV charger connector type, such as SAE J1772 or Tesla’s proprietary connector, as well as your preferred charging speed.
For typical daily use, a 6.2 kW plug-in Level 2 charger offers reliable performance and easy installation, while a 19.2 kW hardwired Level 2 charger delivers significantly faster charging but requires professional installation and may necessitate an electrical panel upgrade. Balance these options with your budget and desired features to choose the optimal charger for your needs.
Assessing Your Electrical Panel
Most homes will require an electrical panel upgrade to support the increased power demand of a Level 2 charger, especially for higher-amperage hardwired units, such as an 80-amp Level 2 charger. This is particularly important when the panel also supplies other significant household loads. It’s essential to have a qualified electrician evaluate your panel’s capacity and recommend any necessary upgrades. For detailed guidance, refer to our EV Charging Electrical Load Calculation guide.
Circuit Installation
A dedicated circuit breaker rated between 15 and 100 amps must be installed to protect your Level 2 EV charger branch circuit, depending on the charger’s maximum current draw.
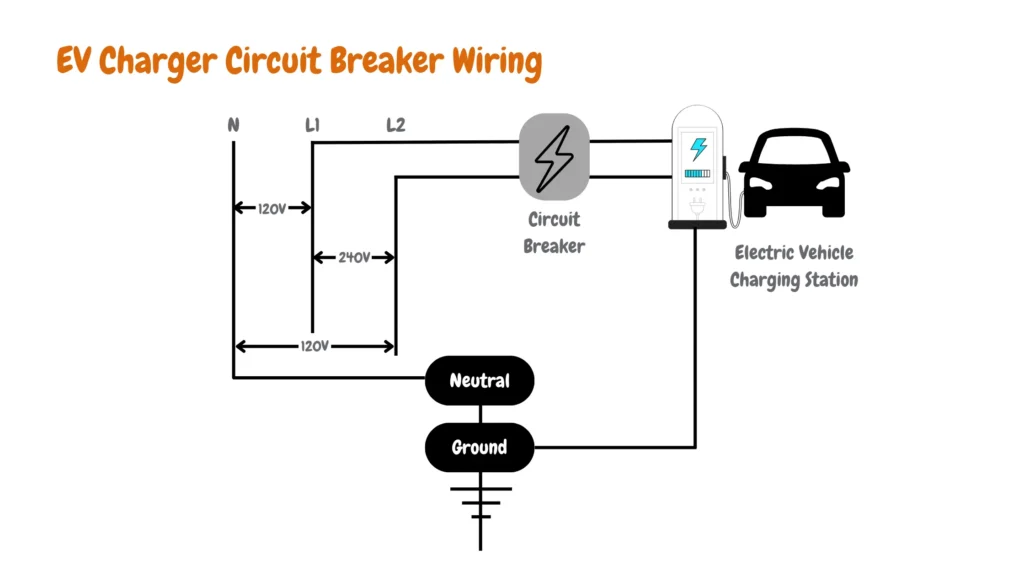
According to NEC 625.41, the circuit must be rated for 125% of the continuous load. For example, a 32-amp Level 2 charger requires a minimum 40-amp breaker (32A × 1.25 = 40A), while higher-capacity chargers, such as an 80-amp EV charger, require a 100-amp breaker.
Depending on your home’s electrical layout, installation may involve running appropriately sized copper conductors, often 14 AWG to 4 AWG, depending on amperage and distance, through walls, attics, or crawl spaces. The wire gauge must comply with both the charger’s requirements and NEC guidelines to ensure safe and efficient operation.
When budgeting for installation, consider the complexity of routing wiring and potential panel upgrades. For detailed guidance on wire sizing and breaker selection, see our Choosing the Right EV Charger Wire Gauge and Electric Vehicle Charger Circuit Breaker Selection Guide.
Permits and Incentives
Check local regulations for any permitting requirements related to EV charger installation. Additionally, explore federal and state-level incentives that can help offset installation costs. Research available programs in your area to maximize savings.
Public Level 2 Charging Options
There are many public Level 2 chargers available throughout the United States for those concerned about range and charging anxiety. You can use the EV charging map on our website to find a vast network of public Level 2 charging stations near you.
You will be able to filter Level 2 chargers by different EV charging networks providers, such as Allego, BC Hydro EV, Blink, bp pulse, Chargefox, ChargeNet, ChargePoint, Circuit Electrique, Electrify America, Electrify Canada, EV Connect, EVgo, Evie Networks, EVUp, Fastned, FLO, GE WattStation, Greenlots, Ionity, IVY, myEVroute, OpConnect, Petro-Canada, SemaConnect, Sun Country, Supercharger, Tesla Destination, Volta, and Webasto
To find the perfect pit stop, you can filter EV charger networks by connector type, availability, and real-time charging speeds.
Are Level 2 Public Chargers Good?
Public Level 2 chargers will not harm your electric vehicle or its battery. Public Level 2 chargers are just like the OEM Level 2 chargers you use at home, and the chargers are made under strict standardization protocols for interoperability purposes.
We love using Level 2 chargers located in workplaces, shopping centers and malls, parking garages, hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues to replenish our EV batteries when we have range anxiety or when our EV will not be able to reach home in time before it runs out of battery power.
The good thing is that most public Level 2 chargers are smart, so there is no fumbling with cash or complicated payment systems since they are integrated seamlessly with mobile apps or RFID cards, allowing you to initiate and pay for charging sessions effortlessly. Some networks even offer subscription plans for frequent users, unlocking discounted rates and added convenience.
The Cost of Level 2 Charging
Investing in a Level 2 EV charger for your home, typically rated between 32-40A, typically ranges from $500 to $800 for the hardware alone. This initial investment covers the charger unit, any potential accessories, and installation costs to tailor your setup to your preferences and needs.
Alternatively, public Level 2 EV charging stations are more cost-effective than Level 3 chargers. In California, for instance, charging at a public Level 2 station typically costs around 30 cents per kWh, whereas utilizing a Level 3 charger can cost up to 40 cents per kWh, as illustrated in the accompanying bar graph.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
So, you’ve embarked on the exciting journey of Level 2 EV charging, and maybe a few questions have popped up along the way. Fear not, this FAQ section is here to address common queries and ensure you’re a charging pro in no time!
Level 2 Charging Times
How long does charging my specific EV with a Level 2 charger take?
Charging times vary depending on your EV’s battery capacity, the charger’s output, and your car’s maximum charging rate. Consult your car’s manual or the charger’s specifications for detailed estimates. Remember, factors like temperature can also slightly impact charging speed.
Can I always leave my EV plugged in with a Level 2 charger?
Yes, most modern EVs have built-in safeguards to prevent overcharging. However, consult your car’s manual for specific recommendations. If you rarely use your vehicle, unplugging it occasionally can help preserve battery health.
Level 2 Charging Safety and Maintenance
Are home Level 2 charger installations safe?
Absolutely! When professionally installed by a qualified electrician using appropriate safety measures and codes, Level 2 chargers are incredibly safe. Always opt for certified products and licensed professionals for installation.
How do I maintain my Level 2 charger?
Maintenance is minimal! Regular visual inspections for damage and keeping the charging connector clean are essential. Consult your charger’s manual for any specific cleaning recommendations.
Troubleshooting and Future Developments
What should I do if my Level 2 charger isn’t working?
First, consult your charger’s manual for troubleshooting tips. Contact the manufacturer’s customer support or a qualified electrician if the issue persists.
What’s the future of Level 2 charging technology?
The future is bright! Expect advancements in innovative charging capabilities, faster charging speeds, and even bidirectional charging, allowing your EV to feed power back into the grid.
Conclusions
Upgrade to Level 2 charging for faster, more reliable power. This guide gives you the tools to make informed decisions and maximize your EV’s potential.
Understand your options, install safely, and utilize public stations efficiently. Stay informed about common issues and future tech. Don’t let slow charging or range anxiety hold you back. Research the best Level 2 chargers, especially based on smart features and emerging technologies, get installation quotes from different EV charger installers, and explore public EV charging options.

James Ndungu is a certified EV charger installer with over five years of experience in EVSE selection, permitting, and installation. He holds advanced credentials, including certification from the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program (EVITP) and specialized training in EV charging equipment and installation, as well as diplomas in EV Technology and Engineering Fundamentals of EVs. Since 2021, James has tested dozens of EV chargers and accessories, sharing expert insights into the latest EV charging technologies.








can you suggest a go between the electric outlet and charging cable that will measure KW usage so the condo management can charge me for my usage in my parking spot, hopefully not China made, many thanks.
I have written about the best smart meters for EV charging monitoring (most useful if you have integrated renewable energy EV charging) that connect to the electrical panel and require professional installation. Most smart plug meters available in the market such as Kill A Watt have limited current ratings (typically 10-15 amps) and can’t safely handle the higher loads of Level 2 EV chargers. I recommend using a plug-in smart EV charger, which is much cheaper, more functional, and versatile if you are using a dumb charger than purchasing and installing a smart energy meter just for EV charging monitoring.